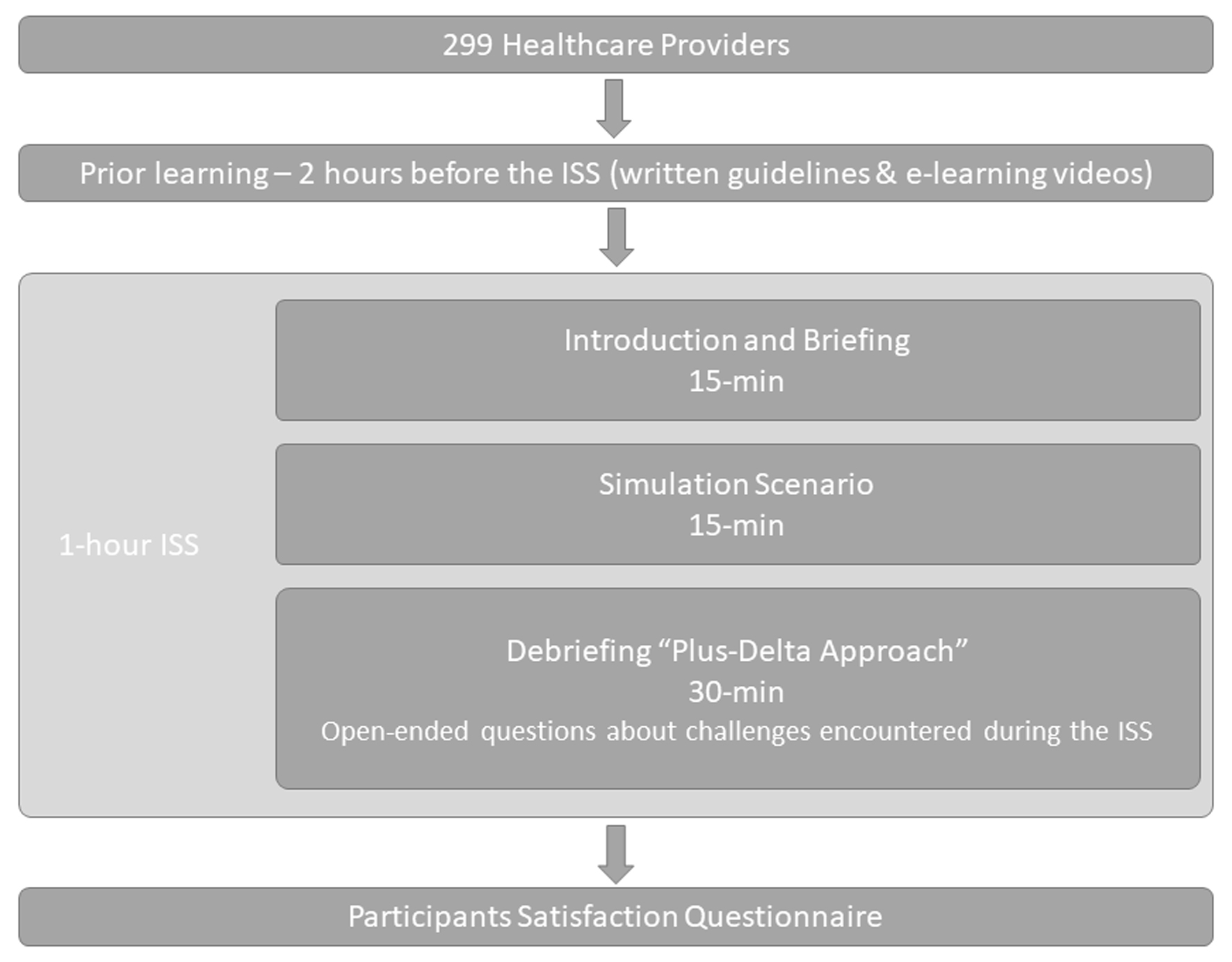
Figure 1. Study flow for in-situ simulation to train interprofessional adult emergency, pediatric emergency, and anesthesiology teams in airway management for suspected or confirmed COVID-19 patients. COVID-19: coronavirus disease 2019.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 14, Number 9, September 2022, pages 377-387
A Newly Developed Interprofessional In-Situ Simulation-Based Training for Airway Management of COVID-19 Patients: Identification of Challenges and Safety Gaps, and Assessment of the Participants’ Reaction
Figure

Tables
| Participants | Pediatric, N (%) | Adult, N (%) | Anesthesia, N (%) | Total, N (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total participants | 71 | 99 | 129 | 299 |
| Consultants | 9 | 20 | 37 | 170 |
| Physician specialists | 12 | 3 | 34 | 49 |
| Fellows | 14 | - | - | 14 |
| Residents | 0 | 16 | 25 | 41 |
| Nurses | 30 | 40 | - | 70 |
| Anesthesia technologist | - | - | 33 | 33 |
| Respiratory therapists | 6 | 20 | - | 26 |
| In-situ simulation session item | Agree, N (%) | Strongly agree, N (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Program objectives | ||
| I understood the learning objectives. | 40 (14.39%) | 235 (84.53%) |
| I was able to relate each of the learning objectives to the learning I achieved. | 45 (16.19%) | 230 (82.73%) |
| I was appropriately challenged by the material. | 50 (17.99%) | 225 (80.94%) |
| Course materials | ||
| I found the course materials easy to navigate. | 65 (23.38%) | 205 (73.74%) |
| I felt that the course materials will be essential for my success. | 64 (23.02%) | 208 (74.82%) |
| Content relevance | ||
| I will be able to immediately apply what I learned. | 59 (21.22%) | 216 (77.70%) |
| Facilitator knowledge | ||
| My learning was enhanced by the knowledge of the facilitator. | 42 (15.11%) | 232 (83.45%) |
| My learning was enhanced by the experiences shared by the facilitator. | 40 (14.39%) | 234 (84.17%) |
| Facilitator delivery | ||
| I was well engaged during the session. | 43 (15.47%) | 232 (83.45%) |
| It was easy for me to get actively involved during the session. | 45 (16.19%) | 230 (82.73%) |
| I was comfortable with the pace of the program. | 47 (16.91%) | 228 (82.01%) |
| I was comfortable with the duration of the session. | 47 (16.91%) | 227 (81.65%) |
| Facilitator style | ||
| I was engaged during the session. | 42 (17.52%) | 234 (84.17%) |
| I was given ample opportunity to get answers to my questions. | 39 (14.03%) | 236 (84.89%) |
| I was given ample opportunity to practice the skills I am asked to learn. | 39 (14.03%) | 236 (84.89%) |
| Program evaluation | ||
| I was given ample opportunity to demonstrate my knowledge. | 44 (15.83%) | 231 (83.09%) |
| I was given ample opportunity to demonstrate my skills. | 43 (15.47%) | 232 (83.45%) |
| Pre-course reading and video | ||
| It was helpful to review knowledge and skills related to the simulation objectives. | 51 (18.35%) | 219 (78.78%) |
| Facility | ||
| I found the room atmosphere to be comfortable. | 62 (22.30%) | 209 (75.18%) |
| I was pleased with the room set-up. | 67 (24.10%) | 205 (73.74%) |
