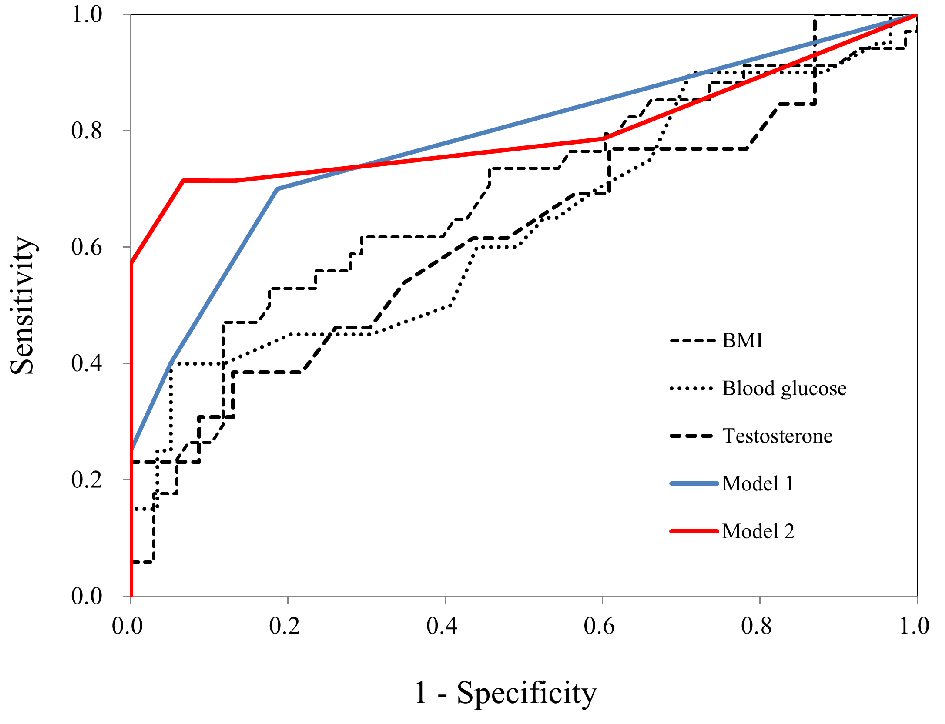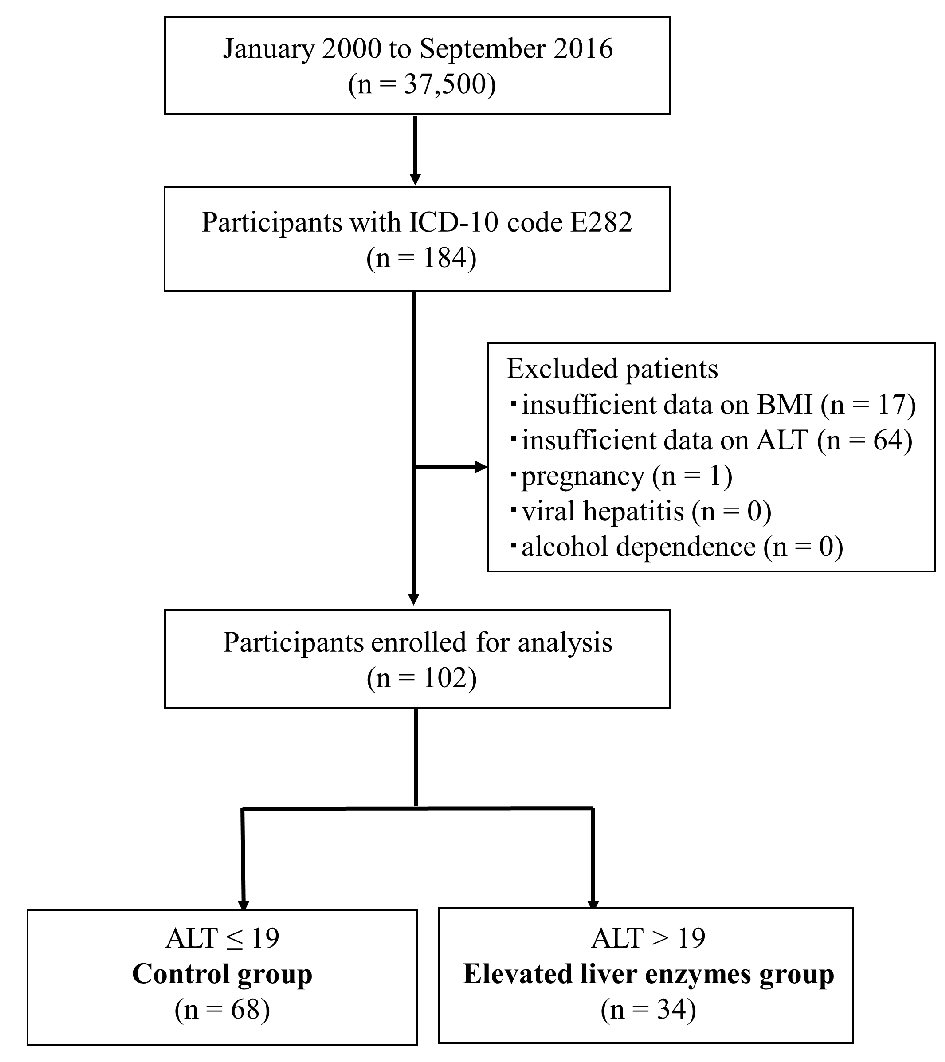
Figure 1. Inclusion and exclusion flow chart. Flow chart representing the selection of subjects during the retrospective study. Data of 37,500 Japanese women were reviewed, and 184 reproductive-aged women with PCOS were identified using ICD-10 codes. After excluding 82 women (see Materials and Methods section), the remaining subjects were divided into two groups using cutoffs for ALT (19 IU/L). ICD-10: International Classification of Diseased, 10th revision, clinical modification; ALT: alanine amino transferase.