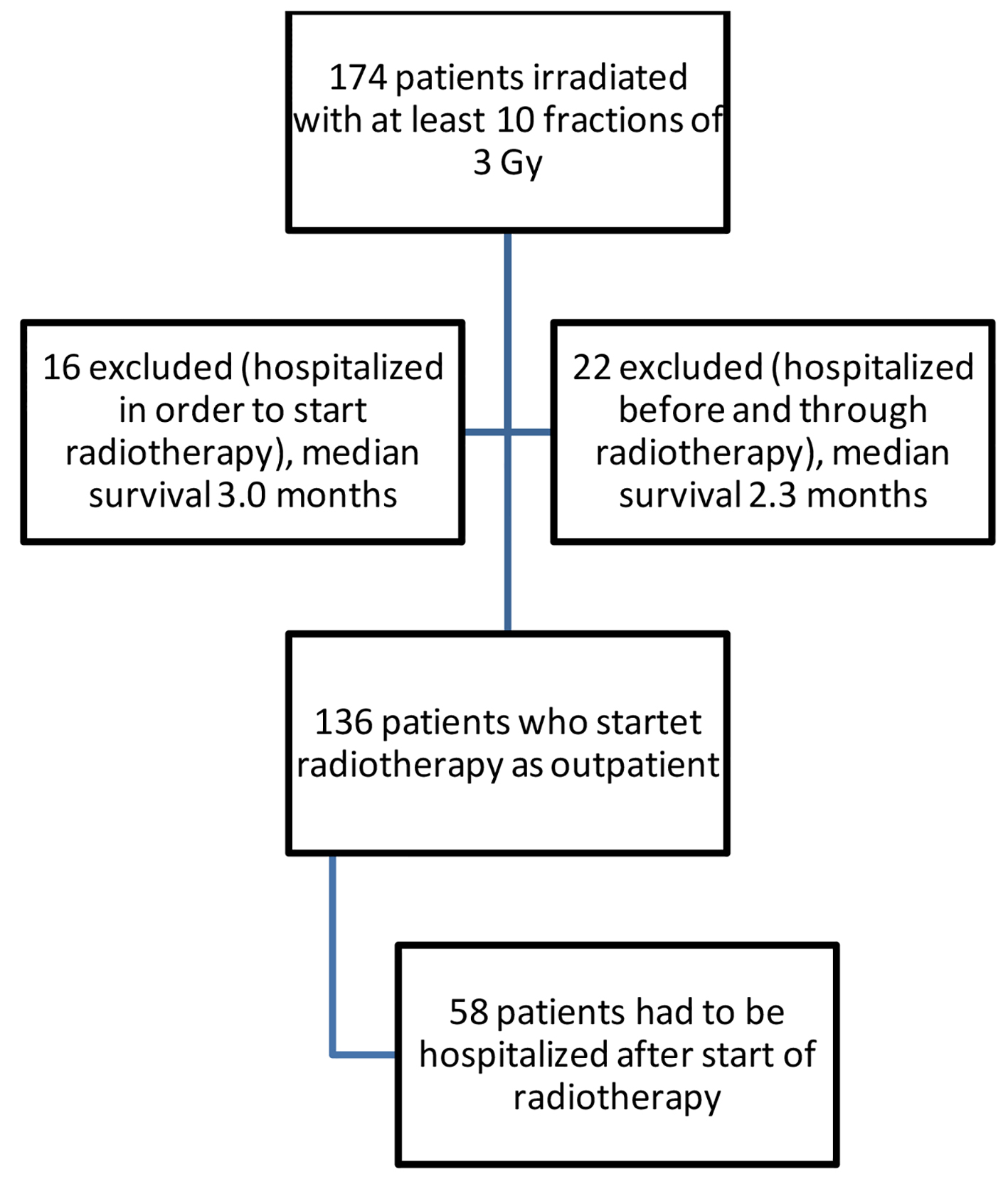
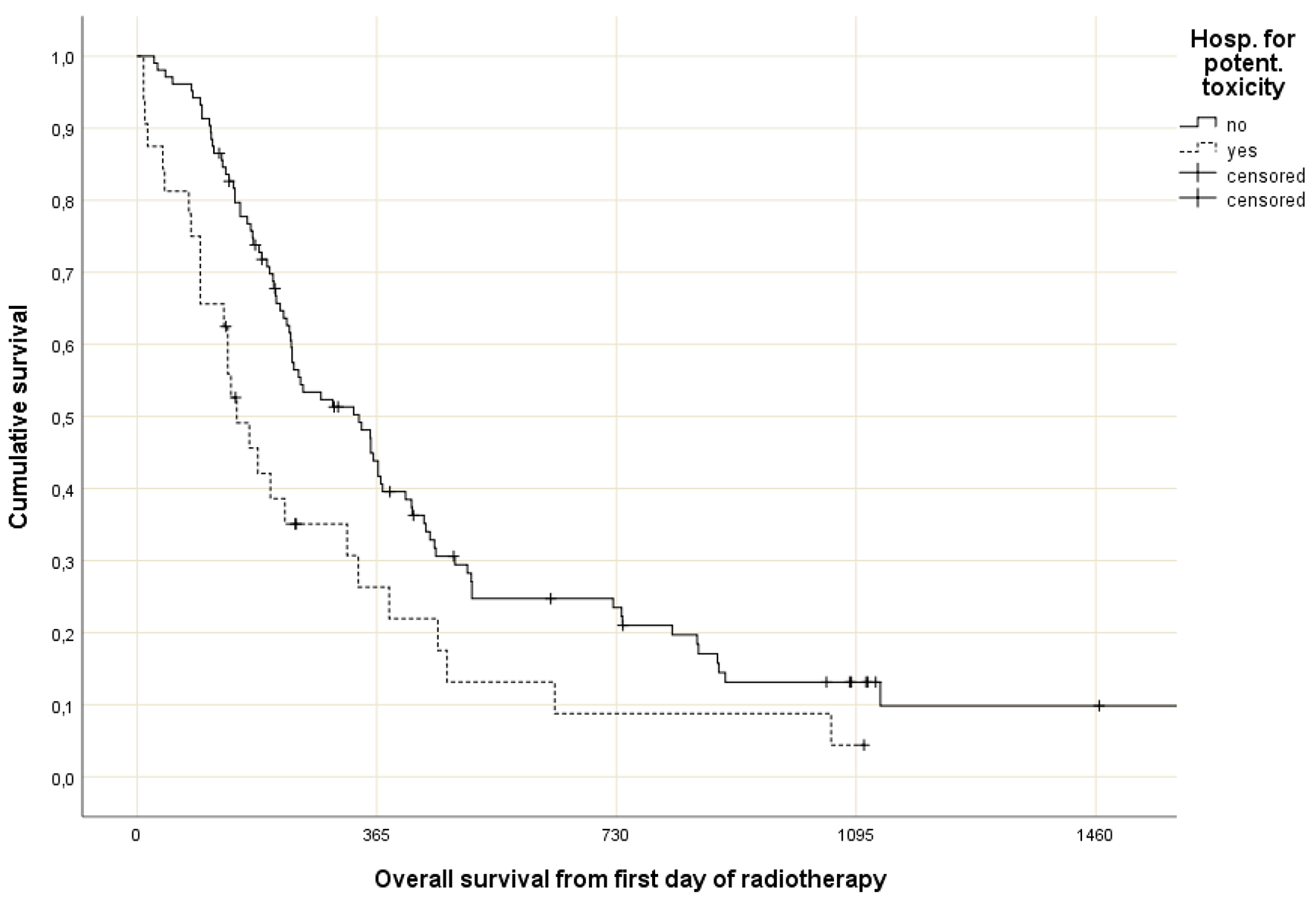
Figure 1. Study flow chart.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 13, Number 3, March 2021, pages 177-183
Palliative Thoracic Radiotherapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in Outpatients: Reasons for Unplanned Hospitalization and Its Impact on Survival
Figures

Tables
| Variable | N (%) |
|---|---|
| COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; RT: radiotherapy. | |
| Gender | |
| Male | 78 (57) |
| Female | 58 (43) |
| History of COPD | |
| Yes | 37 (27) |
| No | 99 (73) |
| Radiation dose | |
| High | 72 (53) |
| Intermediate, e.g., 13 fractions of 3 Gy | 23 (17) |
| Low, largely 10 fractions of 3 Gy | 41 (30) |
| Tumor stage | |
| T1 and 2 | 51 (37) |
| T3 and 4 | 85 (63) |
| Lymph node stage | |
| N0 and 1 | 38 (28) |
| N2 and 3 | 98 (72) |
| Cancer stage | |
| II | 11 (8) |
| III | 64 (47) |
| IV | 61 (45) |
| Histology | |
| Adenocarcinoma | 57 (42) |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 55 (40) |
| Other/unspecified | 24 (18) |
| Active smoking | |
| Yes | 27 (20) |
| No | 109 (80) |
| Systemic cancer treatment | |
| Before RT | 82 (60) |
| Concomitant to RT | 48 (35) |
| Steroid medication | |
| Yes | 45 (33) |
| No | 91 (67) |
| Main discharge diagnosis | Number | Relation to treatment |
|---|---|---|
| COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. | ||
| Pneumonia | 14 | Possible |
| Palliative measures unrelated to radiation | 12 | Unrelated |
| Infection other than pneumonia | 10 | Unrelated |
| Esophagitis | 6 | Possible |
| Dyspnea with established COPD | 5 | Possible |
| Cardiac arrythmia | 3 | Possible |
| Dehydration/malnutrition | 3 | Possible |
| Hemoptysis | 1 | Possible |
| Pre-existing diabetes mellitus | 1 | Unrelated |
| Lumbago | 1 | Unrelated |
| Traumatic injury | 1 | Unrelated |
| New distant metastases | 1 | Unrelated |
| Parameter | Unadjusted odds ratio (95% confidence interval) | P-value (multinominal logistic regression) | P-value (univariate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Including sex in the multinominal logistic regression analysis did not alter the results. Sex was not significantly associated with hospitalization. Tests: Chi-square test, multinominal logistic regression. RT: radiotherapy or chemoradiation. | |||
| Previous hospitalization (last 4 weeks before RT) 21 of 27 (78%) vs. 37 of 109 (34%) hospitalization | 1.8 (1.4 - 2.1) | 0.001 | 0.0001 |
| Steroid medication when starting RT 25 of 45 (56%) vs. 33 of 91 (36%) hospitalization | 1.3 (0.6 - 3.0) | 0.52 | 0.04 |
| Elevated serum C-reactive protein 47 of 98 (48%) vs. 11 of 38 (29%) hospitalization | 1.7 (0.8 - 4.2) | 0.15 | 0.04 |