| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Case Report
Volume 8, Number 5, May 2016, pages 420-423
A Very Rare Cause of Anal Atresia: Currarino Syndrome
Sevgi Buyukbese Sarsua, c, Mehmet Ergun Parmaksiza, Esra Cabalarb, Ali Karapura, Cihat Kayab
aDepartment of Pediatric Surgery, Cengiz Gokcek Obstetrics and Children’s Hospital, 27560, Sehitkamil, Gaziantep, Turkey
bDepartment of Radiology, Ersin Arslan Training and Research Hospital, 27090, Sehitkamil, Gaziantep, Turkey
cCorresponding Author: Sevgi Buyukbese Sarsu, Department of Pediatric Surgery, Cengiz Gokcek Obstetrics and Children’s Hospital, 27560, Sehitkamil, Gaziantep, Turkey
Manuscript accepted for publication February 23, 2016
Short title: Currarino Syndrome and Anal Atresia
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.14740/jocmr2505w
| Abstract | ▴Top |
Currarino syndrome (triad) is an extremely rare condition characterized by presacral mass, anorectal malformation, and sacral bone deformation. The complete form of this syndrome displays all three irregularities. Herein, we report a male case who was admitted to our hospital with symptoms of urinary system infection and persistent constipation 2 years after colostomy operation performed with the indication of rectovestibular fistula and anal atresia, diagnosed as Currarino syndrome based on imaging modalities. In a patient who was admitted because of the presence of anal atresia, in order to preclude potential complications, probable concomitancy of this syndrome should not be forgotten. Early diagnosis is important for the prevention of meningitis, urinary tract infections, and malignant change.
Keywords: Currarino syndrome; Presacral mass; Anorectal malformation; Sacral bone deformation; Urinary tract infections
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Currarino syndrome (CS) is a very rarely seen condition which is termed as Currarino triad. In fact, from 1981 on, nearly 300 cases have been published. It is a hereditary pathology which is characterized by a triad of sacrococcygeal bone defect, presacral mass, and anorectal malformation. Sacrococcygeal bone defect is always a component of this syndrome. When it is associated with all of these three anomalies, it is called complete form, while in the presence of one or two components, it is named incomplete form. Our case was a rarer complete form. MNX1 gene (motor neuron and pancreas homeobox 1, HGNC ID: 4979) mutations have been reported in all cases with familial Currarino triad. The condition demonstrates familial predisposition, and has a autosomal dominant inheritance pattern [1]. Nearly 30% of the cases with CS are sporadic [2]. This triad which was firstly described by Currarino et al is asymptomatic in more than 33% of the affected children. Symptoms such as intractable constipation, urinary retention, incontinence, and bowel obstruction in infancy are frequently associated with this presentation. Rarely association of Hirshsprung disease (HD) with CS has also been reported [3]. It can also accompany urogenital anomalies. Indeed, in more than 15% of the cases with Currarino triad, concomitant Mullerian duct anomalies are detected. General incidence of Mullerian duct anomalies has been reported as 7% [4]. Neonatal diagnosis is rarely established.
Cases with sacral agenesia should be investigated as for presacral masses and anorectal changes [5]. For cases with suspect CS, multidisciplinary approach at an early stage is important [6]. In the presence of anal atresia, prevention of potential complications is possible with raising awareness about this syndrome.
| Case Report | ▴Top |
A 2-year-old male infant was admitted to our hospital with inability to urinate and intractable constipation. From his medical history, it was learnt that 24 h after his birth, he had undergone colostomy operation with the indication of anal atresia and rectovestibular fistula. On physical examination, any abnormal finding apart from abdominal distension was not detected. Complete urinalysis revealed abundant leukocytes and erythrocytes in urine. The plain abdominal X-ray performed in the standing position demonstrated a defect at the right lower side of the sacrum, and a dysplasic image displayed deviation to the left (scimitar sacrum) (Fig. 1). On abdominopelvic ultrasound, a multilocular septated cystic lesion measuring 5.7 × 6 cm in the presacral area was detected (Fig. 2). On abdominal tomogram, hypoplasic appearance of the right sides of S3, and vertebras inferior to S3, leftward deviation of sacrum (scimitar sacrum), and a presacral cystic lesion were detected (Fig. 3). On lumbosacral magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), widening of the right S3-S4 and S4-S5 neural foramens, and a multilocular, septated anterior sacral meningocele (ASM) which continued with sacral spinal canal anteriorly displaced bladder, and rectum were observed (Fig. 4).
