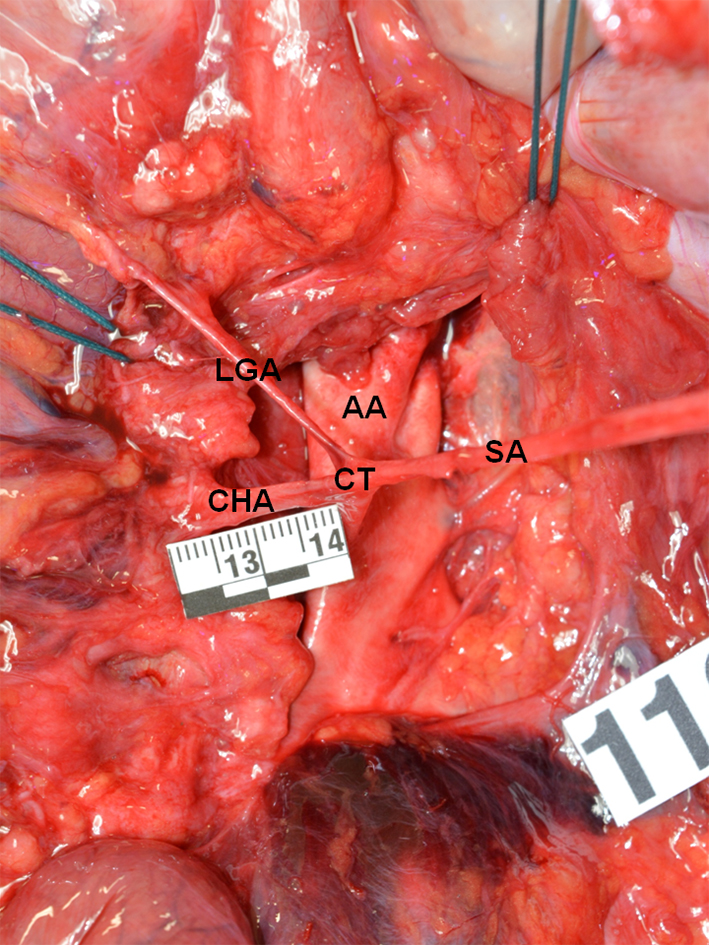
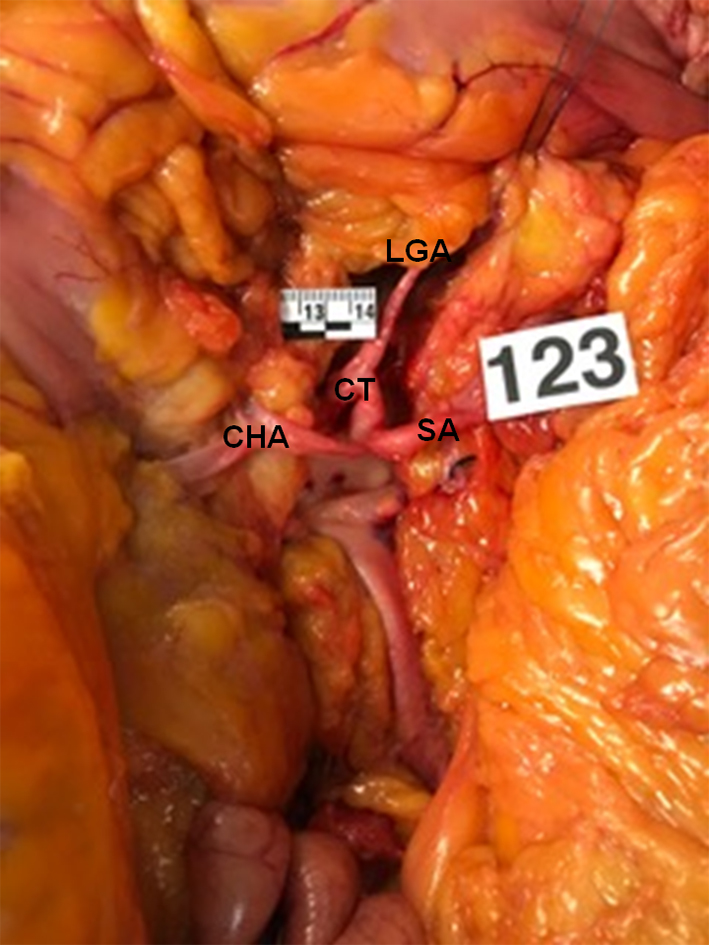
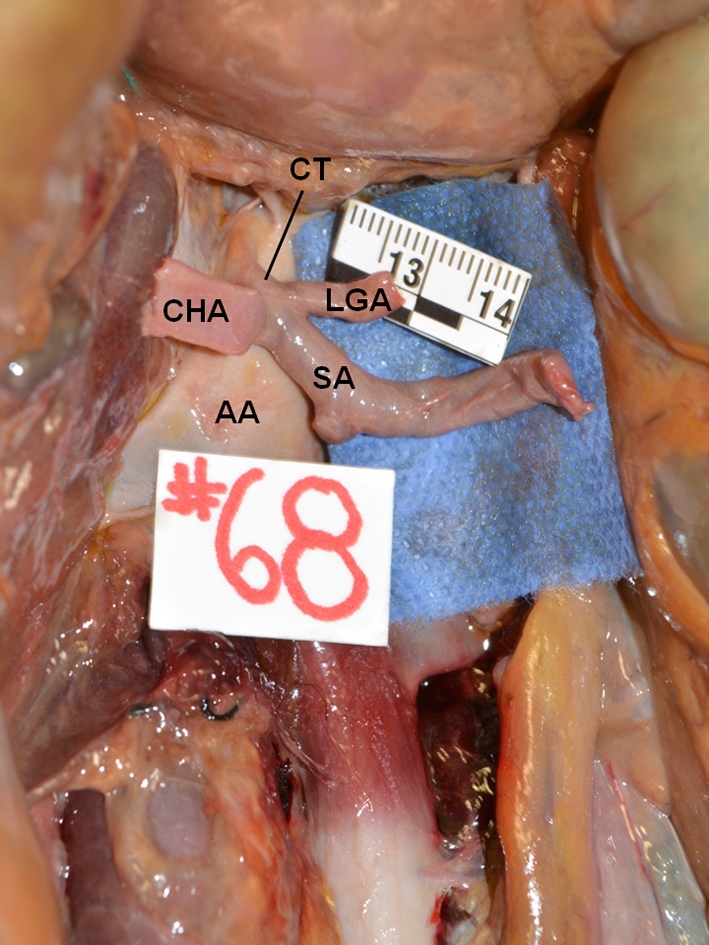
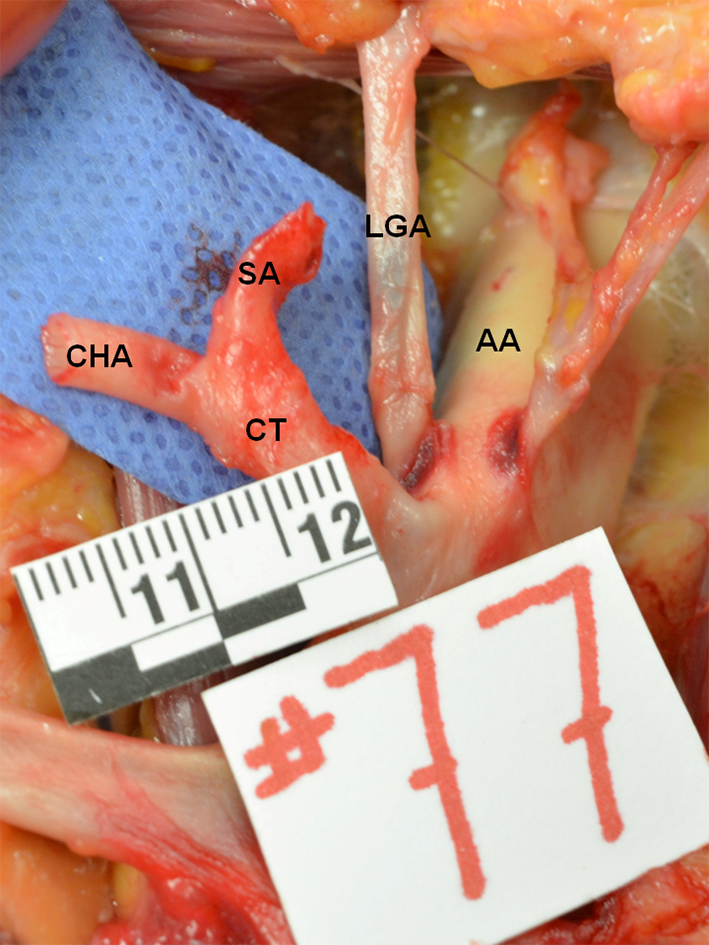
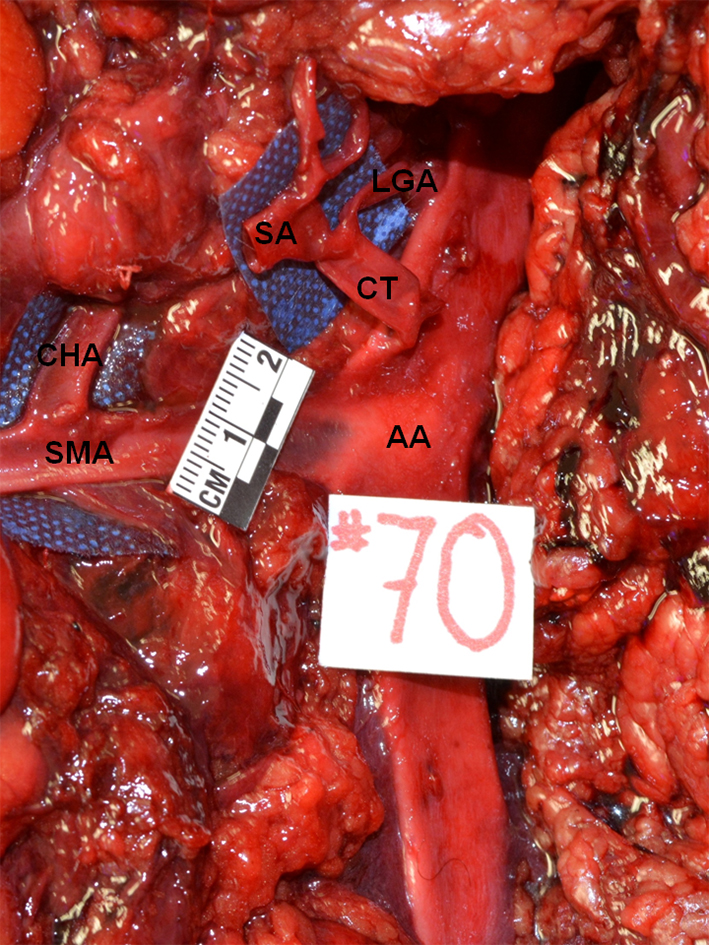
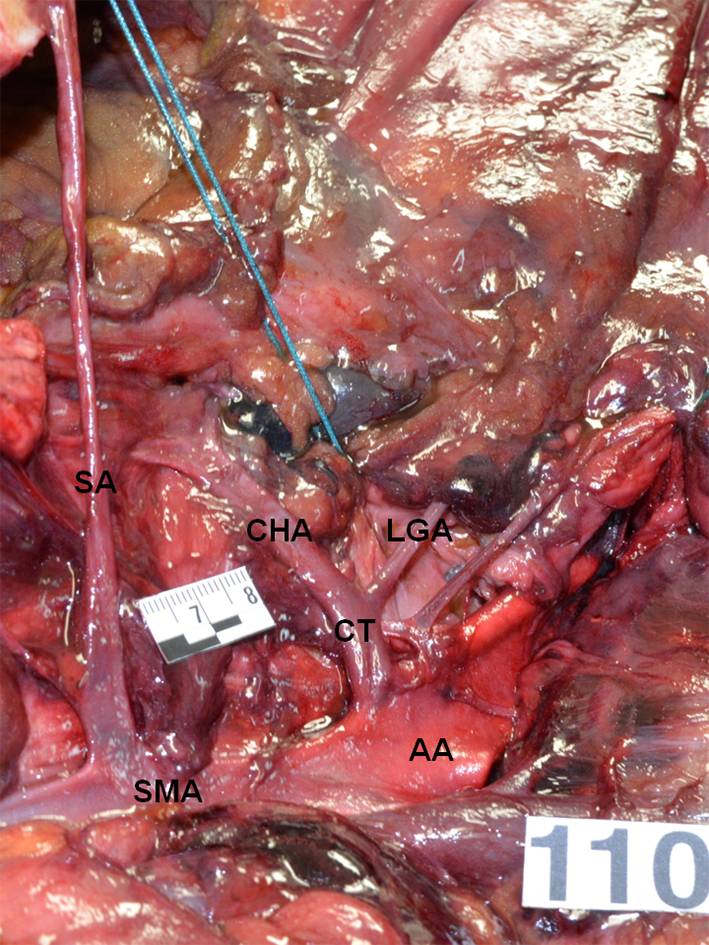
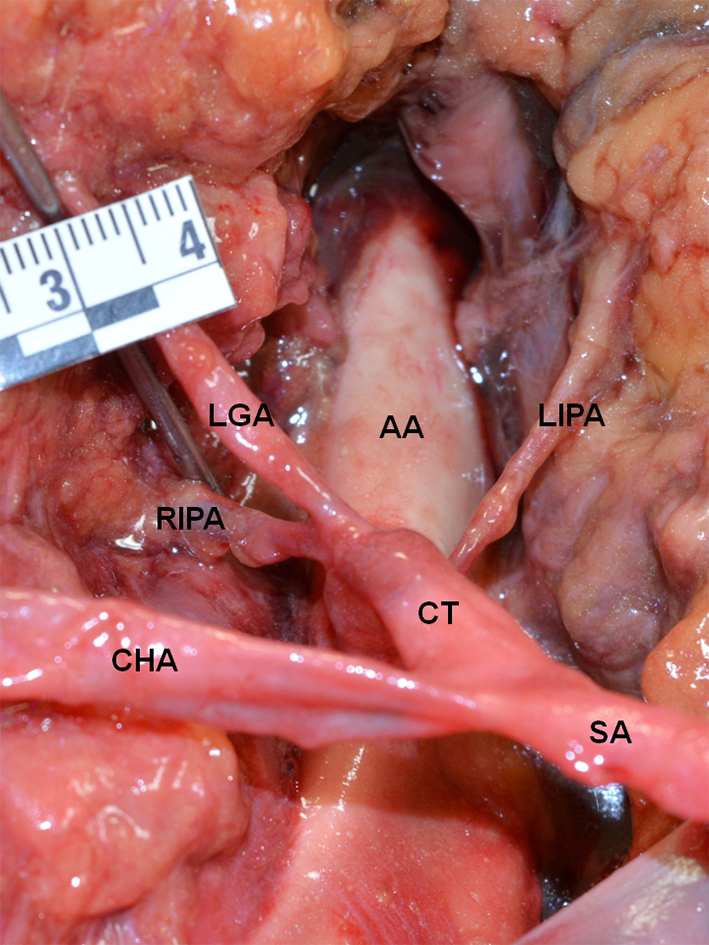
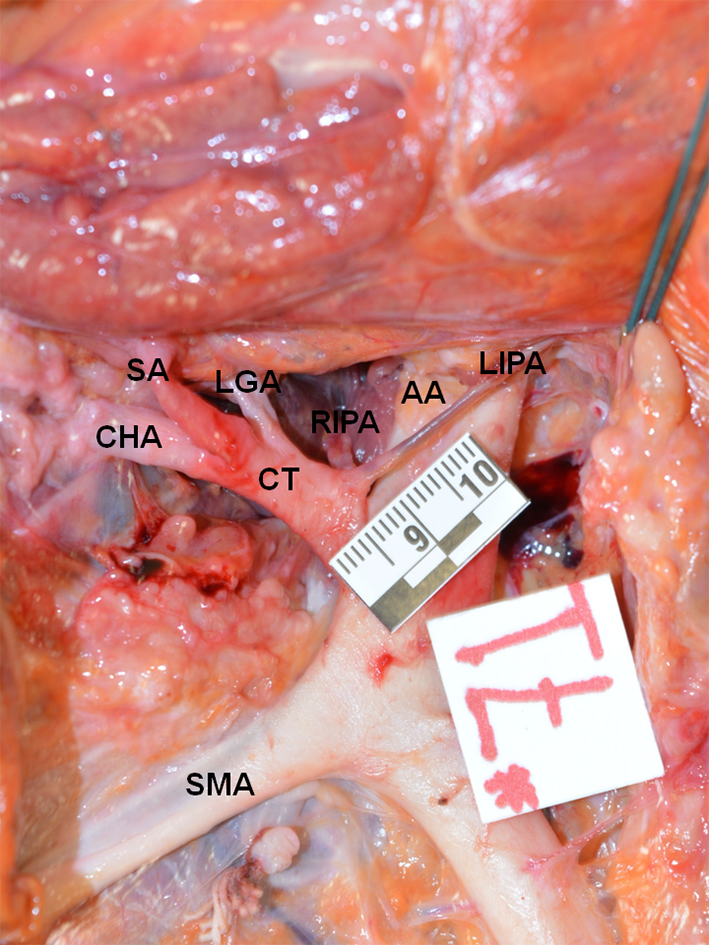
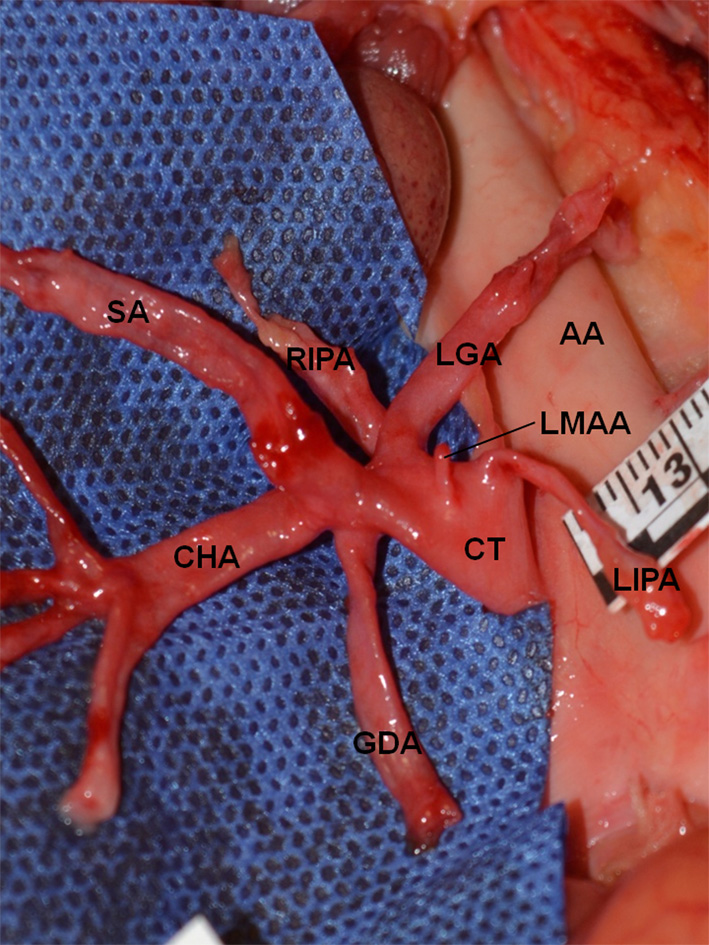
Figure 1. True tripod, “tripus Halleri”. LGA, CHA and SA have a common origin (Panagouli type I, form 1). CT: celiac trunk; LGA: left gastric artery; SA: splenic artery; CHA: common hepatic artery.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 10, Number 4, April 2018, pages 321-329
The Celiac Trunk and Its Anatomical Variations: A Cadaveric Study
Figures

Tables
| Type | Form | Description | Gender | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | |||||||
| % | n | % | n | % | N | |||
