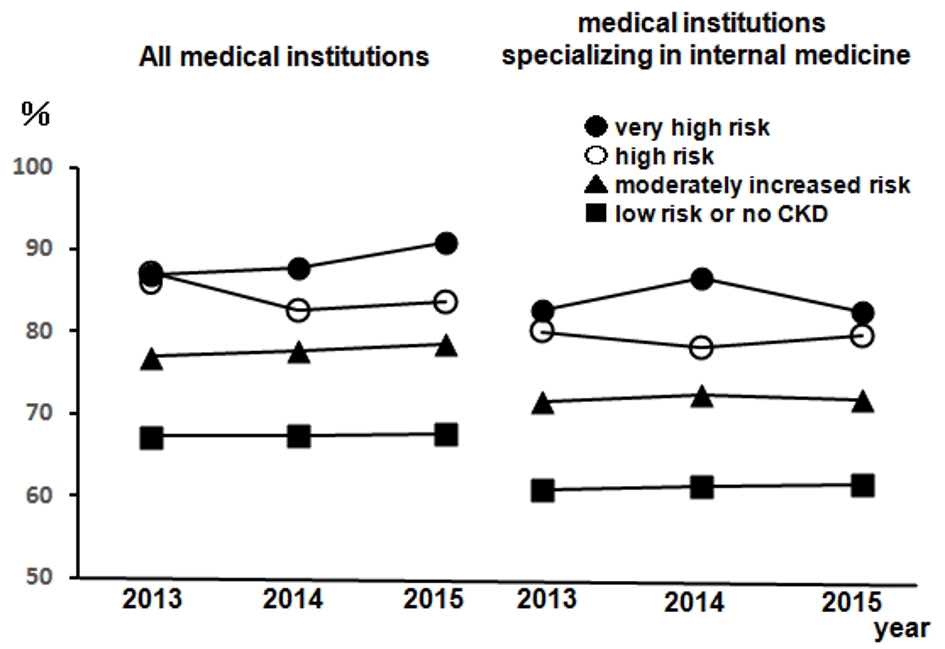
Figure 1. The rates of regular visits at medical institutions of participants undergoing health checkups from 2013 to 2015. Left: all medical institutions; right: medical institutions specializing in internal medicine. •: very high risk; ○: high risk; ▲: moderately increased risk; ■: low risk or no CKD. n = 12,732 (2013), n = 14,150 (2014), and n = 12,274 (2015). CKD: chronic kidney disease.
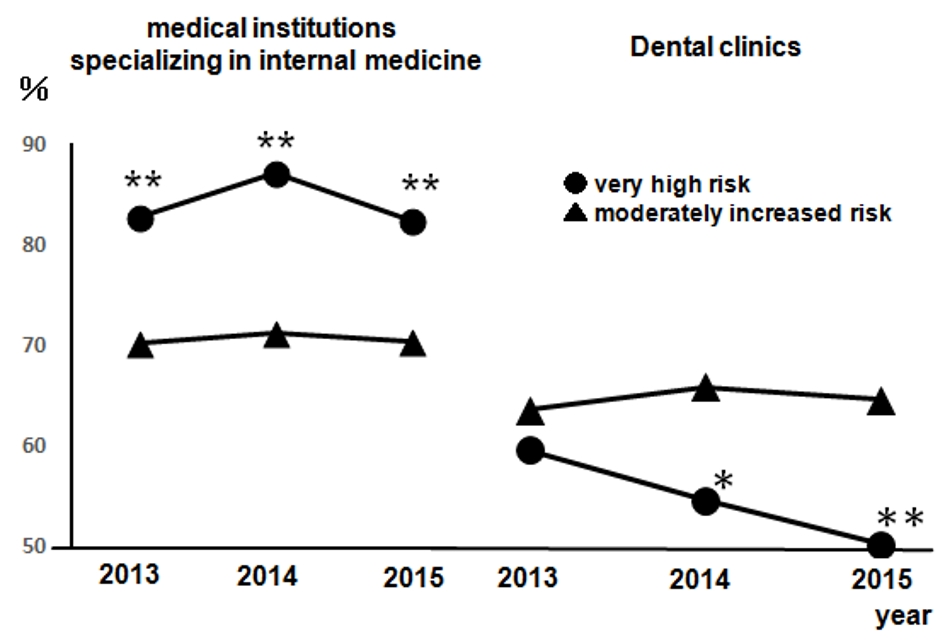
Figure 2. The rates of dental visits of CKD-diagnosed participants from 2013 to 2015 compared to the rates of regular visits at medical institutions specializing in internal medicine. Left: medical institutions specializing in internal medicine; right: dental clinics. •: very high risk; ▲: moderately increased risk. Very high risk: n = 141 (2013), n = 127 (2014), and n = 115 (2015); moderately increased risk: n = 2,056 (2013), n = 2,044 (2014), and n = 1,981 (2015). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 versus moderately increased risk. CKD: chronic kidney disease.