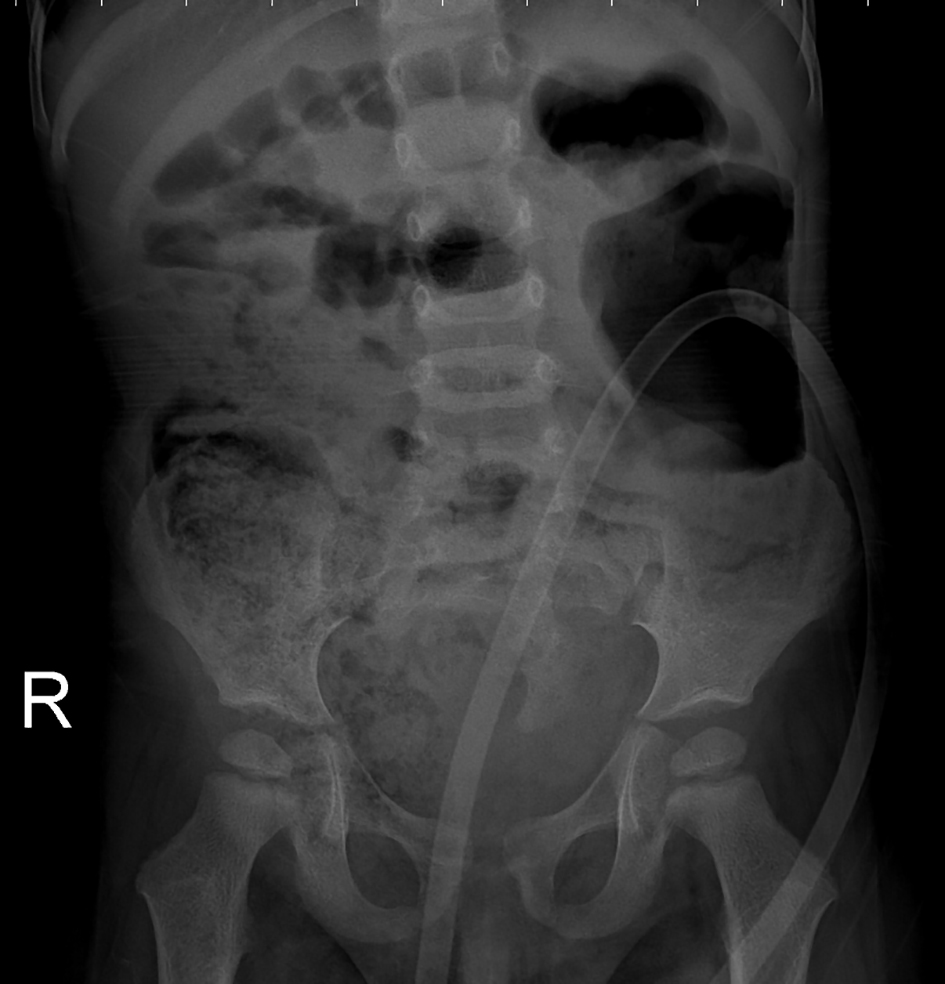 Click for large image | Figure 1. An abdominal radiograph: a defect at the right lower side of the sacrum, and a dysplasic image displaying deviation to the left (scimitar sacrum). |
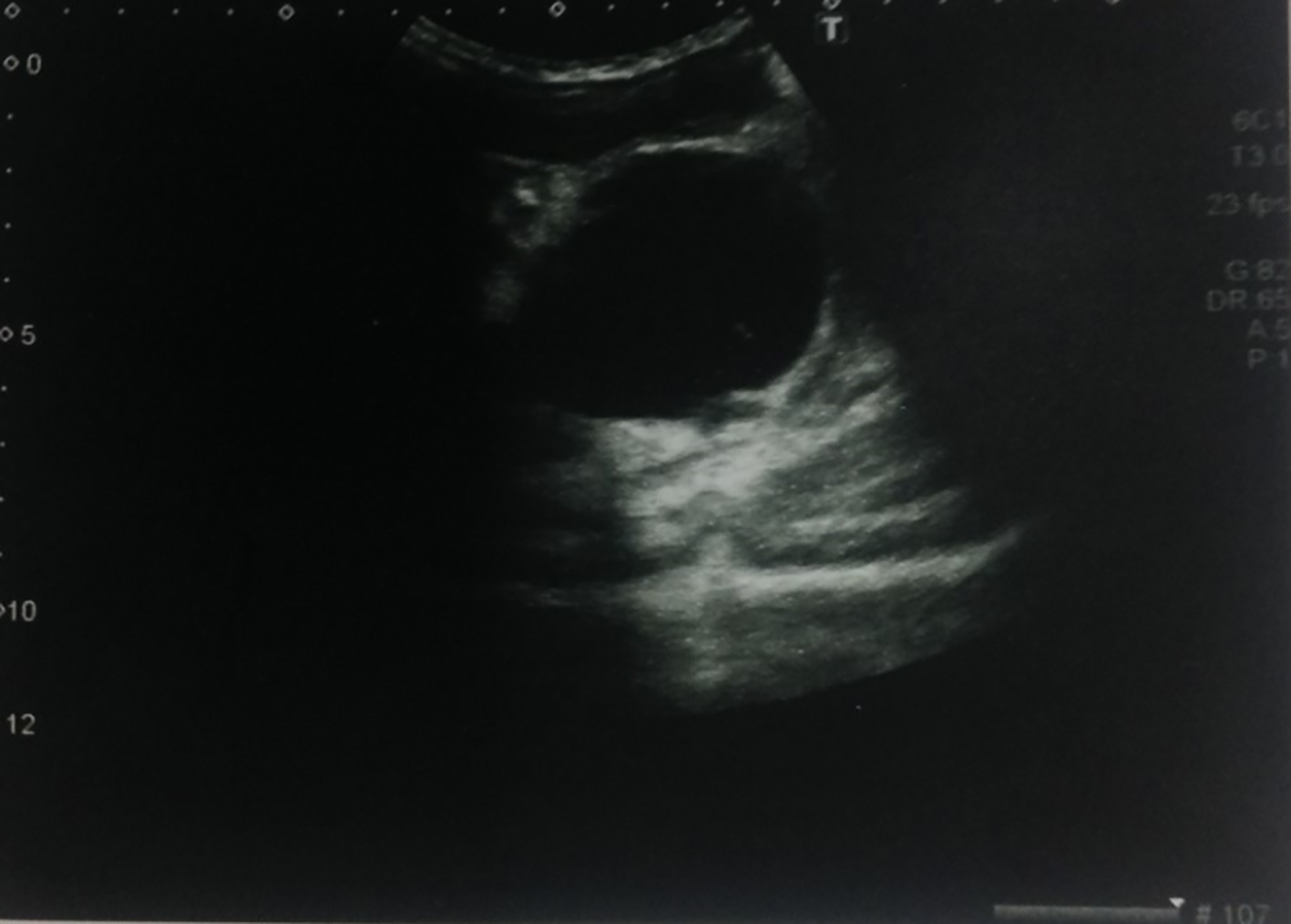 Click for large image | Figure 2. An ultrasound examination revealed a multilocular septated cystic lesion measuring 5.7 × 6 cm in the presacral area. |
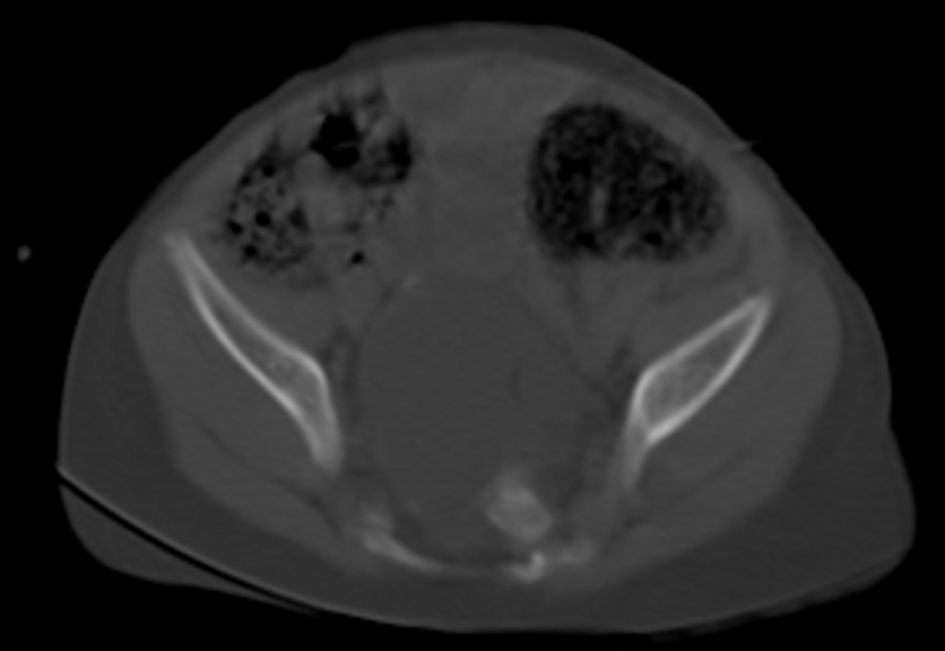 Click for large image | Figure 3. Abdominal tomogram: