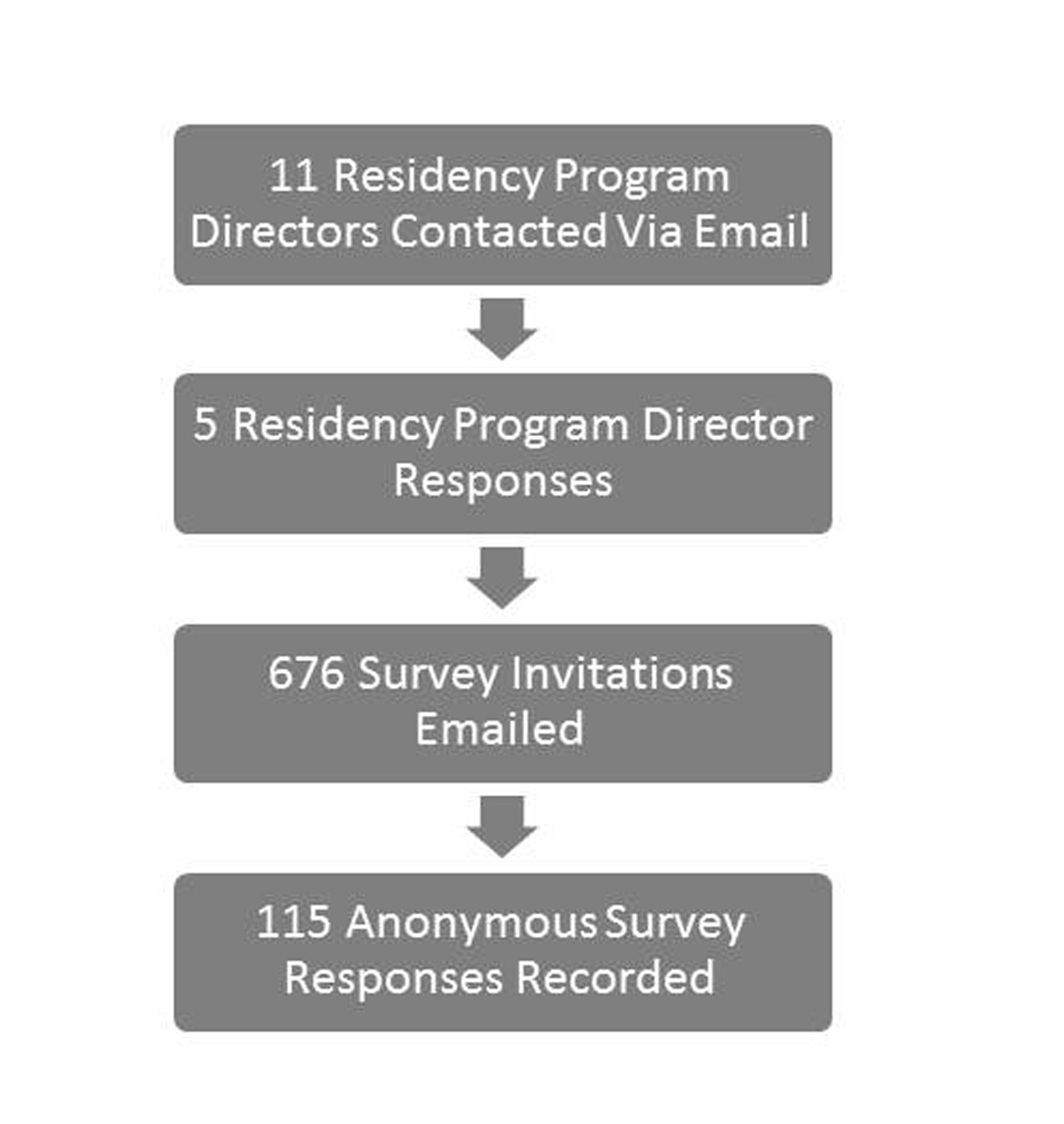
Figure 1. Survey enrollment.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 6, Number 2, April 2014, pages 120-126
Resident Knowledge of Colorectal Cancer Screening Assessed by Web-Based Survey
Figure

Tables
| Screening exam | PGY-1 | PGY-2 | PGY-3 | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Denotes a statistically significant value. | ||||
| Flexible sigmoidoscopy every 5 years | 29 (54.72%) | 17 (53.13%) | 15 (50.00%) | 0.9179 |
| Colonoscopy every 10 years | 49 (92.45%) | 31 (96.88%) | 28 (93.33%) | 0.7852 |
| Virtual colonoscopy every 5 years | 5 (9.43%) | 3 (9.38%) | 4 (13.33) | 0.8332 |
| Annual FOBT performed in the patient’s home | 12 (22.64%) | 12 (37.50%) | 16 (53.33%) | *0.0174 |
| Annual FIT performed in the patient’s home | 3 (5.66%) | 1 (3.13%) | 1 (3.33%) | 1.0000 |
| Fecal DNA testing every 3 years | 0 (0.00%) | 1 (3.13%) | 1 (3.33%) | 0.2885 |
| DCBE every 5 years | 9 (16.98%) | 2 (6.25%) | 5 (16.67%) | 0.3370 |
| When to begin screening?/th> | PGY-1 | PGY-2 | PGY-3 | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Denotes a statistically significant value. ^Appropriate answer as per ACG 2008 guidelines. ^^Appropriate answer as per ACS 2008 guidelines. | ||||
| For average risk patients begin at age 50 | 52 (98.11%) | 31 (96.88%) | 29 (96.67%) | 1.000 |
| For average risk African-American patients begin at age 45 | 11 (20.75%) | 3 (9.38%) | 4 (13.33%) | 0.3460 |
| For patients with a first degree relative with CRC < age 60 begin at age 40 or 10 years younger than the index case | 34 (64.15%) | 20 (62.50%) | 22 (73.33%) | 0.6141 |
| For patients with a first degree relative with CRC > age 60, or two second degree relatives with CRC begin at age 40^^ | 3 (5.66%) | 3 (9.38%) | 3 (10.00%) | 0.7383 |
