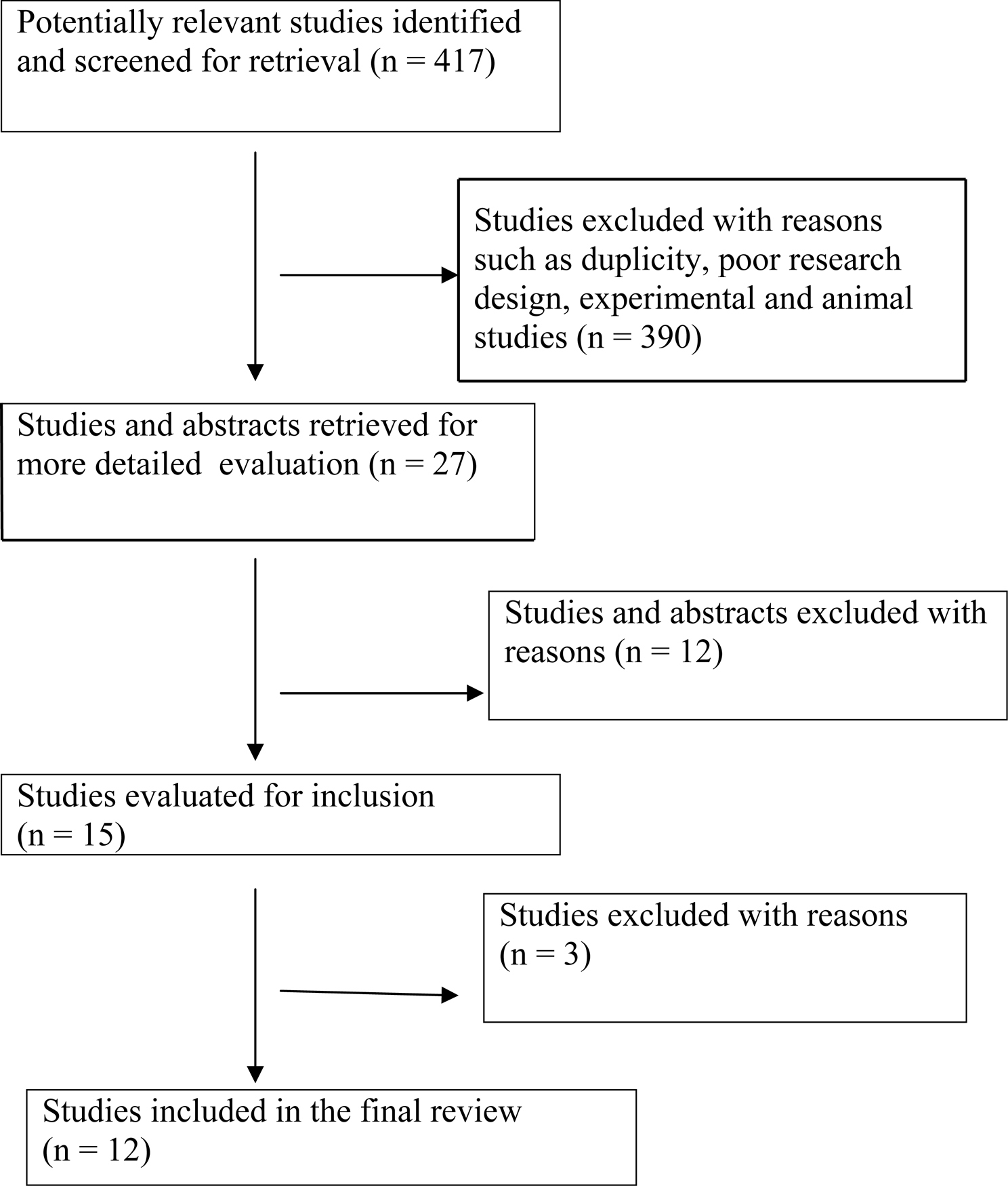
Figure 1. Progress through stages of systematic review of studies predicting progression of HIV virus related disease.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Review
Volume 2, Number 2, April 2010, pages 55-61
Biomarkers Predicting Progression of Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Related Disease
Figure

Table
| Name of the study | Research design | Biomarkers | Results/discussion | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1) Price et al (2007) [40] | Review | Viral: CSF HIV 1 RNA, neuropathogenetic genotypes Immunological: Beta 2 microglobulin,neopterin, quinolinic acid, MCP-1 Neural: molecular products of neurons, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia. Other: reactive aldehydes-4 hydroxy-nonenal | Elevated CSF HIV 1 RNA along with raised MCP-1 or neopterin suggest AIDS-dementia complex or HIV -1 encephalitis. Proviral HIV DNA within peripheral blood mononuclear cellsprognostic marker for ADC (AIDS-dementia complex). Monocytes showing increased expression of CD69, CD16, & TNF alpha. | Combination of blood and CSF markers should be used. Develop objective laboratory based quantitative measures for predicting and establishing diagnosis. |
| 2) Gendelman (2007) [29] | Review | Quinolinic acid, chemokines, proinflammatory cytokines, matrix metalloproteinases surrogates as well as causal. | End-stage disease dementia and encephalitis occurs due to blood-borne macrophage entry in brain. Micro arrays done showed increase in RANTES increase in chronic stage. | Miroglial-macrophage activation underlies many divergent neurodegenerative disorders including neuroaids. There is further need of understanding host-defense as well as cell-signaling mechanisms. |
| 3) Hulgan et al (2007) [41] | Observational study | Absolute CD4, percent CD4, and HIV 1-RNA | Used a cox proportional hazards regression model to determine associations between percent CD4 and disease progression. Prior ART (p < 0.0001), injection drug use (p < 0.04), lower absolute CD4 (p = 0.002), and lower percent CD4 (p = 0.002) predicted disease progression. | Percent CD4 at initiation of first HAART regimen predicted disease progression independent of absolute CD4. Percent CD4 may be used to determine timing of HAART (Highly active Antiretroviral therapy). |
| 4) Nilsson et al (2006) [42] | In-vitro study | T-reg cell numbers(specialized subset of CD4 cells), FOX P3, CTLA-4, IDO, TGF B1(functional markers) | Increased number of FOX P3 positive T-cells and increased expression of T-reg cell associated markers were detected only during progressive HIV disease. T-reg cell exposure to HIV promoted their survival via CD4-gp 120 dependent pathway. | T-reg cells accumulate due to increase in HIV viral load. They negatively affect the immune control of virus replication. Potential novel ways of improving the immune function can be through manipulation of these T-reg cells. |
