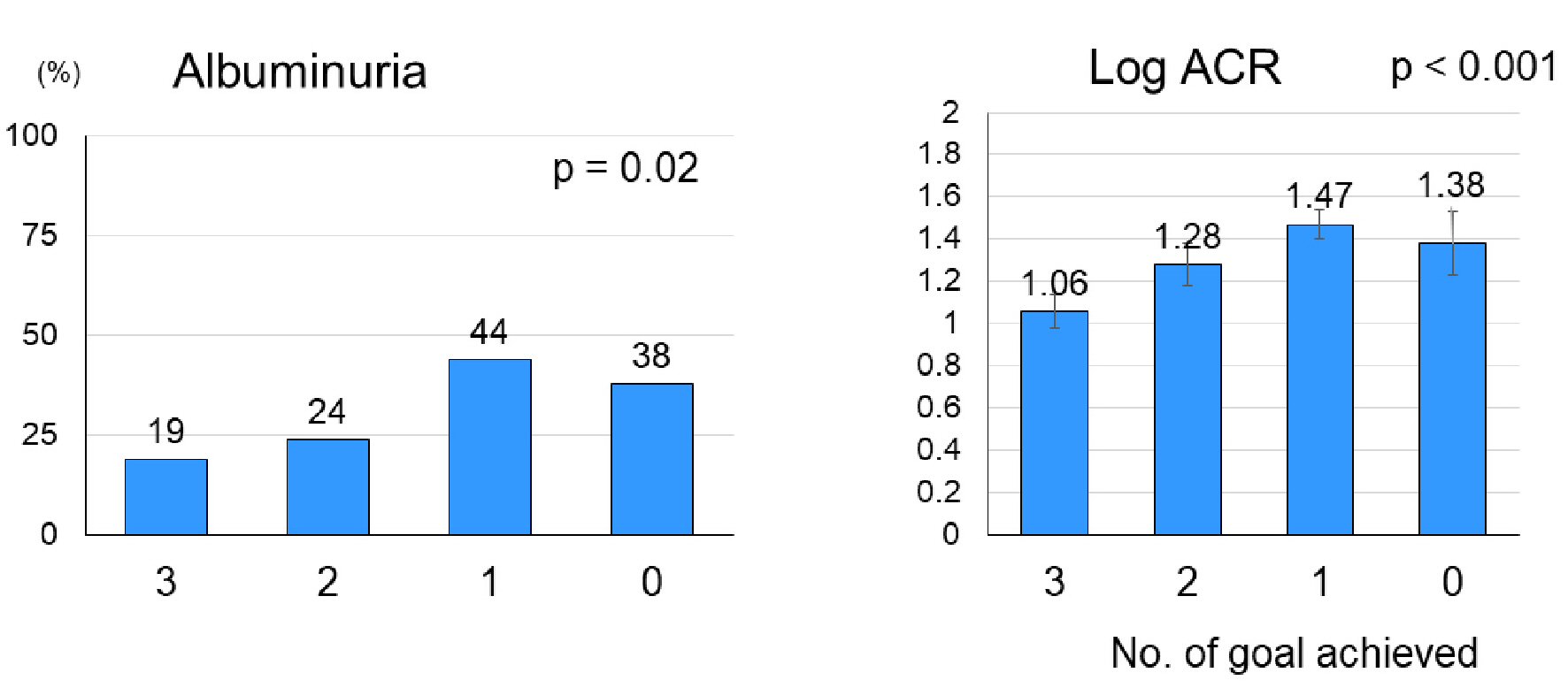
Figure 1. Mean (± SE) log urinary ACR and the percentage of patients with albuminuria (ACR ≥ 30 mg/g) at baseline according to the number of ABC (HbA1c, blood pressure and LDL-C) goal achievement. Among 168 patients with type 2 diabetes, 47, 45, 63 and 13 patients achieved triple-goal, dual-goal, single-goal and no-goal, respectively, at baseline. SE: standard error; ACR: albumin-to-creatinine ratio; HbA1c: hemoglobin A1c; LDL-C: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
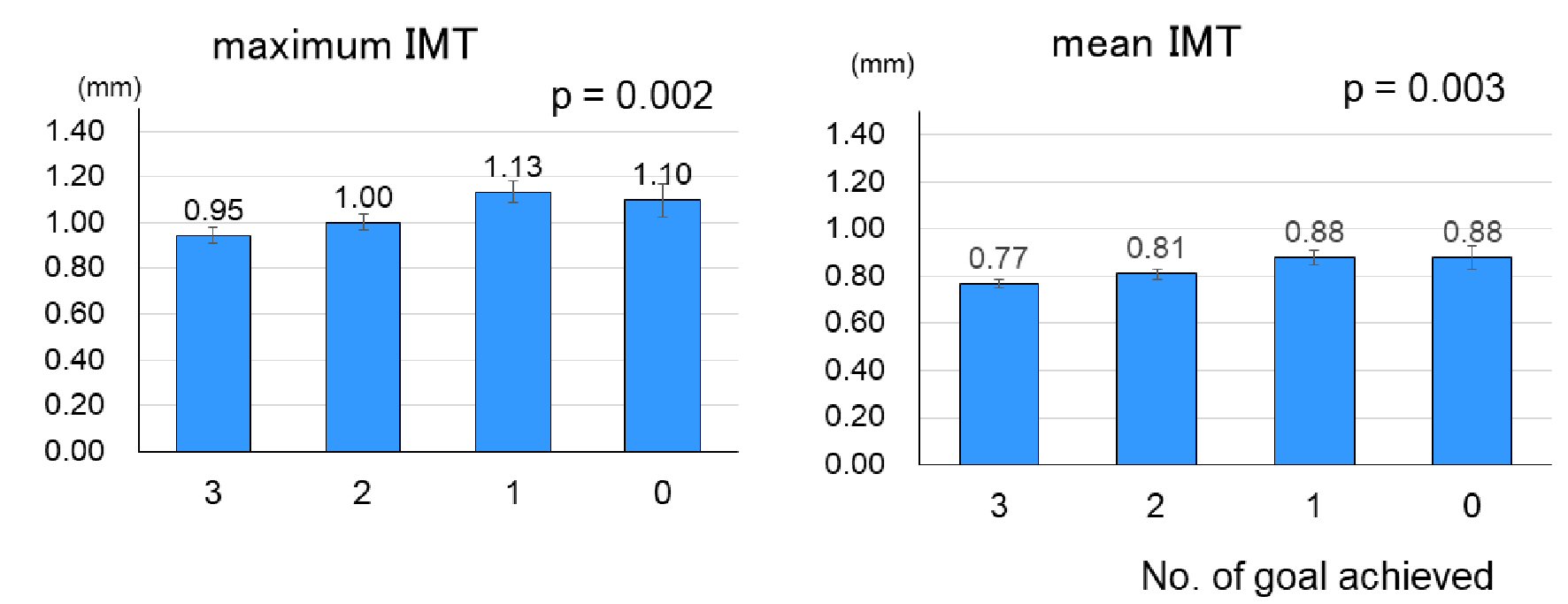
Figure 2. Maximum and mean carotid IMT at baseline according to the number of ABC (HbA1c, blood pressure and LDL-C) goal achievement (mean ± SE). See Figure 1 for the number of patients in each goal achievers. IMT: intima-media thickness; HbA1c: hemoglobin A1c; LDL-C: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; SE: standard error.
