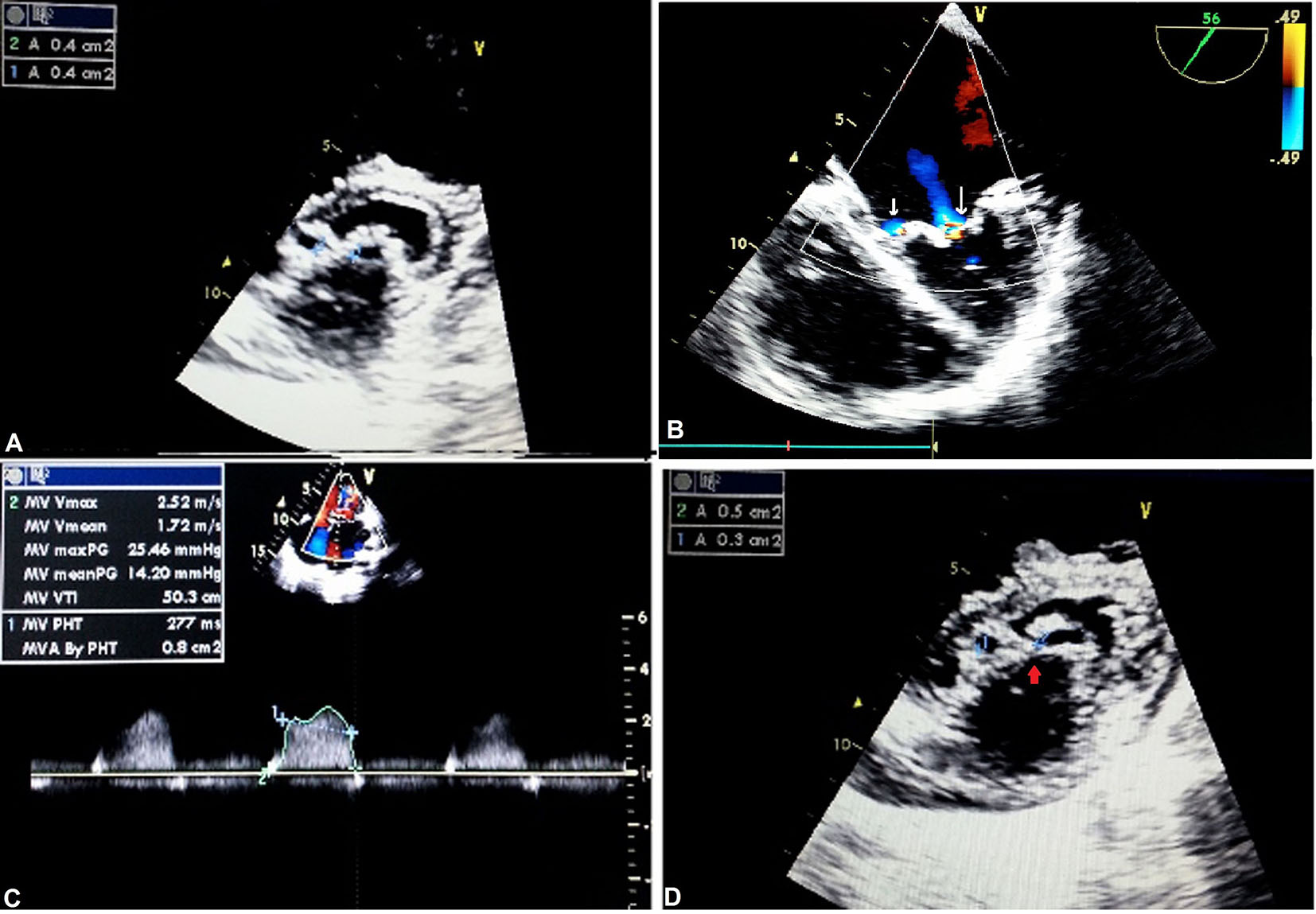
Figure 1. Complete bridge type of DOMV: apical four-chamber view showing TR (A); TEE showing mitral regurgitation, parasternal (B); short-axis (PSAX) view showing severe mitral stenosis by pressure half time (C) and planimetry (D).
