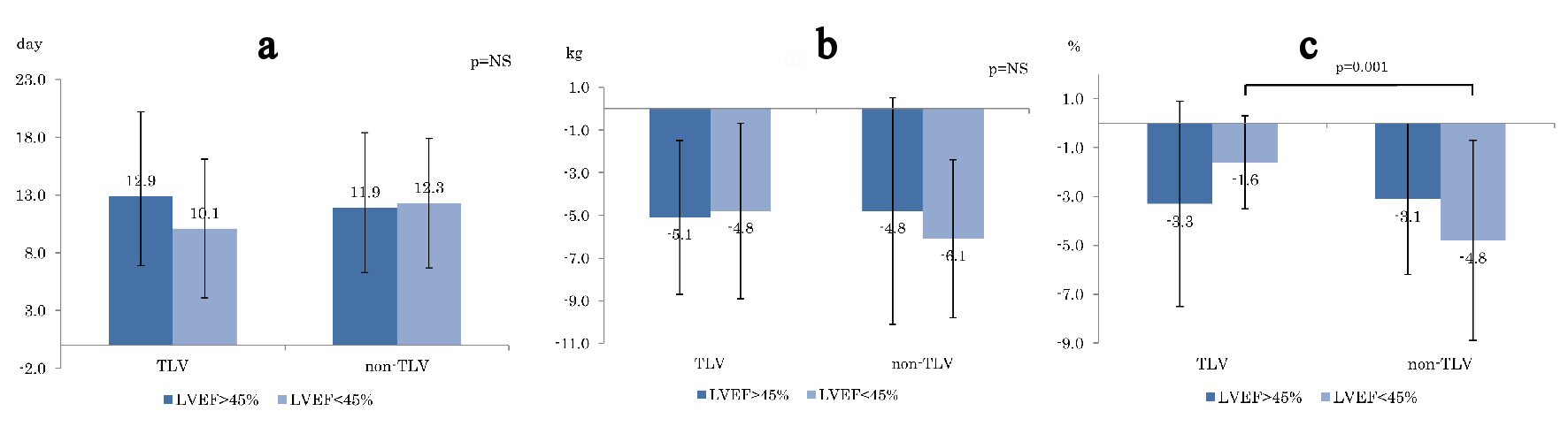
Figure 1. Comparison of (a) days to heart failure improvement, (b) BW reduction , and (c) CTR reducing between TLV and non-TLV. BW: body weight. CTR: cardiac thoracic ratio; LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 11, Number 1, January 2019, pages 49-55
Renoprotective Benefit of Tolvaptan in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure Patients With Loop Diuretic-Resistant Status
Figures

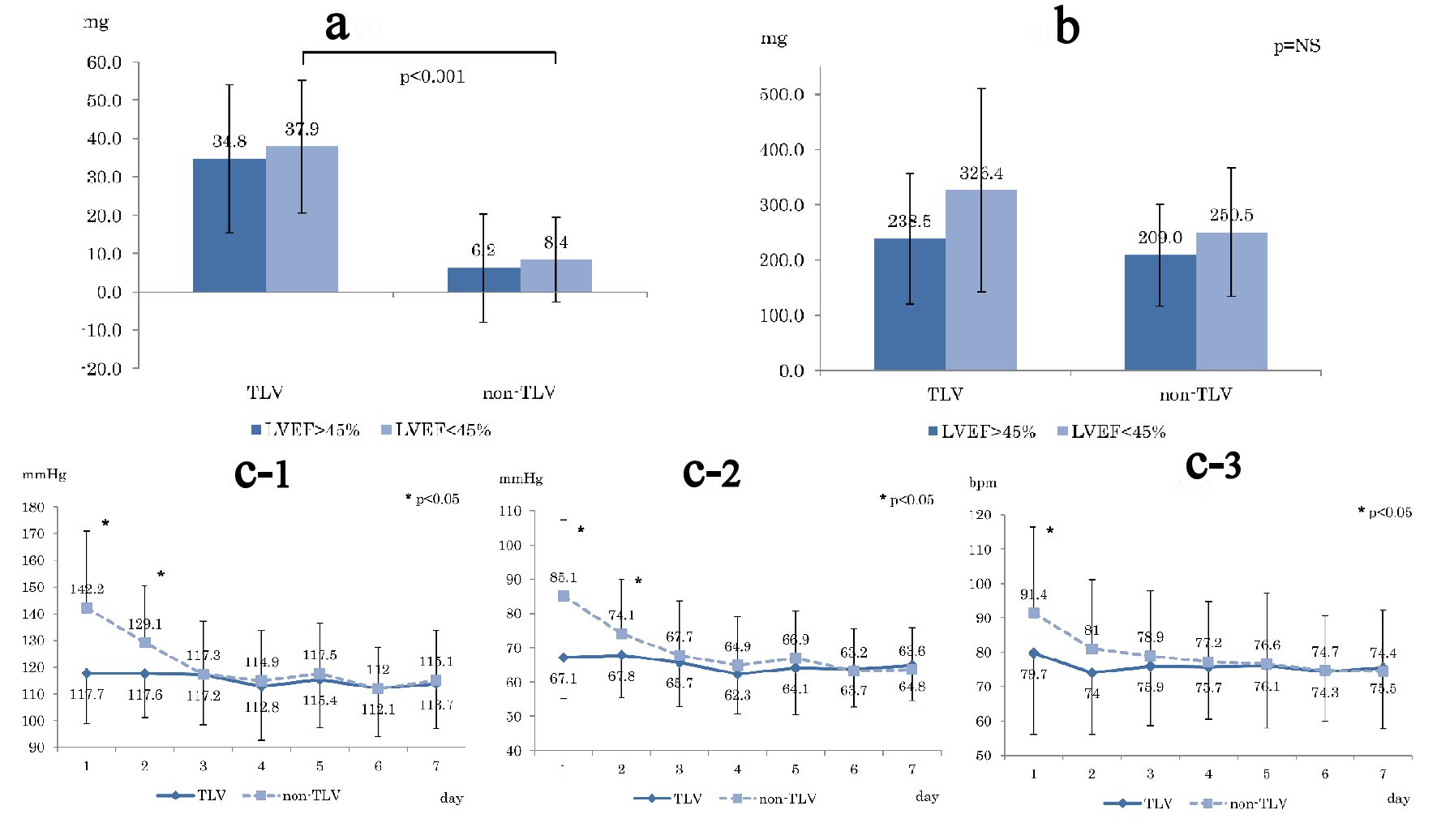
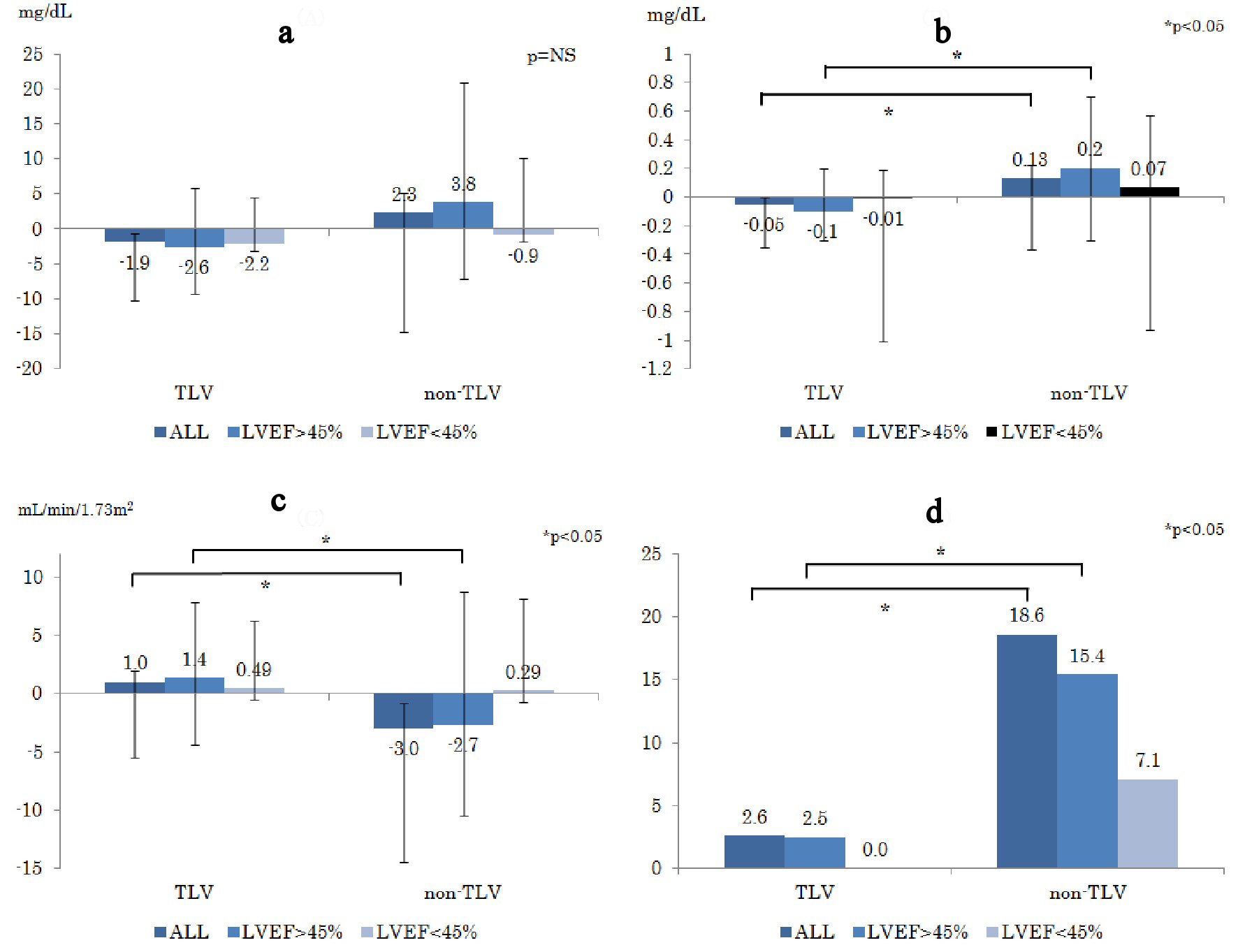
Tables
| All (n = 99) | TLV (n = 39) | non-TLV (n = 60) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data are shown as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) or n (%) or as the median (interquartile range). UCG-LVEF: ultrasonic cardiogram-left ventricular ejection fraction; CTR: cardiac thoracic ratio; NYHA: New York Heart Association; SBP: systolic blood pressure; DBP: diastolic blood pressure; HR: heart rate; ACE-I/ARB: angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor/angiotensin