| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.jocmr.org |
Letter to the Editor
Volume 12, Number 10, October 2020, pages 681-682
De Novo Urinary Symptoms Associated With COVID-19: COVID-19-Associated Cystitis
Nivedita Dhara, b, Sorabh Dharb, c, Ryan Timarc, Steven Lucasb, c, Laura E. Lambd, e, Michael B. Chancellord, e, f
aDetroit Medical Center, Detroit, MI, USA
bJohn D. Dingell VA Medical Center, Detroit, MI, USA
cWayne State University School of Medicine, Detroit, MI, USA
dDepartment of Urology, Beaumont Health System, Royal Oak, MI, USA
eOakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine, Rochester Hills, MI, USA
fCorresponding Author: Michael B. Chancellor, Beaumont Health Research Institute, 3811 W. 13 Mile Road, Suite 504, Royal Oak, MI 48073, USA
Manuscript submitted July 21, 2020, accepted July 27, 2020, published online September 21, 2020
Short title: COVID-19-Associated Cystitis
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/jocmr4294
| To the Editor | ▴Top |
Clinical symptoms that present early in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), which is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), have been well-reported. Although the majority number of patients develop mild symptoms, a small percentage can progressively develop acute respiratory distress syndrome and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome resulting in demise [1]. There is an emergence of new symptoms that involve many organ systems, some more subtle than others. As these symptoms may overlap with other common disease processes, it has been difficult to identify and link these symptoms as direct association with COVID-19 as the underlying cause [2].
Recently Mumm and his colleagues have reported increased urinary frequency in COVID-19 patients [3]. We noticed at our tertiary care medical center’s COVID-19 clinic that patients reported de novo urinary tract symptoms and therefore obtained institutional review board (IRB) approval for a case series. We surveyed urinary symptoms in patients who followed up in the outpatient setting after their hospitalization from COVID-19. All patients had confirmed positive SARS-CoV-2 molecular diagnostic test. Patients filled out their survey responses in the office setting. Urinary symptoms are based on a validated bladder health questionnaire (Overactive Bladder (OAB) Assessment Tool) [4]: The five individual symptom scores range from 0 to 5 based on urinary urgency, urge incontinence, incontinence, frequency, and nocturia. We noted patient’s hospital dates to establish length-of-stay (LOS) and the study was conducted from May 22 to June 26, 2020.
We identified 39 COVID-19-positive patients, including seven females and 32 males, who developed de novo urinary symptoms without urinary tract infection per standard urine culture and sensitivity testing. The patients were all outpatients post hospital discharge and did not have fever or other clinical conditions that would require inpatient health care. All patients were African American. Median LOS was 10 days (range 5 - 30). All 39 patients completed the symptom score survey. The median total OAB symptom score in men and women was 18 (ranges 12 - 20 and 15 - 21, respectively) (Table 1). Our case series bring awareness to the possibility of new onset urinary symptoms in COVID-19 patients and the cause of the symptoms remains unsolved. The most remarkable urologic complaints were increased urinary frequency of ≥ 13 episodes/24 h (85%) and nocturia ≥ four episodes/night (87%).
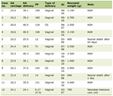 Click to view | Table 1. Demographics and Symptoms |
In conclusion, in a limited survey of patients at a tertiary care COVID-19 clinic, we found COVID-19 patients, both men and women, may report de novo lower urinary tract symptoms. The most bothersome new urinary tract symptoms include urinary frequency and nocturia. Physicians caring for COVID-19 should be aware of COVID-19-associated cystitis (CAC).
Acknowledgments
None to declare.
Financial Disclosure
None to declare.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no relevant conflict of interest to report.
Informed Consent
Informed consents have been obtained from the patients.
Author Contributions
MC and ND contributed to the formulation. SD, ND, LL, and MC planned the study. RT, ML, ND, and SD collected the data. LL, MC, ND, and SD analyzed the data. All authors involved in writing the manuscript.
Data Availability
The data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
| References | ▴Top |
- Wang H, Ma S. The cytokine storm and factors determining the sequence and severity of organ dysfunction in multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Am J Emerg Med. 2008;26(6):711-715.
doi pubmed - Sighinolfi MC, Rocco B, Mussini C. COVID-19: Importance of the Awareness of the Clinical Syndrome by Urologists. Eur Urol. 2020;78(1):e40-e41.
doi pubmed - Mumm JN, Osterman A, Ruzicka M, Stihl C, Vilsmaier T, Munker D, Khatamzas E, et al. Urinary Frequency as a Possibly Overlooked Symptom in COVID-19 Patients: Does SARS-CoV-2 Cause Viral Cystitis? Eur Urol. 2020.
doi pubmed - Overactive Bladder Assessment Tool. 2018. https://www.urologyhealth.org/educational-materials/overactive-bladder-assessment-tool-x4801. Accessed May 1, 2020.
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Clinical Medicine Research is published by Elmer Press Inc.