| CT: celiac trunk; LGA: left gastric artery; CHA: common hepatic artery; SA: splenic artery; AA: abdominal aorta; SMA: superior mesenteric artery. | ||||||||
| I | Trifurcation of the CT into LGA, CHA and SA | |||||||
| 1 | True tripod - common origin of LGA, CHA and SA | 4.3 | 6/140 | 2.9 | 4/140 | 7.1 | 10/140 | |
| 2 | False tripod - division into two branches | |||||||
| 2a | The LGA is the first branch | 32.1 | 45/140 | 2.9 | 4/140 | 35 | 49/140 | |
| 2b | The CHA is the first branch | 1.4 | 2/140 | 1.4 | 2/140 | |||
| 2c | The SA is the first branch | |||||||
| II | Bifurcation of the CT | |||||||
| 1 | Hepatosplenic trunk, LGA arising from the AA | 1.4 | 2/140 | 1.4 | 2/140 | 2.9 | 4/140 | |
| 2 | Hepatosplenic trunk, no normal LGA | |||||||
| 3 | Hepatosplenic trunk, and gastromesenteric trunk | |||||||
| 4 | Splenogastric trunk, CHA arising from the AA | 0.7 | 1/140 | 0.7 | 1/140 | |||
| 5 | Splenogastric trunk, CHA arising from the SMA | 2.1 | 3/140 | 2.1 | 3/140 | |||
| 6 | Splenogastric trunk and hepatomesenteric trunk | |||||||
| 7 | Hepatogastric trunk, SA arising from the AA | 0.7 | 1/140 | 0.7 | 1/140 | |||
| 8 | Hepatogastric trunk, SA arising from the SMA | 0.7 | 1/140 | 0.7 | 1/140 | |||
| 9 | Hepatogastric trunk and splenomesenteric trunk | |||||||
| III | Additional branches | 41.4 | 58/140 | 6.4 | 9/140 | 47.9 | 67/140 | |
| IV | Celiac-mesenteric trunk (CT and SMA) | |||||||
| V | Variations in the origin of the CHA | |||||||
| VI | Hepatosplenomesenteric trunk, LGA arising independently or as a branch | |||||||
| VII | Absence of the CT (LGA, CHA and SA arising independently) | |||||||
| VIII | Splenogastromesenteric trunk, CHA arising independently or as a branch | |||||||
