| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 8, Number 5, May 2016, pages 402-409
Association Between Toxoplasma gondii Exposure and Heart Disease: A Case-Control Study
Cosme Alvarado-Esquivela, g, Misael Salcedo-Jaqueza, Luis Francisco Sanchez-Anguianob, Jesus Hernandez-Tinocob, Elizabeth Rabago-Sancheza, c, Isabel Beristain-Garciad, Oliver Liesenfelde, f, Sergio Estrada-Martinezb, Alma Rosa Perez-Alamosb, Ediyair Alvarado-Sotod
aBiomedical Research Laboratory, Faculty of Medicine and Nutrition, Juarez University of Durango State, Avenida Universidad S/N, 34000 Durango, Mexico
bInstitute for Scientific Research “Dr. Roberto Rivera-Damm”, Juarez University of Durango State, Avenida Universidad S/N, 34000 Durango, Mexico
cHospital General, Servicios de Salud de Durango, Cuauhtemoc 225 norte. 34000 Durango, Mexico
dFacultad de Enfermeria y Obstetricia, Juarez University of Durango State, Cuauhtemoc 223 norte, 34000 Durango, Mexico
eInstitute for Microbiology and Hygiene, Campus Benjamin Franklin, Charite Medical School, Hindenburgdamm 27, D-12203 Berlin, Germany
fPresent address: Roche Molecular Diagnostics, Pleasanton, CA, USA
gCorresponding Author: Cosme Alvarado-Esquivel, Biomedical Research Laboratory, Faculty of Medicine and Nutrition, Juarez University of Durango State, Avenida Universidad S/N, 34000 Durango, Dgo, Mexico
Manuscript accepted for publication March 11, 2016
Short title: Toxoplasma and Heart Disease
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.14740/jocmr2525w
| Abstract | ▴Top |
Background: The parasite Toxoplasma gondii causes infections all around the world. Infections with T. gondii are systemic and the parasite can persist in the heart muscle. Very little is known about the impact of T. gondii on patients with heart disease. We determined the association between T. gondii exposure and patients suffering from heart diseases attending in a public hospital in Durango, Mexico; the association of T. gondii exposure with socio-demographic, behavioral, and clinical characteristics of these patients was also investigated.
Methods: Through a case-control study, we examined the seroprevalence of anti-T. gondii IgG and IgM antibodies in 400 patients with heart diseases and 400 age- and gender-matched controls using enzyme-linked immunoassays. In addition, we analyzed the association of patient characteristics as determined by a standardized questionnaire with T. gondii exposure by bivariate and multivariate analyses.
Results: Fifty-five (13.8%) of 400 patients and 32 (8.0%) of 400 controls had anti-T. gondii IgG antibodies (odds ratio (OR) = 1.83; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.15 - 2.90; P = 0.01). High anti-T. gondii IgG levels (> 150 IU/mL) were found in 28 (50.9%) of the 55 positive cases and in 14 (43.8%) of the 32 positive controls (P = 0.51). Anti-T. gondii IgM antibodies were found in 13 (23.6%) of the 55 anti-T. gondii IgG positive patients and in 19 (59.4%) of 32 anti-T. gondii IgG positive controls (OR = 0.21; 95% CI: 0.08 - 0.54; P = 0.0008). Multivariate analysis showed that T. gondii exposure was positively associated with being born out of Durango State (OR = 2.93; 95% CI: 1.40 - 6.13; P = 0.004), and with consumption of alcohol (OR = 2.04; 95% CI: 1.01 - 4.12; P = 0.04).
Conclusions: Results obtained in this study indicate that T. gondii infection is associated with heart disease, and suggest that heart disease might be related with a chronic infection. This is the first report of an association of T. gondii exposure with alcohol consumption in this population. Results warrant for further research to determine the epidemiological impact of T. gondii exposure on patients with heart diseases. Risk factors associated with T. gondii exposure are critical to design future prevention strategies against T. gondii exposure.
