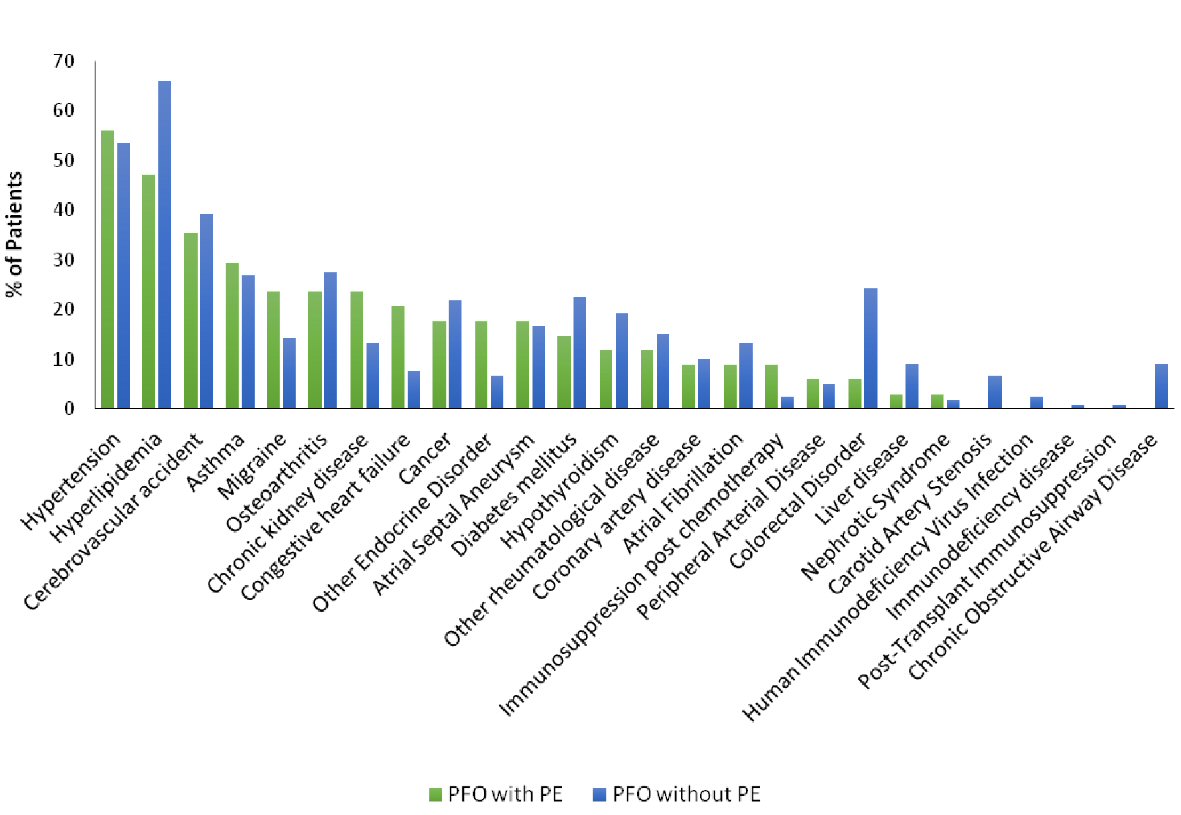
Figure 1. Frequencies of comorbid conditions in patients with patent foramen ovale (PFO) with pulmonary embolism (PE) and in patients with PFO without PE.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 12, Number 3, March 2020, pages 190-199
Risk of Stroke in Patients With Patent Foramen Ovale Who Had Pulmonary Embolism
Figure

Tables
| Variable | PFO with PE (n = 34) | PFO without PE (n = 120) | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| aIndependent t-test. bChi-square and Fisher exact test. PFO: patent foramen ovale; PE: pulmonary embolism; SD: standard deviation; NS: not significant; VTE: venous thromboembolism. | |||
| Age, mean (SD) | 54.8 (14.5) | 57.8 (16.0) | 0.331a |
| Gender | |||
| Male (n, %) | 15 (44.1) | 55 (45.8) | 0.859b |
| Female (n, %) | 19 (55.9) | 65 (54.2) | 0.859b |
| Race | |||
| Caucasian (n, %) | 23 (67.7) | 80 (66.7) | 0.605b |
| African American (n, %) | 9 (26.5) | 24 (20.0) | 0.514b |
| Hispanic (n, %) | 1 (2.9) | 10 (8.3) | NSb |
| Other (n, %) | 1 (2.9) | 6 (5.0) | NSb |
| Social factors | |||
| Alcohol (n, %) | 6 (17.6) | 50 (41.7) | < 0.05b |
| Cigarettes (n, %) | 10 (29.4) | 45 (37.5) | 0.385b |
| Illicit drug use (n, %) | 0 (0.0) | 9 (7.5) | NSb |
| Medical history | |||
| VTE (n, %) | 23 (67.6) | 7 (5.8) | < 0.001b |
| Trauma (n, %) | 7 (20.6) | 19 (15.8) | 0.514b |
| Surgery (n, %) | 28 (82.4) | 97 (80.8) | 0.841b |
| Variable | PFO with PE (n = 34) | PFO without PE (n = 120) | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| *P < 0.05. aIndependent t-test. bChi-square and Fisher exact test. PFO: patent foramen ovale; PE: pulmonary embolism; SD: standard deviation; LDL: low-density lipoprotein; HDL: high-density lipoprotein; PA: pulmonary artery. | |||
| Heart rate (beats per minute) (mean, SD) | 77.6 (14.732) | 74.4 (14.036) | 0.245a |
| Systolic blood pressure (mm Hg) (mean, SD) | 125.9 (17.917) | 125.4 (17.776) | 0.884a |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mm Hg) (mean, SD) | 77.3 (12.525) | 75.0 (10.124) | 0.261a |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) (mean, SD) | 32.5 (8.848) | 28.4 (6.994) | 0.005*, a |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) (mean, SD) | 163.8 (40.739) | 163.8 (44.291) | 1.000a |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) (mean, SD) | 87.8 (32.480) | 90.6 (35.464) | 0.681a |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) (mean, SD) | 55.2 (13.221) | 53.3 (16.064) | 0.519a |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) (mean, SD) | 103.3 (67.503) | 108.8 (61.660) | 0.651a |
