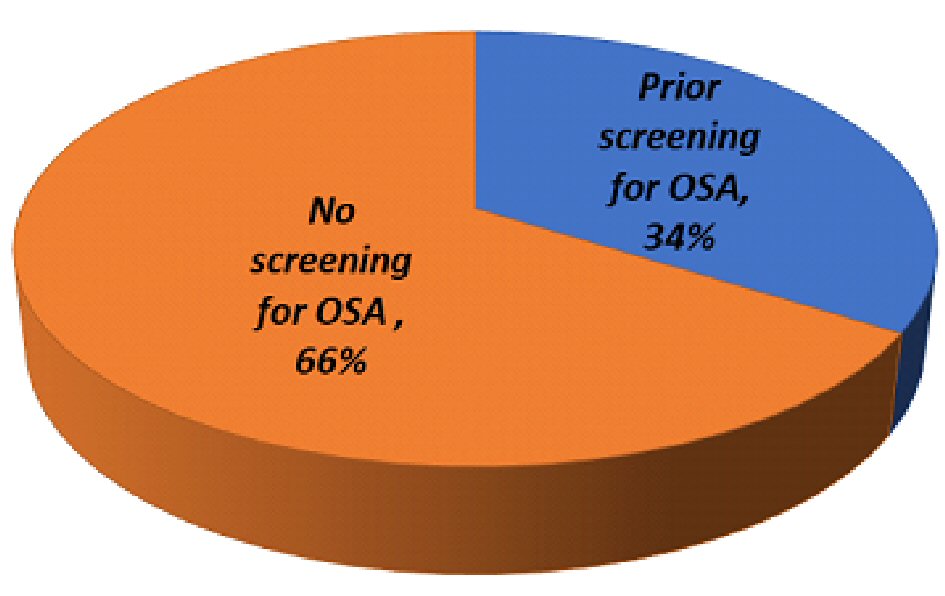
Figure 1. Breakdown of study participants’ OSA screening status.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 11, Number 1, January 2019, pages 21-25
Obstructive Sleep Apnea Screening in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Missed Opportunities for Early Diagnosis
Figures

Tables
| Characteristics | Prior OSA screening | No prior OSA screening | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Participants (n = 254) | 86 (34%) | 168 (66%) | — |
| Age, (mean ± SD) | 70.1 ± 11 | 71.8 ± 14 | 0.337 |
| Gender, n (%) | 0.45 | ||
| Male | 56 (65) | 86 (51) | |
| Female | 30 (35) | 82 (49) | |
| BMI (mean ± SD) | 33 ± 10 | 29 ± 6 | < 0.001 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 71 (83) | 117 (70) | 0.03 |
| Heart failure, n (%) | 48 (56) | 73 (44) | 0.06 |
| Any prior cardioversion, n (%) | 28 (35) | 34 (22) | 0.03 |
| Any hospitalization within the previous year, n (%) | 29 (19) | 27 (35) | 0.02 |
| STOP BANG score, (mean ± SD) | 5.4 ± 1.5 | 3.6 ± 1.5 | < 0.001 |
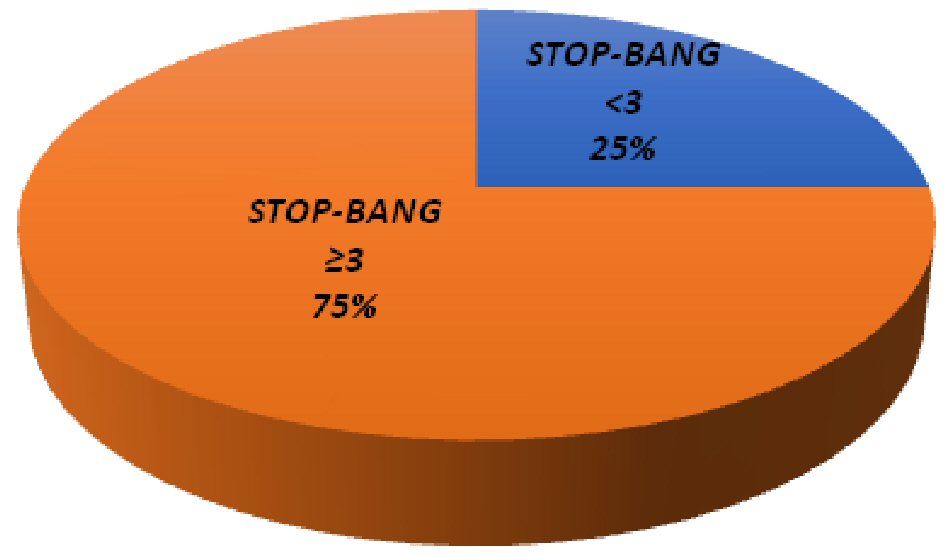
| Risk for OSA by STOP-BANG, n (%) | < 0.001 | ||
| Low risk (score < 3) | 4 (5) | 43 (25) | |
| High risk (score ≥ 3) | 82 (95) | 125 (75) |
| Independent variable | Regression coefficient | P-value | Odds ratio (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | -0.0002 | 0.99 | 1.0 (0.9, 1.0) |
| Gender | -0.28 | 0.37 | 0.8 (0.4, 1.4) |
| BMI | 0.07 | 0.001 | 1.1 (1.0, 1.1) |
| Hypertension | 0.53 | 0.20 | 1.7 (0.7, 3.8) |
| Heart failure | 0.20 | 0.53 | 1.2 (0.7, 2.3) |
| Any prior cardioversion | -0.52 | 0.15 | 0.6 (0.3, 1.2) |
| Any hospitalization within the previous year | -0.60 | 0.10 | 0.5 (0.3, 1.1) |