Keywords: Toxoplasma gondii; Seroprevalence; Heart disease; Case-control study; Epidemiology; Alcohol
| Introduction | ▴Top |
The protozoan parasite Toxoplasma gondii causes infections all around the world [1]. Nearly one-third of the world population is infected with T. gondii [2]. Most infections with T. gondii occur by ingestion of food or water contaminated with oocysts shed by cats [3, 4] and eating undercooked or raw meat containing tissue cysts [3, 5]. The clinical spectrum of T. gondii infection varies from asymptomatic to severe systemic disease [3]. Most commonly, toxoplasmosis is a mild disease with lymphadenopathy. However, some T. gondii-infected individuals develop chorioretinitis that may progress to blindness [6]. Immunocompromised patients infected with T. gondii may develop severe neurological disease [7, 8]. In addition, primary infections with T. gondii during pregnancy may lead to congenital disease [3, 8]. Infections with T. gondii may manifest in the heart in humans [9-13] and animals [14-17] with myocarditis [18-20], pericarditis with myocarditis [21, 22], and acute heart failure [23, 24]. Patients with T. gondii myocarditis may present with pericardial effusion, constrictive pericarditis, congestive heart failure, and arrhythmias [11].
The seroepidemiology of infection with T. gondii in patients suffering from heart diseases has been poorly studied. We are not aware of any data about the epidemiology of T. gondii infection in these patients in Mexico. Therefore, we determined the association between T. gondii exposure and patients with heart disease attending in a public hospital in northern Mexico, and the association of seropositivity to T. gondii with socio-demographic, behavioral, and clinical characteristics of these patients.
| Methods | ▴Top |
Study design and study population
Through a case-control study, we enrolled 400 patients suffering from heart diseases attending in a public Hospital in Durango City, Mexico and 400 control subjects without heart diseases of the same city. All heart patients were enrolled from June to November 2014. Inclusion criteria for the cases were: 1) inpatients with heart disease attending in the Cardiology Department at the General Hospital of the Secretary of Health in Durango City; 2) aged 11 years and older; and 3) that voluntarily accepted to participate. Control subjects were randomly selected and were matched with cases by age and gender. Inclusion criteria for the control subjects were: 1) people without heart diseases from the general population of Durango City; and 2) who voluntarily accepted to participate in the study. Patients included 156 (39%) males and 244 (61%) females with a mean age of 58.87 ± 14.59 years (range 11 - 93 years). Controls included 156 males and 244 females with a mean age of 58.76 ± 14.54 years (range 9 - 91). Age was comparable between cases and controls (P = 0.91).
Ethical aspects
This study was approved by the Ethical Committee of the General Hospital of the Secretary of Health in Durango City, Mexico. The purpose and procedures of the study were explained to all patients. Participation in the study was voluntary. A written informed consent was obtained from all participants and from the next of kin of minor participants.
Sample size
For calculation of the sample size, we used a 95% confidence level, a power of 80%, a 1:1 proportion of cases and controls, a reference seroprevalence of 6.1% [25] as the expected frequency of exposure in controls, and an odds ratio (OR) of 2.1. The result of the sample size calculation was 370 cases and 370 controls.
Socio-demographic, clinical, and behavioral characteristics of patients
The socio-demographic, clinical, and behavioral characteristics of the patients were obtained with the aid of a standardized questionnaire. Socio-demographic data included age, sex, birthplace, residence, educational level, occupation, and socioeconomic status. Clinical data included diagnosis of the heart disease, evolution time (years) of the heart disease, functional classification of the heart disease, and response to treatment. To evaluate the functional class of heart disease, we used the criteria of the New York Heart Association [26]. In addition, we obtained clinical data about the presence of underlying diseases, history of lymphadenopathy, surgery, blood transfusion or transplants, presence of frequent headaches, dizziness, and impairments of memory, reflexes, hearing, and vision. Obstetric data in women were also obtained. Behavioral data included contact with animals, cleaning cat excrement, foreign traveling, consumption of meat (pork, beef, goat, lamb, boar, chicken, turkey, pigeon, duck, rabbit, venison, squirrel, horse, opossum, or other), frequency of meat consumption, consumption of raw or undercooked meat, unpasteurized milk, dried or processed meat (ham, sausages or chorizo), consumption of unwashed raw vegetables or fruits, untreated water, frequency of eating away from home (in restaurants or fast food outlets), contact with soil (gardening or agriculture), hand washing before eating, and type of flooring at home.