| 5) Lau et al (2006) [32] | Cross-sectional study | C-reactive protein | The association of log10CRP(C-reactive protein) were inversely correlated with CD4 lymphocyte counts (r = -0.17, p < 0.001) and directly with log10HIV RNA levels (r = 0.20, p < 0.001). Levels of CRP of > 2.3 mg/l were associated with decreased time to AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). | Levels of C-reactive protein were associated with HIV disease progression independent of CD4 lymphocyte counts and HIV RNA levels. |
| 6) Kiepala et al (2005) [43] | Review | Viral markers: Plasma HIV RNA load, serum p24 antigen load, serum p 24 antibodies, syncitium inducing strains. Surrogate markers: Anti-p27 nef Immune markers: CD4 cell counts, percentage of CD4 cells, CD8 cell counts, neopterin, beta 2 micro globulin Other markers: CCR5, HLA type and resistance genotyping and phenotyping. | Plasma viral load (HIV RNA) is most representative and sensitive laboratory test as a predictor of risk for disease progression and response to antiretroviral therapy. P24 antigen was more specific, and cheaper but less sensitive. CD4 cell counts should be followed longitudinally and percentage of CD4 cells more accurately predicts progression. | Various statistical tests have indicated that CD4 cells, serum level of B2 microglobulin and p24 antigenemia in a descending order were best predictors of disease progression. Host genetic factors may be incorporated in assessment in the future. |
| 7) Carbone et al (2004) [30] | Retrospective cohort study using cox proportional hazards model. | Immunoglobulin levels | High levels of soluble markers IgG (relative hazard (RH):1.06, p = 0.006), IgA (RH 1.67, p = 0.02), IgM (RH 1.28, p = 0.0001), B2-M (RH 2.38, p < 0.0001) and sTNF-R (RH 1.07, p = 0.002) individually showed progression to AIDS. | This is the first demonstration in a cohort of injection drug users that immunoglobulin level measurements have predictive value for HIV progression independent of CD4 T-cell counts and HIV RNA. |
| 8) Heggelund et al (2004) [31] | Cross-sectional | sTLR 2- (soluble Toll-like 2 receptor) levels. | Chi-square analysis showed undetectable levels of sTLR 2 receptors in AIDS patients controlled with healthy controls (p = 0.02). No statistically significant correlation was found between sTLR levels and CD4 and CD8-T cell counts. HIV infected progressors to AIDS had decreased sTLR at all time points returned to baseline levels at last time point. | There is an association between sTLR levels and disease progression to AIDS. There can be an increased cytokine response to bacterial lipoproteins after sTLR levels depletion causing further progression of HIV disease. |
