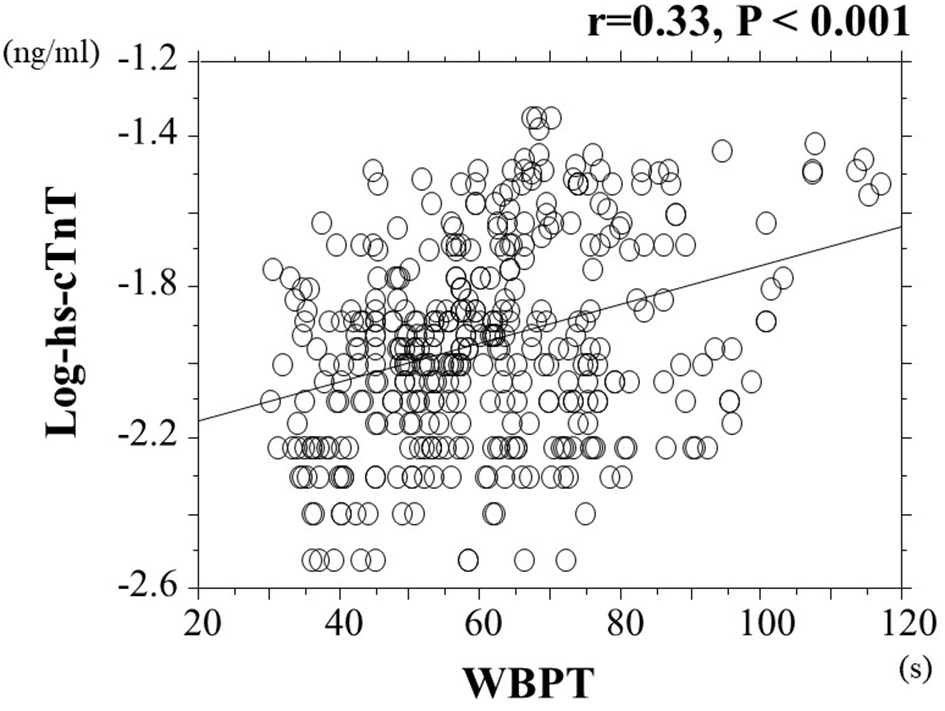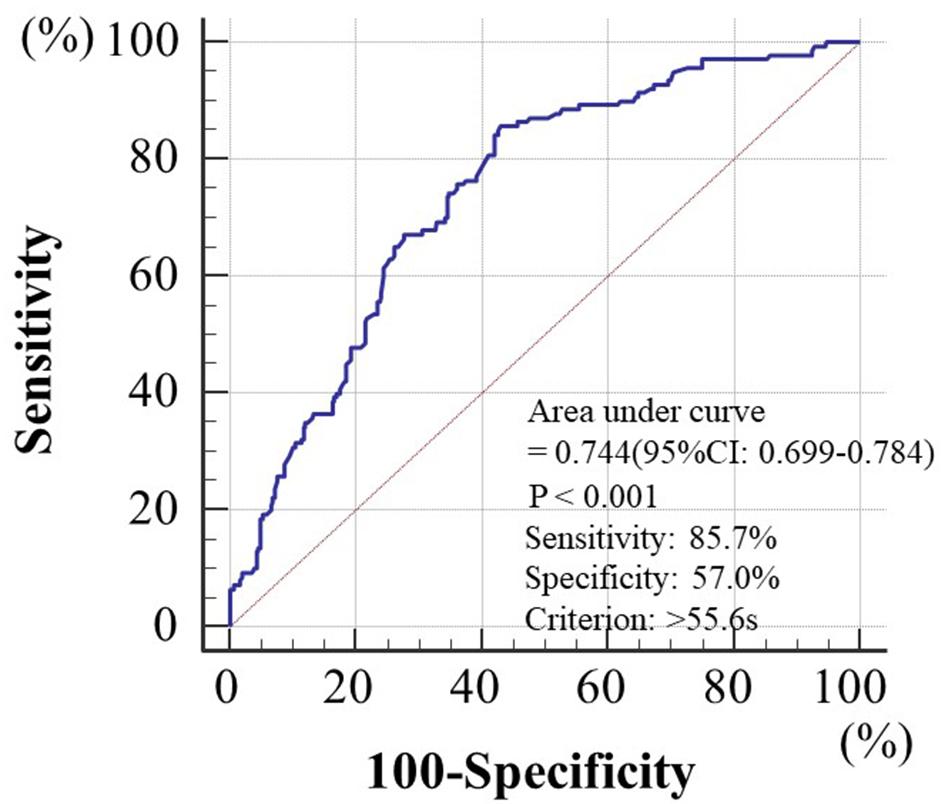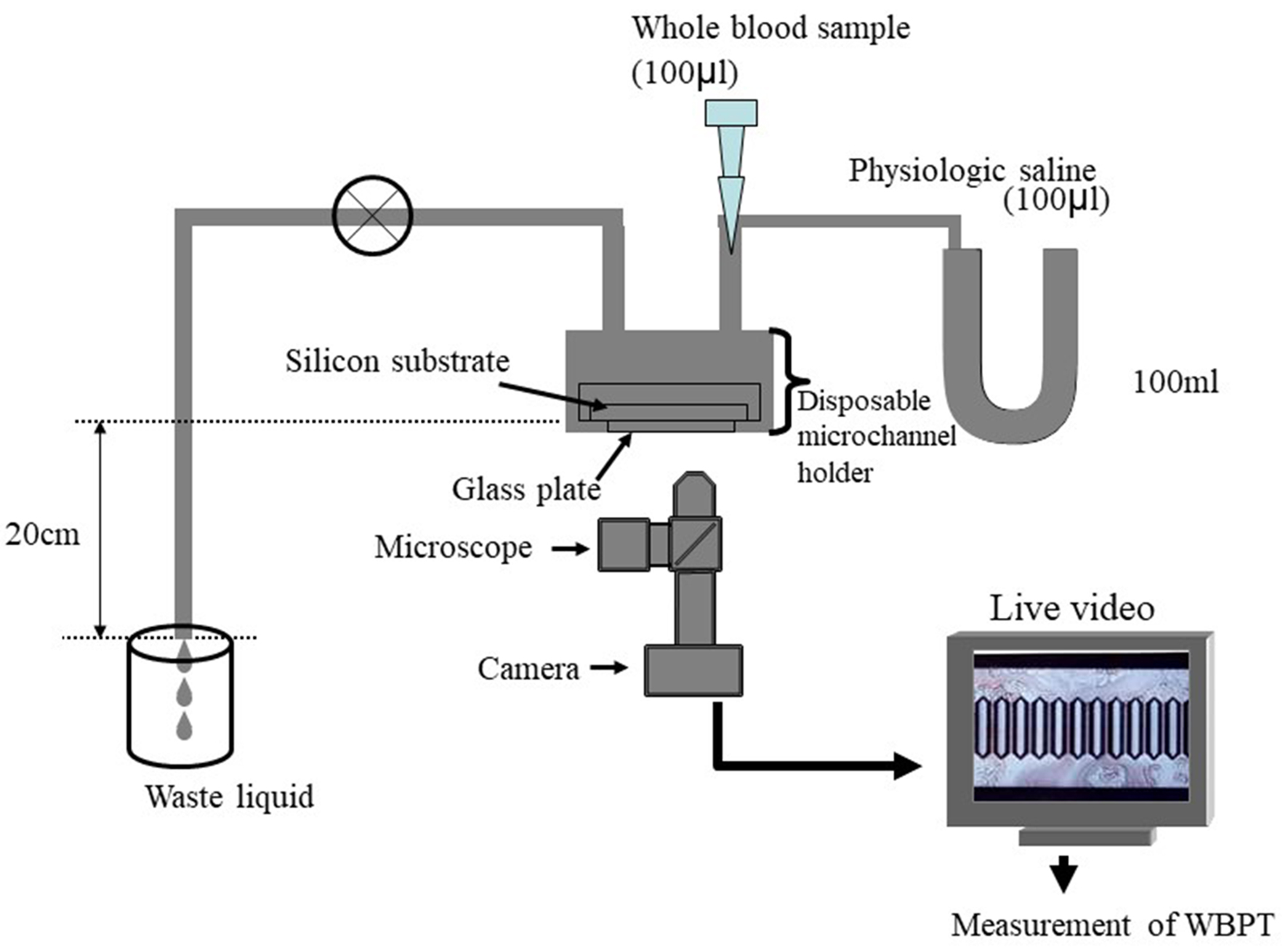
Figure 1. System of microchannel array flow analyzer. The microchannel passage time of 100 µL of physiological saline was measured as a control, and then that of venous whole blood obtained from the subjects with 5% heparinization was determined. The WBPT of the subjects was expressed after correction for the passage time of physiological saline. Inter- and intra-assay coefficients of variation for WBPT were 8% and 5%, respectively. WBPT: whole blood passage time.