Detection of T. gondii antibodies
A blood sample (about 3 mL) was obtained from each participant. Blood was centrifuged and serum samples were obtained. Serum samples were kept frozen at -20 °C until analyzed. Sera were analyzed for anti-T. gondii IgG antibodies with a commercially available enzyme immunoassay “Toxoplasma IgG” (Diagnostic Automation Inc., Calabasas, CA, USA). Anti-T. gondii IgG antibody levels were expressed as International Units (IU)/mL. A cut-off of ≥ 8 IU/mL was used for seropositivity. In addition, sera of patients positive for anti-T. gondii IgG antibodies were further analyzed for anti-T. gondii IgM antibodies by a commercially available enzyme immunoassay “Toxoplasma IgM” kit (Diagnostic Automation Inc., Calabasas, CA, USA). All assays were performed following the manufacturer’s instructions. We included positive and negative controls in each run.
Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis was performed with the software: Epi Info version 7 and SPSS version 15.0. We used the Student’s t-test to compare age among cases and controls. The Pearson’s Chi-square test and the Fisher exact test (when values were small) were used for comparison of the frequencies among groups. Multivariate analysis was used to assess the association between the characteristics of the patients and the seropositivity to anti-T. gondii antibodies. Socio-demographic and behavioral characteristics of the patients were included in the multivariate analysis if they had a P value ≤ 0.20 in the bivariate analysis. OR and 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated by multivariate analysis with the Enter method. A P value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
| Results | ▴Top |
Anti-T. gondii IgG antibodies were detected in 55 (13.8%) of 400 patients with heart diseases and in 32 (8.0%) of 400 controls. Seroprevalence of anti-T. gondii IgG antibodies was significantly higher in cases than in controls (OR = 1.83; 95% CI: 1.15 - 2.90; P = 0.01). High anti-T. gondii IgG levels (> 150 IU/mL) were found in 28 (50.9%) of the 55 positive cases and in 14 (43.8%) of the 32 positive controls (P = 0.51). Anti-T. gondii IgM antibodies were found in 13 (23.6%) of the 55 anti-T. gondii IgG positive patients and in 19 (59.4%) of 32 anti-T. gondii IgG positive controls. Seroprevalence of anti-T. gondii IgM antibodies was significantly lower in cases than in controls (OR = 0.21; 95% CI: 0.08 - 0.54; P = 0.0008).
General socio-demographic characteristics of the 400 patients studied and their correlation with T. gondii seroprevalence are shown in Table 1. Seroprevalence of T. gondii infection was not associated with age, sex, residence, educational level, occupation or socioeconomic level of the patients by bivariate analysis. In contrast, patients born out of Durango State had a significantly higher seroprevalence of T. gondii infection than patients born in Durango State (P = 0.008).
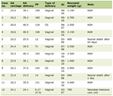 Click to view | Table 1. Socio-Demographic Characteristics of Patients With Heart Diseases and Seroprevalence of T. gondii Infection |
With respect to the clinical characteristics, the variables “ischemic disease”, “memory impairment”, and “blood transfusion” showed P values ≤ 0.20 by bivariate analysis. Whereas other diagnoses of heart disease, functional stages of heart disease, response to treatment, presence of underlying diseases, history of lymphadenopathy, surgery or transplants, presence of frequent headaches, dizziness, and impairments of memory, reflexes, hearing, and vision showed P values > 0.20 by bivariate analysis. A selection of clinical characteristics of the patients and their correlation with T. gondii seroprevalence is shown in Table 2. In female patients, seropositivity to T. gondii did not correlate with obstetric history.