| I experienced minimal distraction during the session. | 67 (24.10%) | 203 (73.02%) |
| Theme | Category | Subcategory | Number of codes | Example of facilitators’ summaries of participants’ comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPE: personal protective equipment; PEEP: positive end-expiratory pressure; HEPA: high-efficiency particulate air; COVID-19: coronavirus disease 2019; PAWP: pulmonary artery wedge pressure; ETT: endotracheal tube; RSI: rapid sequence intubation; CDC: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; AGPs: aerosol-generating procedures; PAPR: powered air-purifying respirator. | ||||
| Airway management | Anticipation | Anticipation of difficult airway | 33 | Anticipated difficult airway |
| Preparation | Preparation of intubation equipment | 29 | Equipment checks before intubation | |
| Connection of the catheter (extension) device in pediatric patients | 6 | Use the catheter (extensor) | ||
| Connection of the bag-mask ventilation device to the PEEP valve device | 5 | Do not forget the PEEP valve | ||
| Pre-oxygenation | Pre-oxygenation using two-handed bag-mask ventilation technique (V-E) for 3 - 5 min | 18 | Pre O2 with two hands technique, V shape holding the mask | |
| Administration of low flow O2 in case desaturation with minimal pressure < 20 mm Hg | 15 | Low flow O2 | ||
| Application of high flow nasal cannula in case of desaturation | 6 | Need to improve oxygenation for COVID-19 patients by using high flow nasal cannula and minimize using Ambu bag | ||
| Application of high flow non-rebreathing mask in case desaturation | ||||
| Avoidance of non-invasive ventilation | ||||
| Protection | Closure of the suction system | 19 | Close suction | |
| Placement | Assignment of the expert to intubate | 14 | Intubation need to be done by a most expert in the room | |
| Usage of video laryngoscopy | 9 | Order video laryngoscope | ||
| Performance RSI | 9 | RSI medication | ||
| Post-intubation management | Inflation of the cuffed endotracheal tube 5 mm Hg > PAWP | 9 | Inflating the cuff before the ventilation | |
| Assure of the placement of the endotracheal tube | 12 | Check the tube position | ||
| Assure clamping of ETT | 22 | Clamp ETT | ||
| Infection control | Equipment | Familiarization with the equipment placement in the emergenct room | 5 | Need to be more familiar with equipment place |
| Prepare all the needed equipment outside the intubation room | 33 | Bring all the needed equipment inside to prevent going outside and inside the room, or assign a runner to prepare equipment from outside | ||
| Crowd control | Minimization the number of personnel inside the room | 24 | Limit the number of personnel in the room to limit exposure | |
| COVID-19 protection | Consideration of use of plastic cover for pediatric patients or plastic box for adults | 23 | Order the plastic cover for pediatric or the plastic box for adult | |
| Attachment of viral filter | 24 | Need to use a viral filter for the Ambu bag | ||
| Follow CDC/institutional guidelines for AGPs | 13 | Follow KFMC protocol | ||
| Application of surgical mask on the patient to minimize aerosolization | 5 | Keep an eye to minimize aerosolization by applying a mask | ||