| 9) Sacktor et al (2004) [34] | Cohort analysis | Sphingomyelin, ceramide, 2- pentylpyrrole lysine adduct. | There was an increase in two HNE (hydroxynonenal) adducts in medial frontal, cerebellum and cerebrospinal fluid of HIV dementia patients. Massive amounts of oxidative stress was seen with HIV encephalitis. Spingomyelins were raised in inactive dementia cases compared to HIV + cases without dementia; ceramides were elevated in active dementia cases. | Sphingomyelin metabolic products and markers of oxidative stress such as HNE and ceramide are elevated in actively progressive dementia cases. Surrogate markers must be correlated with clinical progression of HIV disease. |
| 10) Fernandes et al (2003) [33] | Cross-sectional study | HLA-markers such as HLA- A1, A11, B8, B35, DR3, DR1, DQ2, DQ1, Bw4, B44, B57. | At least one of these HLA markers were exhibited by 56.4% of the patients associated with rapid progression to AIDS and 7.2% presented with at least one marker associated with slow progression to AIDS. The frequency of markers associated with rapid progression to AIDS was significantly increased in patients with CMV(cytomegalovirus) retinitis in relation to those without retinitis (P < 0.002). | HLA-markers associated with rapid progression to AIDS were significantly raised in CMV-retinitis group. HLA-markers may simultaneously predispose to AIDS and CMV-retinitis. |
| 11) Lau et al (2003) [35] | Prospective cohort study | Total lymphocyte count and hemoglobin concentration | A total lymphocyte decline greater than 10% and Hgb decline greater than 2.2% was present in over 77% of HIV positive men who developed AIDS but only 23% of HIV positive who did not. | Both total lymphocyte count and hemoglobin concentration showed a period of stability which was followed by a rapid decline beginning before the onset of AIDS. Hence these markers are useful in monitoring disease progression in resource limited setting. |
| 12) Jacobson et al (2002) [36] | Cohort study | CD4 lymphocyte cell counts. | Within 3.5 years of HAART (highly active antiretroviral therapy) initiation 11.3% of subjects developed AIDS and determinants of AIDS was a CD4 cell count of < 200cells/microl (relative hazard = 2.25 95% CI = 1.13, 4.49). An increase in CD4 counts of 50microlit. Immediately after HAART initiation also improved prognosis (RH = 0.34, 95% CI = 0.16, 0.71) | There is no difference between men who started HAART at a lower CD4 count and men who started HAART at a higher CD4 count from the time point of progression to AIDS. HIV RNA levels were good for prognosis but less informative in predicting death. |