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 8, Number 12, December 2016, pages 893-898
Bi-Luminal Mitral Valve: Incidence, Clinical Features, Associated Anomaly and Echocardiographic Evaluation
Figures

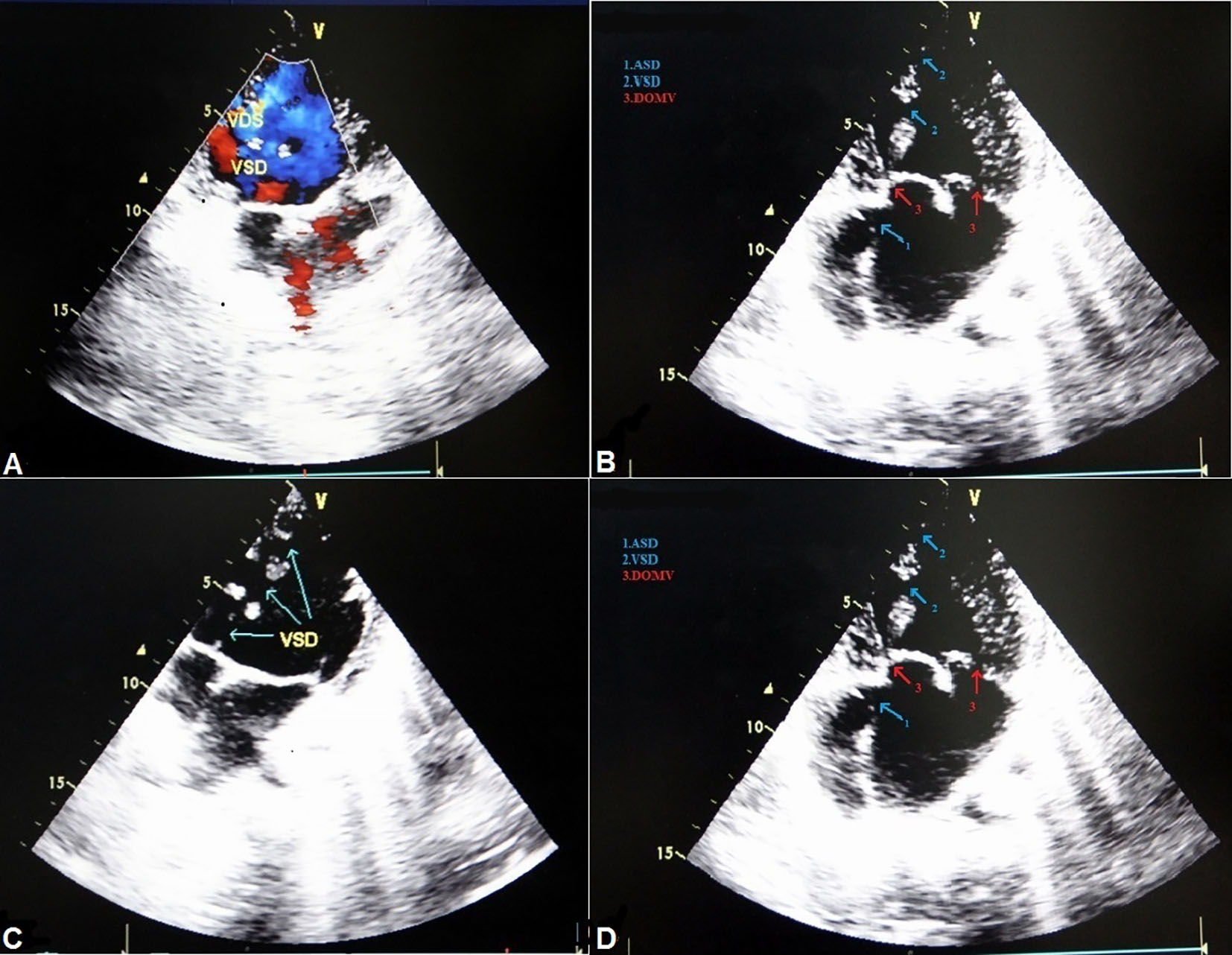
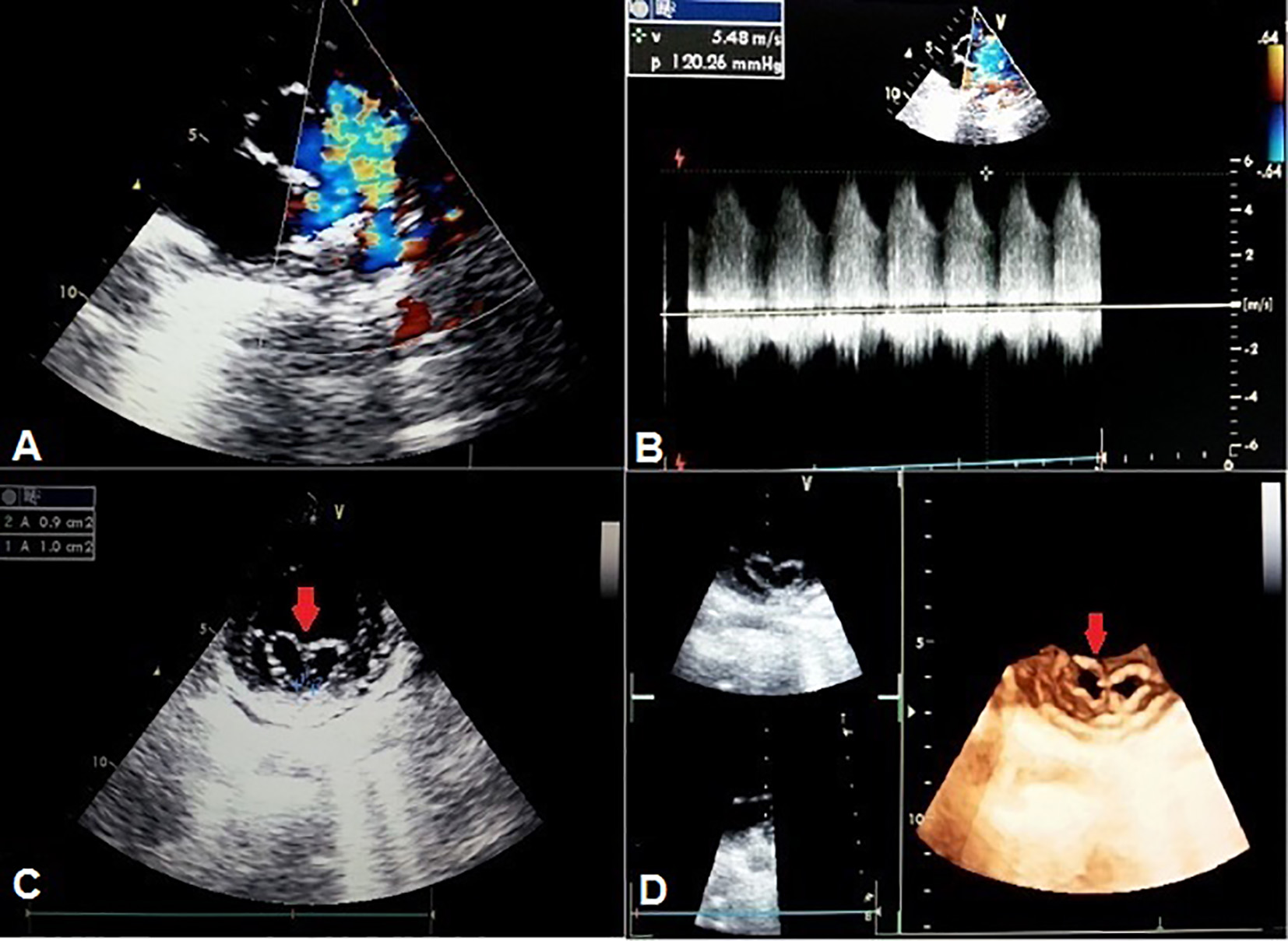
Tables
| Variables | No. (%) |
|---|---|
| CVS: cardiovascular system; ECG: electrocardiogram; LAD: left axis deviation; NYHA: New York Heart Association. | |
| Age (mean ± SD) | 20.1 ± 4.9 |
| Gender (male/female) | 10/18 (1:1.8) |
| Clinical presentation | |
| Dyspnea | 19 (67.8) |
| Palpitation | 6 (21.4) |
| Fatigue | 4 (14.2) |
| Hemoptysis | 2 (7.1) |
| Embolic phenomenon | 2 (7.1) |
| NYHA functional class | |
| I | 7 (25) |
| II | 17 (60.7) |
| III | 4 (14.3) |
| IV | - |
| CVS examination | |
| Diastolic thrill | 4 (14.3) |
| Systolic thrill | 4 (14.3) |
| Continuous thrill | 3 (10.7) |
| Diastolic murmur | 19 (67.8) |
| Pansystolic murmur | 12 (42.8) |
| Continuous murmur | 3 (10.7) |
| ECG | |
| Normal sinus rhythm | 25 (89) |
| Atrial flutter/fibrillation | 3 (10.7) |
| LAD | 3 (10) |
| Type of DOMV | Mitral stenosis | Associated lesions | N (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Severity | MVA (cm2) | Gradient (mean mm Hg) | |||
| DOMV: double orifice mitral valve; MVA: mitral valve area; TR: tricuspid regurgitation; VSD: ventricular septal defect; MR: mitral regurgitation; ECD: endocardial cushion defect; ASD: atrial septal defect; PDA: patent ductus arteriosus; Vmax: maximum peak velocity; PGmax: maximum peak gradient. | |||||
| Complete bridge type (89%) | Severe | 0.4 - 0.8 | 14 - 28 | Severe TR | 13 (46) |
| VSD | 3 (11) | ||||
| Mild to moderate MR | 2 (7) | ||||
| ECD (complete) - primum ASD and VSD | 3 (11) | ||||
| Moderate | 1.5 - 1.7 | 5 - 8 | Moderate MR | 4 (14) | |
| Incomplete bridge type (11%) | Severe | 0.9 - 1 | 17 - 32 | PDA (Vmax/PGmax) = 5.4/120 | 3 (11) |