| For patients with a first degree relative with CRC > age 60, or two second degree relatives with CRC begin at age 50^ | 12 (22.64%) | 11 (34.38%) | 14 (46.67%) | *0.0756 |
| When to begin screening?/th> | ACS | USPSTF | ACG | ASGE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Our study concept was designed with the ACS/USPSTF/ACG guidelines. The ASGE guidelines are provided for further comparison. | ||||
| For average risk patients | Begin at age 50 | Begin at age 50 | Begin at age 50 | Begin at age 50 |
| For average risk African-American patients | Begin at age 45 | Not addressed | Not addressed | Not addressed |
| For patients with a first degree relative with CRC < age 60 | Begin at age 40 or 10 years younger than the index case | Not addressed | Begin at age 40 or 10 years younger than the index case | Begin at age 40 or 10 years younger than the index case |
| For patients with a first degree relative with CRC > age 60, or two second degree relatives with CRC | Begin at age 40 | Not addressed | Begin at age 50 (same as average risk screening) | Begin at age 40 |
| ACS | USPSTF | ACG | ASGE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| *Our study concept was designed with the ACS/USPSTF/ACG guidelines. The ASGE guidelines are provided for further comparison. | ||||
| Flexible sigmoidoscopy | Every 5 years | Not recommended | Every 5 - 10 years | Every 5 years |
| Colonoscopy | Every 10 years | Every 10 years | Every 10 years | Every 10 years |
| DCBE | Every 5 years | No recommendation given | No recommendation given | Not recommended, but if used, perform every 5 years |
| Virtual colonography | Every 5 years | No recommendation given | Every 5 years | Not recommended |
| FOBT | Annually | Annually | Annually | Annually |
| FIT | Annually | Annually | Annually | No recommendation given |
| Fecal DNA | Interval uncertain | No recommendation given | Every 3 years | Not recommended |