| Ipragliflozin | [5] | Type 2 diabetic mice | Improvement of hepatic steatosis and liver injury; reduction of plasma and liver levels of oxidative stress biomarkers and inflammatory markers |
| Ipragliflozin | [6] | Type 1 diabetic rats | Improvement of hepatic steatosis and liver injury; reduction of liver levels of oxidative stress biomarkers and plasma levels of inflammatory markers |
| Ipragliflozin | [7] | NAFLD rats | Prevention of hepatic triglyceride accumulation, large lipid droplet formation and liver fibrosis |
| Ipragliflozin | [8] | Obese mice | Prevention of ectopic fat accumulation in the liver |
| Luseogliflozin | [9, 10] | Type 2 diabetic patients with NAFLD | Reduction of hepatic fat content |
| Empagliflozin | [11] | Well-controlled type 2 diabetic patients | Lowering of liver fat content |
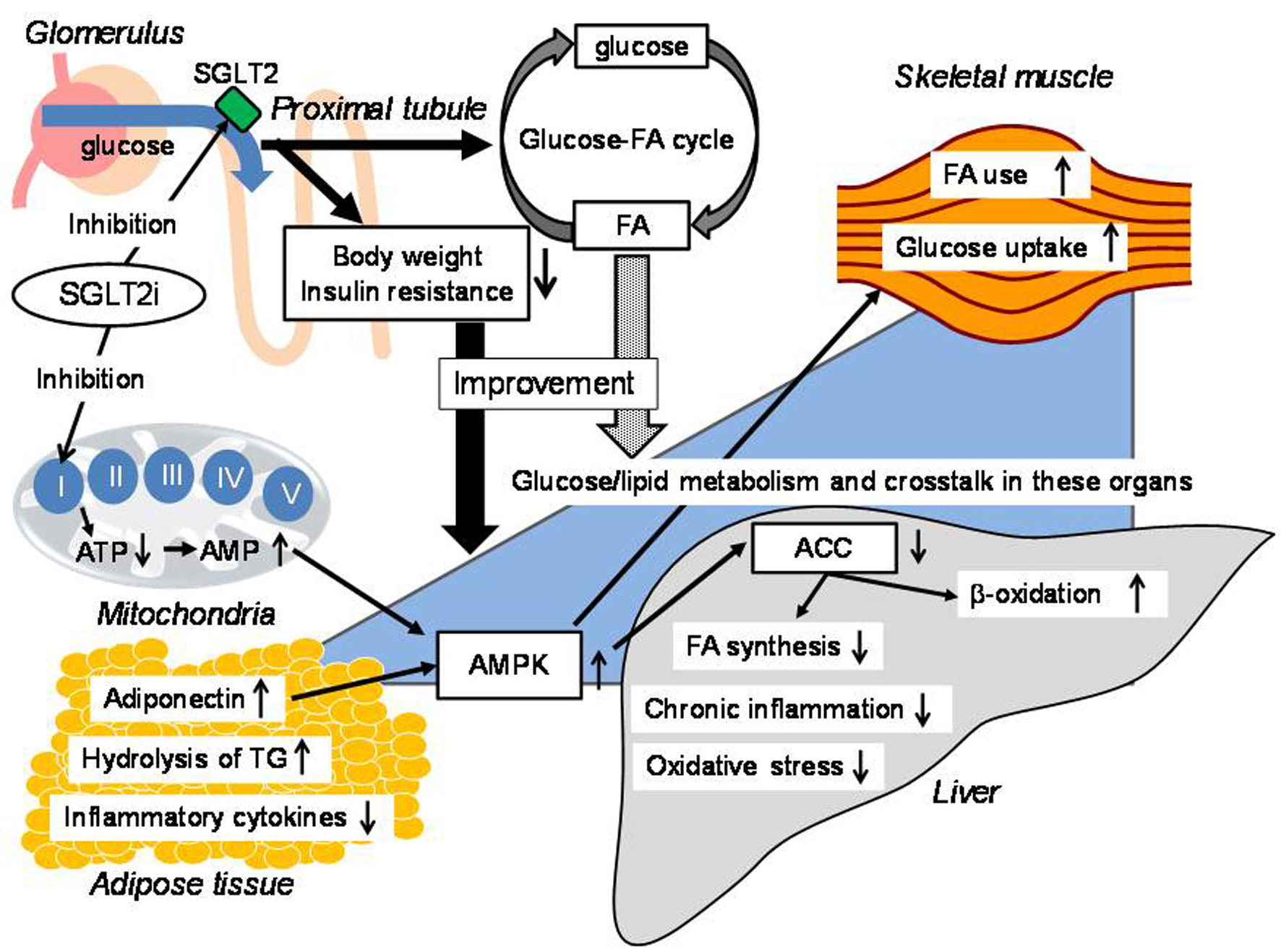
| Canagliflozin | [12] | HEK-293 cells | AMPK activation by inhibition of Complex I of the respiratory chain; inhibition of lipid synthesis, by phosphorylation of ACC at the AMPK sites in human hepatocytes, which leads to downregulation of fatty acid synthesis-related molecules and upregulation of β oxidation-associated molecules |
| Tofogliflozin | [13] | C57BL/6 mice | Decrease of hepatic triglyceride content; acceleration of lipolysis in adipose tissue and hepatic β-oxidation |