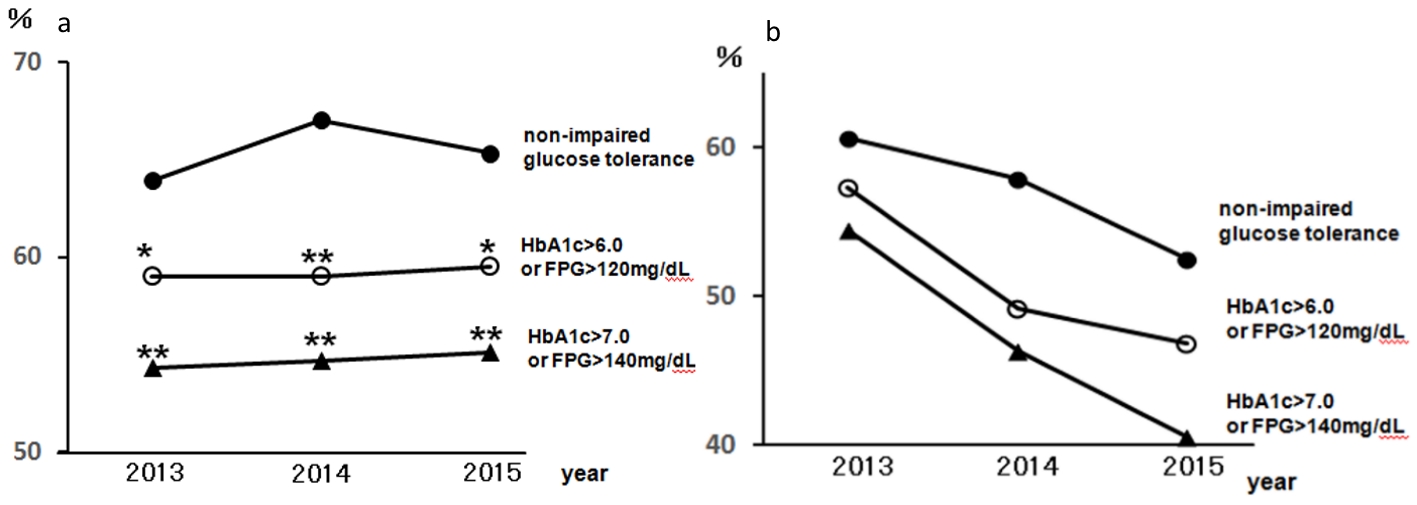
Figure 3. The rates of dental visits of CKD-diagnosed participants depending on the degree of impaired glucose tolerance from 2013 to 2015. (a) The rates of dental visits of CKD moderately increased risk group. •: Moderately increased risk with HbA1c ≤ 6.0 and FPG ≤ 120 mg/dL and not receiving medical treatment for diabetes: non-impaired glucose tolerance; ○: moderately increased risk with HbA1c > 6.0 or FPG > 120 mg/dL; ▲: moderately increased risk with HbA1c > 7.0 or FPG > 140 mg/dL. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 versus non-impaired glucose tolerance. (b) The rates of dental visits of CKD very high risk group. •: very high risk with HbA1c ≤ 6.0 and FPG ≤ 12 0 mg/dL and not receiving medical treatment for diabetes: non-impaired glucose tolerance; ○: very high risk with HbA1c > 6.0 or FPG > 120 mg/dL; ▲: very high risk with HbA1c > 7.0 or FPG > 140 mg/dL. CKD: chronic kidney disease; HbA1c: hemoglobin A1c; FPG: fasting plasma glucose.