| Red blood cells (× 106/µL) (mean, SD) | 4.1 (1.203) | 4.5 (0.596) | 0.031*, a |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) (mean, SD) | 1.2 (1.437) | 0.9 (0.447) | 0.272a |
| Left ventricular ejection fraction (%) (mean, SD) | 54.9 (13.005) | 59.6 (6.848) | 0.049*, a |
| Mean PA pressure (mm Hg) (mean, SD) | 27.3 (10.073) | 27.4 (8.329) | 0.983a |
| Right atrial dysfunction (n, %) | 1 (2.9) | 5 (4.2) | 1.000b |
| Atrial septal aneurysm (n, %) | 6 (17.6) | 20 (16.7) | 0.893b |
| Variable | PFO with PE (n = 34) | PFO without PE (n = 120) | Pa |
|---|---|---|---|
| *P < 0.05. aChi-square and Fisher exact test. PFO: patent foramen ovale; PE: pulmonary embolism; NS: not significant. | |||
| Hypertension (n, %) | 19 (55.9) | 64 (53.3) | 0.792 |
| Hyperlipidemia (n, %) | 16 (47.1) | 79 (65.8) | 0.047* |
| Cerebrovascular accident (n, %) | 12 (35.3) | 47 (39.2) | 0.682 |
| Asthma (n, %) | 10 (29.4) | 32 (26.7) | 0.751 |
| Migraine (n, %) | 8 (23.5) | 17 (14.2) | 0.191 |
| Osteoarthritis (n, %) | 8 (23.5) | 33 (27.5) | 0.644 |
| Chronic kidney disease (n, %) | 8 (23.5) | 16 (13.3) | 0.148 |
| Congestive heart failure (n, %) | 7 (20.6) | 9 (7.5) | 0.027* |
| Cancer (n, %) | 6 (17.6) | 26 (21.7) | 0.610 |
| Other endocrine disorder (n, %) | 6 (17.6) | 8 (6.7) | 0.083 |
| Atrial septal aneurysm (n, %) | 6 (17.6) | 20 (16.7) | 0.893 |
| Diabetes mellitus (n, %) | 5 (14.7) | 27 (22.5) | 0.323 |
| Hypothyroidism (n, %) | 4 (11.8) | 23 (19.2) | NS |
| Other rheumatological disease (n, %) | 4 (11.8) | 18 (15.0) | NS |
| Coronary artery disease (n, %) | 3 (8.8) | 12 (10.0) | NS |
| Atrial fibrillation (n, %) | 3 (8.8) | 16 (13.3) | NS |
| Immunosuppression post chemotherapy (n, %) | 3 (8.8) | 3 (2.5) | NS |
| Peripheral arterial disease (n, %) | 2 (5.9) | 6 (5.0) | NS |
| Colorectal disorder (n, %) | 2 (5.9) | 29 (24.2) | NS |
| Liver disease (n, %) | 1 (2.9) | 11 (9.2) | NS |
| Nephrotic syndrome (n, %) | 1 (2.9) | 2 (1.7) | NS |
| Carotid artery stenosis (n, %) | 0 (0.0) | 8 (6.7) | NS |
| Human immunodeficiency virus infection (n, %) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (2.5) | NS |
| Immunodeficiency disease (n, %) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.8) | NS |
| Post-transplant immunosuppression (n, %) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.8) | NS |
| Chronic obstructive airway disease (n, %) | 0 (0.0) | 11 (9.2) | NS |
| Variable | PFO with PE (n = 34) | PFO without PE (n = 120) | Pa |
|---|---|---|---|
| aChi-square and Fisher exact test. PFO: patent foramen ovale; PE: pulmonary embolism. | |||
| Oral anticoagulant (n, %) | 19 (55.9) | 18 (15.0) | < 0.001 |
| Statin (n, %) | 13 (38.2) | 61 (50.8) | 0.194 |
| Aspirin (n, %) | 11 (32.4) | 61 (50.8) | 0.057 |
| Estrogen (n, %) | 1 (2.9) | 8 (6.7) | 0.685 |