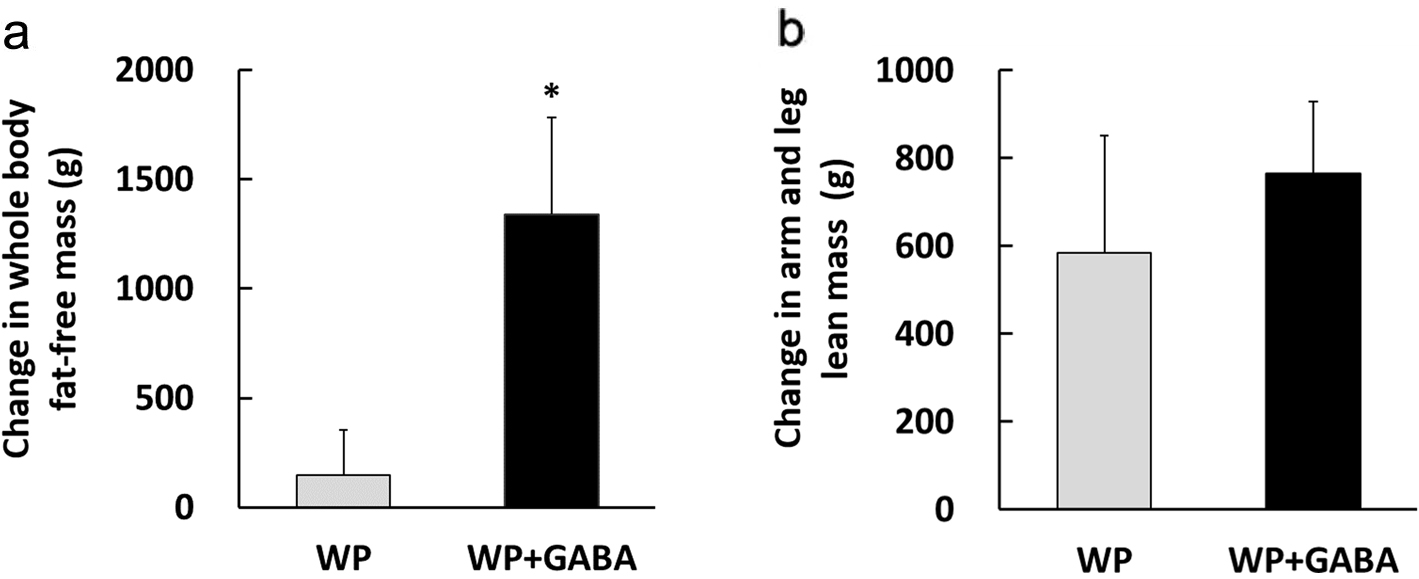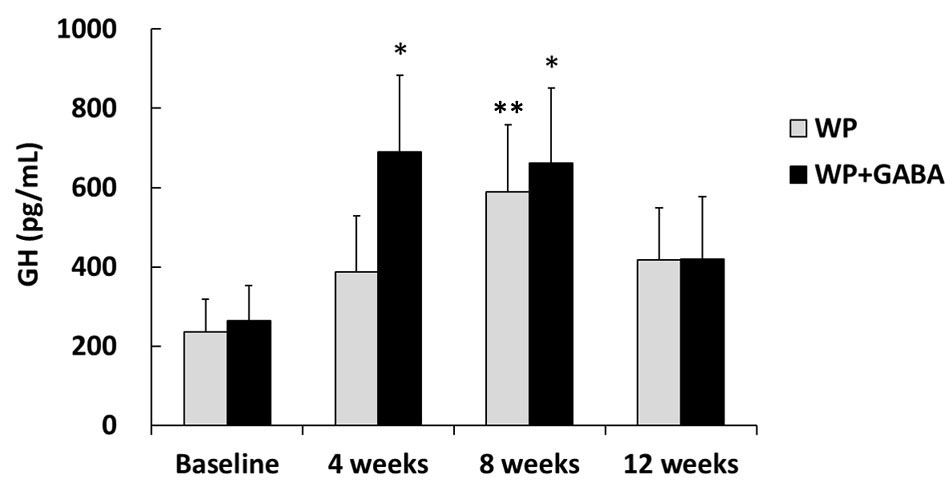
Figure 1. Resting plasma growth hormone concentrations. Values represent the mean ± standard error for 10 subjects (the whey protein group (WP)) or 11 subjects (the whey protein + gamma-aminobutyric acid group (WP + GABA)). *P < 0.05 vs. baseline of the WP + GABA group; **P < 0.05 vs. baseline of the WP group.