 Click to view | Table 2. Correlation of T. gondii Seroprevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Patients With Heart Diseases |
Among the behavioral characteristics, a number of variables showed P values ≤ 0.20 in the bivariate analysis including national trips (P = 0.12), consumption of meat from squirrel (P = 0.08), opossum (P = 0.05), armadillo (P = 0.18), iguana (P = 0.14), and snake (P = 0.19), degree of meat cooking (P = 0.05), consumption of unwashed raw fruits (P = 0.06), frequency of eating out of home (P = 0.07), frequency of meat consumption (P = 0.16), and alcohol consumption (P = 0.02). A selection of behavioral characteristics of the patients and their correlation with T. gondii seroprevalence are shown in Table 3. Other behavioral characteristics of patients including contact with cats, cleaning cat excrement, raising animals, consumption of meat other than those from squirrel, opossum, armadillo, iguana and snake, consumption of unpasteurized milk, processed meat, unwashed raw vegetables, and untreated water, and contact with soil showed P values > 0.20 in the bivariate analysis. Further analysis by using logistic regression showed that T. gondii exposure was positively associated with being born out of Durango State (OR = 2.93; 95% CI: 1.40 - 6.13; P = 0.004), and with consumption of alcohol (OR = 2.04; 95% CI: 1.01 - 4.12; P = 0.04) (Table 4).
 Click to view | Table 3. Bivariate Analysis of Selected Putative Risk Factors for Infection With T. gondii in Patients With Heart Disease |
 Click to view | Table 4. Multivariate Analysis of Selected Characteristics of Patients and Their Association With T. gondii Infection |
| Discussion | ▴Top |
The seroepidemiology of T. gondii infection in patients with heart diseases is largely unknown. The present study was performed to investigate the association of T. gondii infection with patients suffering from heart diseases attending in a public hospital in Durango City, Mexico and to determine the correlates of infection in these patients. We found a 13.8% seroprevalence of anti-T. gondii IgG antibodies in patients suffering from heart disease. This seroprevalence is higher than the 8.0% seroprevalence found in controls, and the 6.1% seroprevalence of T. gondii infection reported in the general population in Durango City [25]. Results indicate that patients with heart diseases represent a risk group for T. gondii infection. Seroprevalence of T. gondii infection increases with age in our region [25, 27]. Therefore, we matched cases and controls by age and this strategy allowed us to evaluate properly the association between T. gondii exposure and patients with heart disease. It is hypothesized that patients with T. gondii infection have a higher risk for heart disease caused by the presence of cysts in the heart muscle. The interaction of T. gondii within skeletal muscle cells has been nicely described recently [28]. However, to the best of our knowledge, the interaction of T. gondii within heart muscle cells has not been studied. It is unclear how T. gondii may affect the function of heart muscle.
With respect to IgM seropositivity to T. gondii, it is remarkable that seroprevalence of anti-T. gondii IgM antibodies was significantly lower in cases than in controls. This finding suggests that heart disease might be related with a chronic rather than a recent infection with T. gondii. However, the high frequency of IgM antibodies should be interpreted with caution since IgM ELISA kits have a high rate of false positive results [29]. Seroprevalence of T. gondii infection varied among heart diseases. However, this difference was not statistically significant. This might be due to a small sample size of some subgroups of specific diagnosis.
We searched for factors associated with the T. gondii exposure in patients. Logistic regression showed that seropositivity was positively associated with being born out of Durango State, and with consumption of alcohol. The characteristic “born out of Durango State” has been associated with T. gondii seropositivity in some previous epidemiological studies in Durango including adults [25] and elderly people of the general population [27]. On the other hand, the association of T. gondii exposure with consumption of alcohol was unexpected. To the best of our knowledge, this association has not been reported in alive people. It is unclear why subjects with alcohol consumption had a higher seroprevalence of T. gondii infection than those without alcohol consumption. It is uncertain whether subjects with alcohol consumption have behaviors that might favor T. gondii exposure. In a recent study of postmortem examinations in people who died suddenly in Warsaw, Poland, the frequency of T. gondii IgG antibodies was higher in subjects with positive blood alcohol test than that in subjects with negative test [30]. Researchers also found the highest seroprevalence of T. gondii infection among persons who died because of suicide and with positive alcohol test [30]. Interestingly, ethanol has been involved in T. gondii invasion to and egress from the host cells [31], and ethanol produces a dose-dependent stimulation of microneme secretion leading to adhesion of T. gondii to host cells [32]. Furthermore, exposure of T. gondii tachyzoites to ethanol induced conoid extrusion - an event of cell invasion - without affecting parasite viability [33]. These facts support the association of T. gondii exposure and alcohol consumption found in the present study. Further research to elucidate the role of alcohol consumption with T. gondii exposure should be conducted.