hypoplasic appearance of the right sides of S3, and vertebras inferior to S3, leftward deviation of sacrum (scimitar sacrum), and a presacral cystic lesion. |
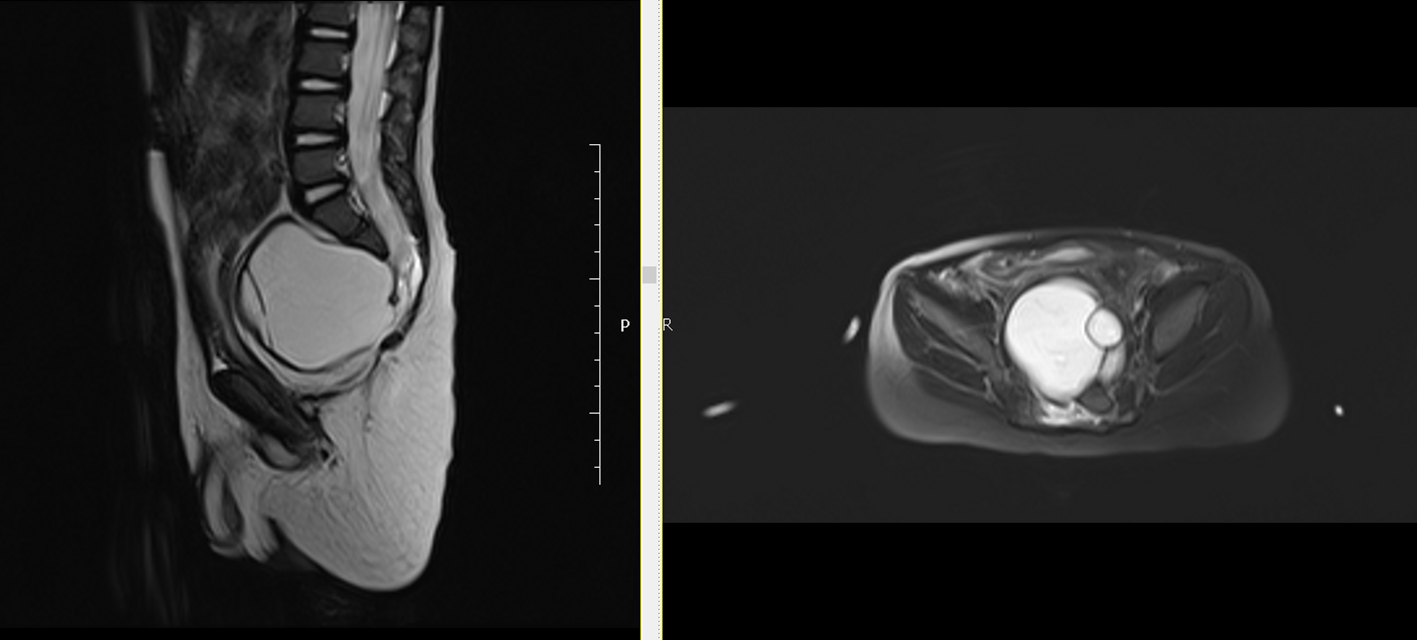 Click for large image | Figure 4. Lumbosacral MRI: widening of the right S3-S4 and S4-S5 neural foramens, and a multilocular, septated anterior sacral meningocele (ASM) which continued with sacral spinal canal anteriorly displaced bladder, and rectum were observed. |
We performed posterior sagittal anorectoplasty (PSARP). The patient was also operated in the Clinics of Neurosurgery with the indication of ASM.
| Discussion | ▴Top |
This syndrome which was named after scientist Guldo Currarino who first discovered this triad is characterized by a sacral bone defect, a congenital hindgut anomaly, and a presacral tumor. This syndrome has been reported to stem from the HLXB9 gene mutations on the chromosome 7. Therefore, presacral masses and sacral ageneses w/o anorectal anomalies are suggestive of possible familial CS [5].