receptor blocker; CCB: calcium channel blocker; BUN: blood urea nitrogen; Cr: creatinine; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; Na: sodium; K: potassium; Cl: chloride ion; NT-proBNP: n-terminal pro b-type natriuretic peptide. | ||||
| Age, yrs | 81 (73 - 87) | 79 (74.5 - 86) | 83 (72 - 88) | 0.85 |
| Male, n (%) | 53 (54) | 23 (59) | 30 (50) | 0.43 |
| Body weight, kg | 55.9 (49.6 - 65.4) | 57.8 (52.9 - 69.5) | 52.9 (46.9 - 60.7) | 0.09 |
| UCG-LVEF, % | 46.1 (31.5 - 60.9) | 48.8 (38.4 - 60.4) | 45.7 (30 - 60.8) | 0.45 |
| Chest X-ray CTR, % | 61 (58 - 65) | 61 (58 - 66) | 61 (58 - 64.5) | 0.32 |
| NYHA classification | ||||
| Class III, n (%) | 39 (39) | 18 (46) | 21 (35) | 0.29 |
| Class IV, n (%) | 18 (18) | 4 (10) | 14 (23) | 0.09 |
| Etiology | ||||
| Ischemia, n (%) | 28 (28) | 6 (15) | 15 (25) | 0.24 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 66 (67) | 7 (18) | 14 (23) | 0.49 |
| Arrhythmia, n (%) | 12 (12) | 3 (8) | 9 (15) | 0.26 |