| IX | Splenogastric trunk giving rise to a common inferior phrenic trunk | 1.4 | 2/140 | 1.4 | 2/140 | |||
| X | Celiac-bimesenteric trunk (CT, SMA and IMA) | |||||||
| Type | Form | Tripod Description | Additional branches | Gender | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | ||||||||
| % | n | % | n | % | N | ||||
| LGA: left gastric artery; CHA: common hepatic artery; AA: aortic artery; IPAs: inferior phrenic arteries; LIPA: left inferior phrenic artery; RIPA: right inferior phrenic artery; GDA: gastroduodenal artery; DPA: dorsal pancreatic artery; LMAA: left medial adrenal artery; SMA: superior mesenteric artery. | |||||||||
| III | 1 | True tripod | Separated IPAs | 1.5 | 1/67 | 1.5 | 1/67 | ||
| 2 | True tripod | Both IPAs from a common trunk | 1.5 | 1/67 | 1.5 | 1/67 | 3 | 2/67 | |
| 3 | True tripod | LIPA | 1.5 | 1/67 | 1.5 | 1/67 | |||
| 4 | False tripod, LGA first | Separated IPAs | 19.4 | 13/67 | 3 | 2/67 | 22.4 | 15/67 | |
| 5 | False tripod, LGA first | Both IPAs from a common trunk | 13.4 | 9/67 | 3 | 2/67 | 16.4 | 11/67 | |
| 6 | False tripod, LGA, first | LIPA | 13.4 | 9/67 | 13.4 | 9/67 | |||
| 7 | False tripod, LGA first | RIPA | 16.4 | 11/67 | 1.5 | 1/67 | 17.9 | 12/67 | |
| 8 | False tripod, LGA first | GDA | 3 | 2/67 | 3 | 2/67 | |||
| 9 | False tripod, LGA first | DPA | 6 | 4/67 | 1.5 | 1/67 | 7.5 | 5/67 | |
| 10 | True tripod | Separated IPAs + DPA | 1.5 | 1/67 | 1.5 | 1/67 | |||
| 11 | False tripod, LGA first | Separated IPAs + DPA | 1.5 | 1/67 | 1.5 | 1/67 | |||
| 12 | False tripod, LGA first | LIPA + DPA | 1.5 | 1/67 | 1.5 | 1/67 | |||
| 13 | False tripod, LGA first | RIPA + LMAA | 1.5 | 1/67 | 1.5 | 1/67 | |||
| 14 | False tripod, LGA first | Separated IPAs + GDA + LMAA | 1.5 | 1/67 | 1.5 | 1/67 | |||