Presacral mass which accompanies CS may consist of a teratoma, a hamartoma, a neuroenteric cyst, anterior meningocele or a combination of these four entities [7]. Sacral agenesis is defined as partial or complete congenital absence of sacrum. Most cases are asymptomatic. It has been reported that presacral mass results in symptoms such as intractable constipation, urinary incontinence, sacral anesthesia, paraesthesia of the lower extremities, disturbance of anal sphincter control, etc. Among them, constipation is the most commonly reported symptom [8]. Other symptoms are related to recurrent urinary tract infections, nausea, headache, and lumbar pain [8]. In our case, clinical symptoms of urinary infection were associated with constipation. Though rarely its association with HD has been reported [9]. Still, presence of CS was reported in an adult case with chronic anal fistula [6]. In the diagnosis and follow-up of CS, radiological imaging modalities such as ultrasonography (US), computed tomography (CT), and MRI play a vital role [10].
Kassir et al reported MRI as a specific and sensitive non-invasive diagnostic tool in cases with anorectal malformation [6]. MRI can be used reliably in the diagnosis of this syndrome, associated mass lesions, and other pathologies, and also during post-treatment follow-up period of cases with CS [10].
Regardless of its anatomical characteristics, presacral mass should be completely removed during surgical resection. In our case, anterior meningocele was detected, and sacral laminectomy was applied through retroperitoneal approach. In these cases, in order to avoid serious neurological complications, the connection between spinal canal and tumor should not be overlooked. Though rarely, since its malignant transformation into teratoma has been reported, multidisciplinary approach is very important in cases with CS which can result in morbidities and mortality.
Conclusion
Anal atresia can be one of the components of Currarino triad. In a patient who was admitted because of the presence of anal atresia, in order to preclude potential complications, probable concomitancy of this syndrome should not be forgotten.
Source of Support
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Funding
None.
Author Contributions
Sevgi Buyukbese Sarsu has contributed to writing this paper. Sevgi Buyukbese Sarsu, Mehmet Ergun Parmaksiz, Esra Cabalar, Ali Karapur and Cihat Kaya have contributed to data collections.
| References | ▴Top |
- Markljung E, Adamovic T, Cao J, Naji H, Kaiser S, Wester T, Nordenskjold A. Novel mutations in the MNX1 gene in two families with Currarino syndrome and variable phenotype. Gene. 2012;507(1):50-53.
doi pubmed - Merello E, De Marco P, Ravegnani M, Riccipetitoni G, Cama A, Capra V. Novel MNX1 mutations and clinical analysis of familial and sporadic Currarino cases. Eur J Med Genet. 2013;56(12):648-654.
doi pubmed - Furuta S, Sato H, Hamano S, Kitagawa H. Currarino syndrome associated with Hirschsprung's disease: Case report and literature review. J Ped Surg Case Reports. 2015; 3:308-311.
doi - Robbins JB, Broadwell C, Chow LC, Parry JP, Sadowski EA. Mullerian duct anomalies: embryological development, classification, and MRI assessment. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015;41(1):1-12.
doi pubmed - Perez Vega-Leal C, Sainz Gomez C, Ubis Rodriguez E, Garrido-Dominguez E, Diez Fernandez A, Rubio Viguera V. Hallazgos radiologicos en el sindrome de Currarino. Radiologia. 2013;55:233-238.
doi pubmed - Kassir R, Kaczmarek D. A late-recognized Currarino syndrome in an adult revealed by an anal fistula. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2014;5(5):240-242.
doi pubmed - Djordjevic I, Pejcic T, Rancic M, Radovic M, Bosnjakovic P, Radjenovic-Petkovic T, Nastasijevic-Borovac D, et al. Difficulties in establishing a timely diagnosis of pulmonary artery sarcoma misdiagnosed as chronic thrombo-embolic pulmonary disease: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2009;3:64.
doi pubmed - Arora P, Purai N, Rajpurkar M, Kamat D. A missed case of Currarino syndrome. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2010;49(2):183-185.
doi pubmed - Ohno K, Nakamura T, Azuma T, Nakaoka T, Takama Y, Hayashi H, Horiike M, et al. Familial Currarino syndrome associated with Hirschsprung disease: two cases of a mother and daughter. J Pediatr Surg. 2013;48(1):233-238.
doi pubmed - Akay S, Battal B, Karaman B, Bozkurt Y. Complete currarino syndrome recognized in adulthood. J Clin Imaging Sci. 2015;5:10.
doi pubmed
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Clinical Medicine Research is published by Elmer Press Inc.