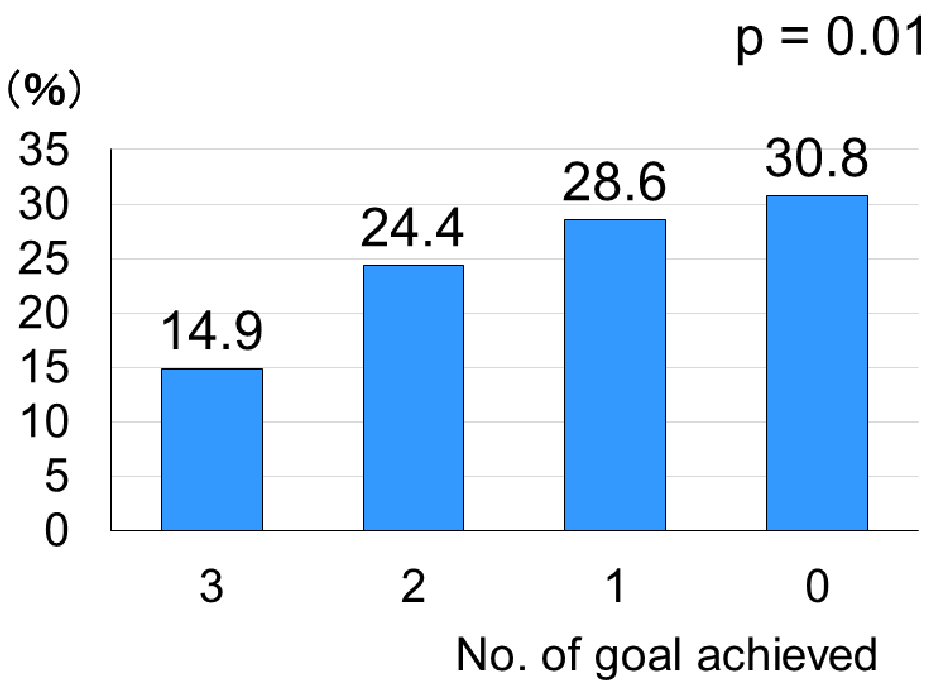
Figure 3. The percentage of deterioration of glomerular filtration rate stages over a median follow-up of 6.0 years according to the number of ABC (HbA1c, blood pressure and LDL-C) goal achievement at baseline. See Figure 1 for the number of patients in each goal achievers. HbA1c: hemoglobin A1c; LDL-C: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
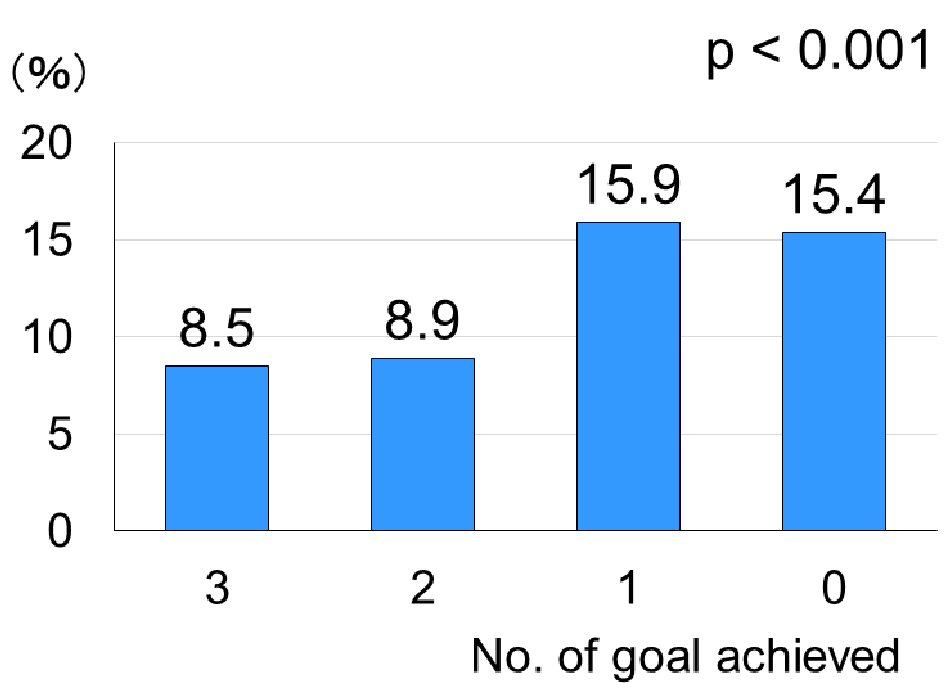
Figure 4. The percentage of deterioration of albuminuric stages over a median follow-up of 6.0 years according to the number of ABC (HbA1c, blood pressure and LDL-C) goal achievement at baseline. See Figure 1 for the number of patients in each goal achievers. HbA1c: hemoglobin A1c; LDL-C: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.