| 15 | Hepatosplenic trunk. LGA from AA | RIPA | 1.5 | 1/67 | 1.5 | 1/67 | |||
| 16 | Splenogastric trunk. CHA from SMA | LIPA | 1.5 | 1/67 | 1.5 | 1/67 | |||
| 17 | Splenogastric trunk. CHA from SMA | GDA | 3 | 2/67 | 3 | 2/67 | |||
| Vertebral body level | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| T10: 10th vertebral thoracic body; T11: 11th vertebral thoracic body; T12: 12th vertebral thoracic body; L1: first vertebral lumbar body. | ||
| T10 | 1 | 0.7 |
| T10 to T11 | 0 | 0 |
| T11 | 8 | 5.6 |
| T11 to T12 | 5 | 3.6 |
| T12 | 67 | 47.9 |
| T12 to L1 | 19 | 13.6 |
| L1 | 40 | 28.6 |
| Authors | Arteries derived from the celiac trunk | Number of branches | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| LGA: left gastric artery; SA: splenic artery; CHA: common hepatic artery; LIPA: left inferior phrenic artery; RIPA: right inferior phrenic artery; LGEA: left gastroepiploic artery; GDA: gastroduodenal artery; LSAA: left superior adrenal artery; LMAA: left middle adrenal artery; AAPD: aberrant artery supplying the pancreas and duodenum; IPA: inferior phrenic artery; DAB: duodenal arterial branch. | |||
| Cicekcibaşi et al, 2005 | LGA + SA + CHA + LIPA + RIPA + LGEA | 6 | [26] |
| Chitra, 2010 | LGA + SA + CHA + IPA + MCA + DAB | 6 | [9] |
| Astik and Dave, 2011 | LGA + SA + CHA + RIPA + GDA + LSAA + LMAA | 7 | [27] |
| Alashkham, 2012 | LGA + SA + CHA + AAPD + LIPA + RIPA | 6 | [28] |
| Agarwal et al, 2016 | LGA + SA + CHA + LIPA + RIPA +DPA | 6 | [29] |
| Case 1, present series | LGA + SA + CHA + LIPA + LIPA + DPA | 6 | |
| Case 2, present series | LGA + SA + CHA + LIPA + RIPA + LMAA | 6 | |
| Case 3, present series | LGA + SA + CHA + LIPA + RIPA + LMAA + GDA | 7 | |