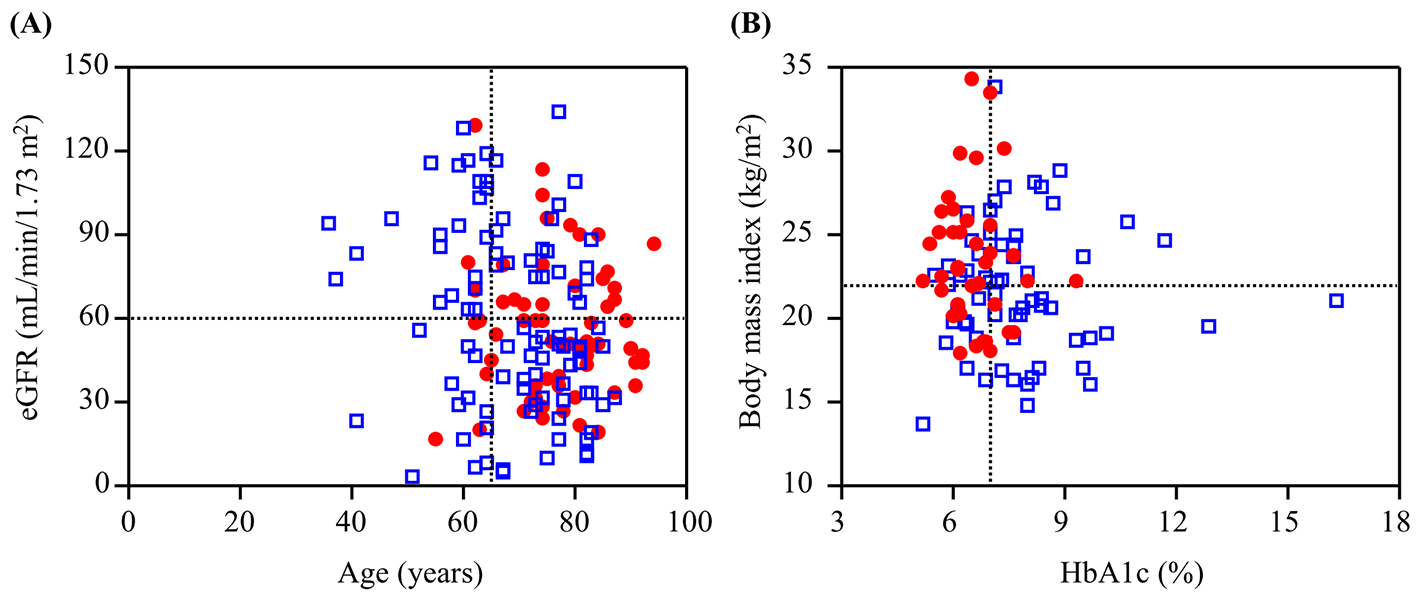
Figure 1. Scatter plots of (A) eGFR and patients’ age and (B) body mass index and HbA1c value categorized by the antidiabetic agents during the entire study period. Open blue squares and closed red circles indicate the patients with severe hypoglycemia induced by insulin and sulfonylureas, respectively.