| Valvular, n (%) | 11 (11) | 4 (10) | 7 (12) | 0.81 |
| Cardiomyopathy, n (%) | 7 (7) | 4 (10) | 3 (5) | 0.33 |
| Others, n (%) | 26 (26) | 15 (38) | 11 (18) | 0.03 |
| Hemodynamics | ||||
| SBP, mm Hg | 128 (110.5 - 149.8) | 116 (102 - 131) | 141 (122 - 157.5) | < 0.0001 |
| DBP, mm Hg | 74.5 (64.3 - 89.8) | 65 (60.5 - 74.5) | 81 (68 - 98.5) | < 0.0001 |
| HR, bpm | 82.5 (65.5 - 105) | 73 (62.5 - 90) | 90 (70 - 108) | 0.02 |
| Drugs | ||||
| ACE-I/ARB, n (%) | 57 (58) | 23 (59) | 21 (35) | 0.89 |
| CCB, n (%) | 31 (31) | 15 (38) | 13 (33) | 0.24 |
| Β-blocker, n (%) | 67 (68) | 29 (74) | 22 (56) | 0.29 |
| Laboratory data | ||||
| BUN, mg/dL | 23 (18 - 31) | 24 (20.5 - 35) | 23 (15.5 - 29) | 0.08 |
| Cr, mg/dL | 1.1 (0.9 - 1.5) | 1.3 (1.1 - 1.7) | 0.9 (0.8 - 1.3) | 0.01 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73m2 | 40.6 (32.0 - 56.4) | 35.3 (27.1 - 43.5) | 48.2 (36.4 - 59.2) | 0.003 |
| Na, mEq/L | 140 (138 - 142) | 139 (136 - 141) | 141 (139 - 142.5) | 0.21 |
| K, mEq/L | 4.1 (3.8 - 4.4) | 4.2 (4 - 4.5) | 4.0 (3.7 - 4.5) | 0.10 |