The current study was limited for the scanty number of certain heart diseases among the studied population. This limitation did not allow properly assessing differences in T. gondii seroprevalence among the diagnoses and functional stages of heart diseases.
Conclusion
Our results indicate that T. gondii infection is associated with heart disease and suggest that heart disease might be related with a chronic infection. Results warrant for further research to determine the epidemiological impact of T. gondii exposure on heart diseases. The association of T. gondii infection with alcohol consumption deserves further research. Risk factors associated with T. gondii exposure found in the present study may help to design future prevention strategies against T. gondii infection.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Financial Support
This work was supported by Juarez University of Durango State.
| References | ▴Top |
- Dubey JP. Toxoplasmosis of animals and humans. Boca Raton, Florida: Second Edition. CRC Press; 2010.
- Hill DE, Chirukandoth S, Dubey JP. Biology and epidemiology of Toxoplasma gondii in man and animals. Anim Health Res Rev. 2005;6(1):41-61.
doi pubmed - Montoya JG, Liesenfeld O. Toxoplasmosis. Lancet. 2004;363(9425):1965-1976.
doi - Torrey EF, Yolken RH. Toxoplasma oocysts as a public health problem. Trends Parasitol. 2013;29(8):380-384.
doi pubmed - Jones JL, Dubey JP. Foodborne toxoplasmosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;55(6):845-851.
doi pubmed - Pleyer U, Torun N, Liesenfeld O. Ocular toxoplasmosis. Ophthalmologe. 2007;104(7):603-615, quiz 616.
doi pubmed - Munoz M, Liesenfeld O, Heimesaat MM. Immunology of Toxoplasma gondii. Immunol Rev. 2011;240(1):269-285.
doi pubmed - Weiss LM, Dubey JP. Toxoplasmosis: A history of clinical observations. Int J Parasitol. 2009;39(8):895-901.
doi pubmed - Hofman P, Drici MD, Gibelin P, Michiels JF, Thyss A. Prevalence of toxoplasma myocarditis in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Br Heart J. 1993;70(4):376-381.
doi pubmed - Lobzin Iu V, Boitsov SA, Filippov AE, Linchak RM, Mangutov DA. Effect of respiratory infections on the clinical course of coronary artery disease. Klin Med (Mosk). 2005;83(11):22-26.
- Hidron A, Vogenthaler N, Santos-Preciado JI, Rodriguez-Morales AJ, Franco-Paredes C, Rassi A, Jr. Cardiac involvement with parasitic infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2010;23(2):324-349.
doi pubmed - Chandenier J, Jarry G, Nassif D, Douadi Y, Paris L, Thulliez P, Bourges-Petit E, et al. Congestive heart failure and myocarditis after seroconversion for toxoplasmosis in two immunocompetent patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2000;19(5):375-379.
doi pubmed - Lanjewar DN, Agale SV, Chitale AR, Joshi SR. Sudden death due to cardiac toxoplasmosis. J Assoc Physicians India. 2006;54:244-245.
pubmed - Bossart GD, Mignucci-Giannoni AA, Rivera-Guzman AL, Jimenez-Marrero NM, Camus AC, Bonde RK, Dubey JP, et al. Disseminated toxoplasmosis in Antillean manatees Trichechus manatus manatus from Puerto Rico. Dis Aquat Organ. 2012;101(2):139-144.
doi pubmed - Silva AF, Oliveira FC, Leite JS, Mello MF, Brandao FZ, Leite RI, Frazao-Teixeira E, et al. Immunohistochemical identification of Toxoplasma gondii in tissues from Modified Agglutination Test positive sheep. Vet Parasitol. 2013;191(3-4):347-352.
doi pubmed - Las RD, Shivaprasad HL. An outbreak of toxoplasmosis in an aviary collection of Nicobar pigeons (Caloenas nicobaria). J S Afr Vet Assoc. 2008;79(3):149-152.
pubmed - Dubey JP, Alvarado-Esquivel C, Herrera-Valenzuela VH, Ortiz-Diaz JJ, Oliveira S, Verma SK, Choudhary S, et al. A new atypical genotype mouse virulent strain of Toxoplasma gondii isolated from the heart of a wild caught puma (Felis concolor) from Durango, Mexico. Vet Parasitol. 2013;197(3-4):674-677.