| Prioritization of healthcare workers safety | 12 | Check with the team and make sure everyone is wearing a proper mask, and request PAPR if needed. | ||
| Donning | Adherence to the proper sequence of donning | 25 | The sequence of donning and doffing Do not wear a surgical mask under N95 | |
| Doffing | Adherence to the proper sequence of doffing | 30 | Doffing is done outside | |
| PPE | Assignments of compliance observer during the procedure | 15 | Having a person outside to monitor appropriate donning and doffing | |
| Room ventilation | Assure the presence of HEPA filter maximum power | 5 | Check if filter inside the room | |
| Assure closure of the door during intubation | Closing the door throughout the procedure | |||
| Team dynamics | Clear orders | Loudness and clearness of the team leader voice | 15 | Avoid floating order Raise voices |
| Speaking up | Speaking up | 29 | The team needs to speak up if they have suggestions for the team leader. | |
| Role assignment | Assignment of the team members and roles clarity | 23 | Know your role | |
| Share mental model | A shared mental model with the team members | 17 | Share mental model | |
| Communication | Insure closed-loop communication | 20 | Close the loop of communication | |
| Leadership | Synchronous communication between the team leader and team | 14 | Avoid floating order and assign it to a specific person | |
| Anticipation | Anticipation of the challenges | 25 | Anticipate and act properly | |
| Situation awareness | Acquaintance with the equipment | 11 | The team leader needs to make sure that his team is familiar and knows how to use the equipment | |
| Pediatric emergency | Adult emergency | Anesthesia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CDC: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; PPE: personal protective equipment. | |||
| Airway management | Anticipation of difficult airway | Preparation of intubation equipment | Anticipation of difficult airway |
| Assignment of the most expert provider to perform intubation | Using non-rebreathing mask/using high flow nasal cannula/avoidance non-invasive ventilation | Closure of the suction system | |
| Use of video laryngoscopy | Anticipation of difficult airway | Administration of low flow O2 in case desaturation with minimal pressure < 20 mm Hg | |
| Infection control | Minimization of the total number of personnel inside the room | Adherence to the proper sequence of doffing | Preparation of all needed equipment outside the intubation room |
| Prioritization of healthcare workers safety | Avoidance of incomplete donning or doffing of the PPE | Attachment of a viral filter | |
| Adherence to the proper sequence of donning | Consideration of using plastic cover for the pediatric or plastic box for adult | Following CDC/institutional guidelines in aerosol-generating procedure | |
| Team dynamic | Speaking up | Assure closed-loop communication | Speaking up |
| Assignment of the team and clarity of roles | Speaking up | Assignment of the team and clarity of roles | |
| Loudness and clarity of the team leader voice | Synchronous communication between the team leader and team | Loudness and clarity of the team leader voice | |