| Cl, mEq/L | 105 (103 - 108) | 104.5 (101 - 107) | 106 (104 - 108) | 0.33 |
| Albumin, g/dL | 3.5 (3.1 - 3.7) | 3.6 (3.2 - 3.8) | 3.4 (3.1 - 3.7) | 0.88 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 11.9 (10.2 - 12.8) | 11.7 (10.2 - 12.5) | 12.1 (9.8 - 13.3) | 0.51 |
| NT-proBNP | 6,430 (2,596 - 13,541) | 5,503 (3,152 - 15,244) | 6,490 (2,619 - 13,478) | 0.34 |
| Type of used diuretics | ||||
| Carperitide, n (%) | 45 (45) | 17 (44) | 28 (47) | 0.71 |
| Carperitide, γ | 0.009 ± 0.012 | 0.009 ± 0.012 | 0.009 ± 0.012 | 0.96 |
| Frosemide, mg | 21.7 ± 15.3 | 24.4 ± 18.2 | 20.0 ± 12.9 | 0.21 |
| Spironolactone, mg | 17.9 ± 13.0 | 14.7 ± 13.7 | 20.1 ± 12.2 | 0.05 |
| Catecholamine, n(%) | 14 (14) | 7 (18) | 7 (12) | 0.39 |
| Odds ratio | 95% CI | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CI: confidence interval; HT: hyper tension; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate. | |||
| HT | 2.07 | 0.49 - 8.72 | 0.32 |
| eGFR | 1.36 | 0.26 - 7.25 | 0.72 |
| Tolvaptan | 0.14 | 0.02 - 0.98 | 0.04 |