doi pubmed - Strabelli TM, Siciliano RF, Vidal Campos S, Bianchi Castelli J, Bacal F, Bocchi EA, Uip DE. Toxoplasma gondii Myocarditis after Adult Heart Transplantation: Successful Prophylaxis with Pyrimethamine. J Trop Med. 2012;2012:853562.
doi pubmed - Dixit PG, Umap PS, Bardale RV. Toxoplasma myocarditis presenting as myocardial infarction. Indian J Med Sci. 2007;61(4):218-220.
doi pubmed - Eza DE, Lucas SB. Fulminant toxoplasmosis causing fatal pneumonitis and myocarditis. HIV Med. 2006;7(6):415-420.
doi pubmed - Pergola G, Cascone A, Russo M. Acute pericarditis and myocarditis by Toxoplasma gondii in an immunocompetent young man: a case report. Infez Med. 2010;18(1):48-52.
pubmed - Mroczek-Czernecka D, Rostoff P, Piwowarska W. Acute toxoplasmic perimyocarditis in a 67-year-old HIV-negative woman--a case report. Przegl Lek. 2006;63(2):100-103.
pubmed - Guillot JP, Beylot J, Turner K, Lacoste D, Gabinski C, Besse P. Acute cardiac insufficiency and toxoplasmosis. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 1989;82(10):1767-1770.
pubmed - Rostoff P, Mroczek-Czernecka D, Piwowarska W, Gackowski A, Konduracka E, Trzos M, Pasowicz M. Elevated CA-125 level in acute heart failure due to Toxoplasma gondii perimyocarditis. Int J Cardiol. 2008;130(3):e114-116.
doi pubmed - Alvarado-Esquivel C, Estrada-Martinez S, Pizarro-Villalobos H, Arce-Quinones M, Liesenfeld O, Dubey JP. Seroepidemiology of Toxoplasma gondii infection in general population in a northern Mexican city. J Parasitol. 2011;97(1):40-43.
doi pubmed - Bennett JA, Riegel B, Bittner V, Nichols J. Validity and reliability of the NYHA classes for measuring research outcomes in patients with cardiac disease. Heart Lung. 2002;31(4):262-270.
doi pubmed - Alvarado-Esquivel C, Liesenfeld O, Burciaga-Lopez BD, Ramos-Nevarez A, Estrada-Martinez S, Cerrillo-Soto SM, Carrete-Ramirez FA, et al. Seroepidemiology of Toxoplasma gondii infection in elderly people in a northern Mexican city. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012;12(7):568-574.
doi pubmed - Swierzy IJ, Muhammad M, Kroll J, Abelmann A, Tenter AM, Luder CG. Toxoplasma gondii within skeletal muscle cells: a critical interplay for food-borne parasite transmission. Int J Parasitol. 2014;44(2):91-98.
doi pubmed - Liesenfeld O, Press C, Montoya JG, Gill R, Isaac-Renton JL, Hedman K, Remington JS. False-positive results in immunoglobulin M (IgM) toxoplasma antibody tests and importance of confirmatory testing: the Platelia Toxo IgM test. J Clin Microbiol. 1997;35(1):174-178.
pubmed - Samojlowicz D, Borowska-Solonynko A, Golab E. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii parasite infection among people who died due to sudden death in the capital city of Warsaw and its vicinity. Przegl Epidemiol. 2013;67(1):29-33, 115-118.
pubmed - Arrizabalaga G, Boothroyd JC. Role of calcium during Toxoplasma gondii invasion and egress. Int J Parasitol. 2004;34(3):361-368.
doi pubmed - Carruthers VB, Moreno SN, Sibley LD. Ethanol and acetaldehyde elevate intracellular [Ca2+] and stimulate microneme discharge in Toxoplasma gondii. Biochem J. 1999;342(Pt 2):379-386.
doi pubmed - Del Carmen MG, Mondragon M, Gonzalez S, Mondragon R. Induction and regulation of conoid extrusion in Toxoplasma gondii. Cell Microbiol. 2009;11(6):967-982.
doi pubmed
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Clinical Medicine Research is published by Elmer Press Inc.


