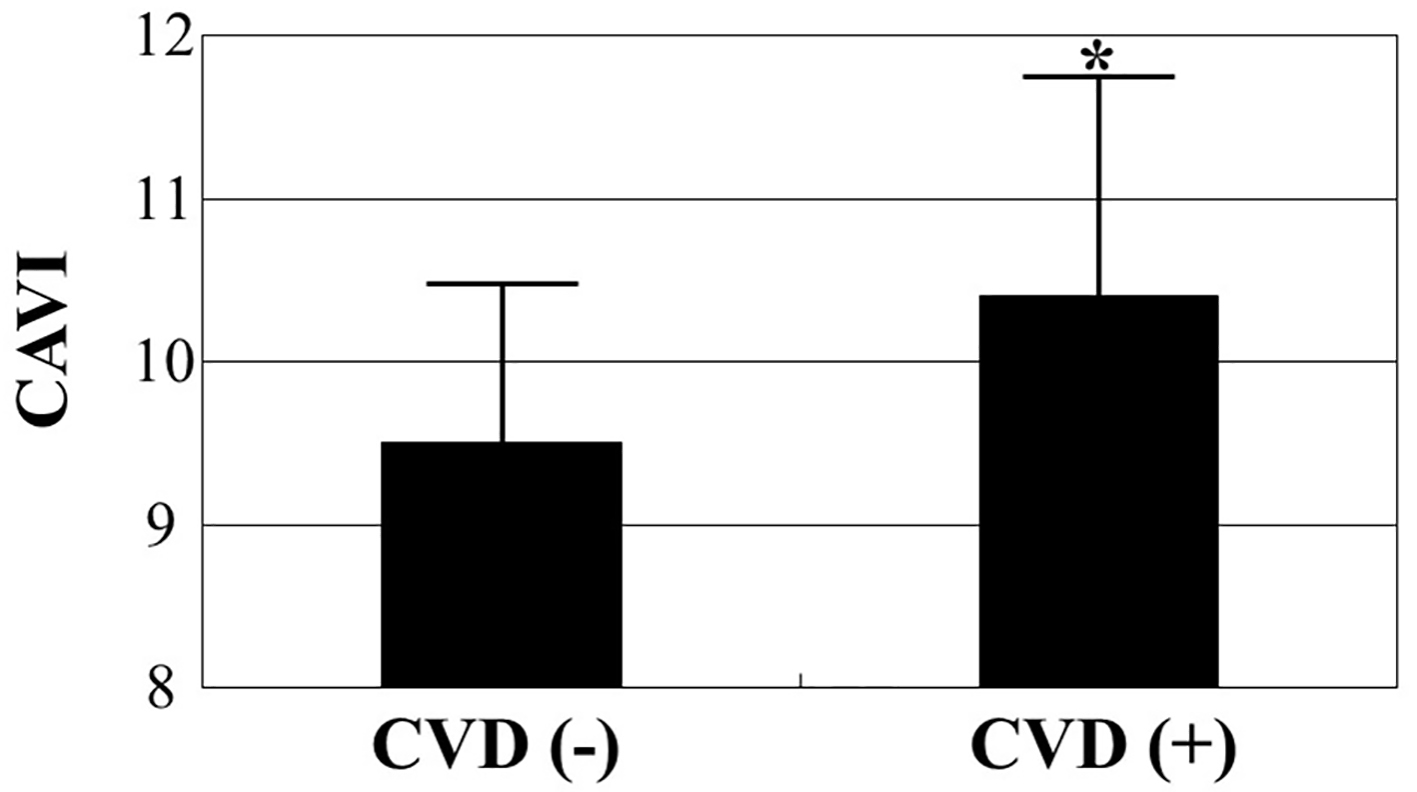
Figure 1. Comparisons of CAVI values between patients with and without CVD. CAVI was significantly higher in patients with CVD than in those without CVD (10.4 ± 1.4 vs. 9.5 ± 1.0, respectively, P < 0.001) even though mean age was similar between the two groups (76 ± 7 years vs. 75 ± 7 years, respectively). *P < 0.001 vs. CVD (-). CAVI: cardio-ankle vascular index; CVD: cardiovascular disease.
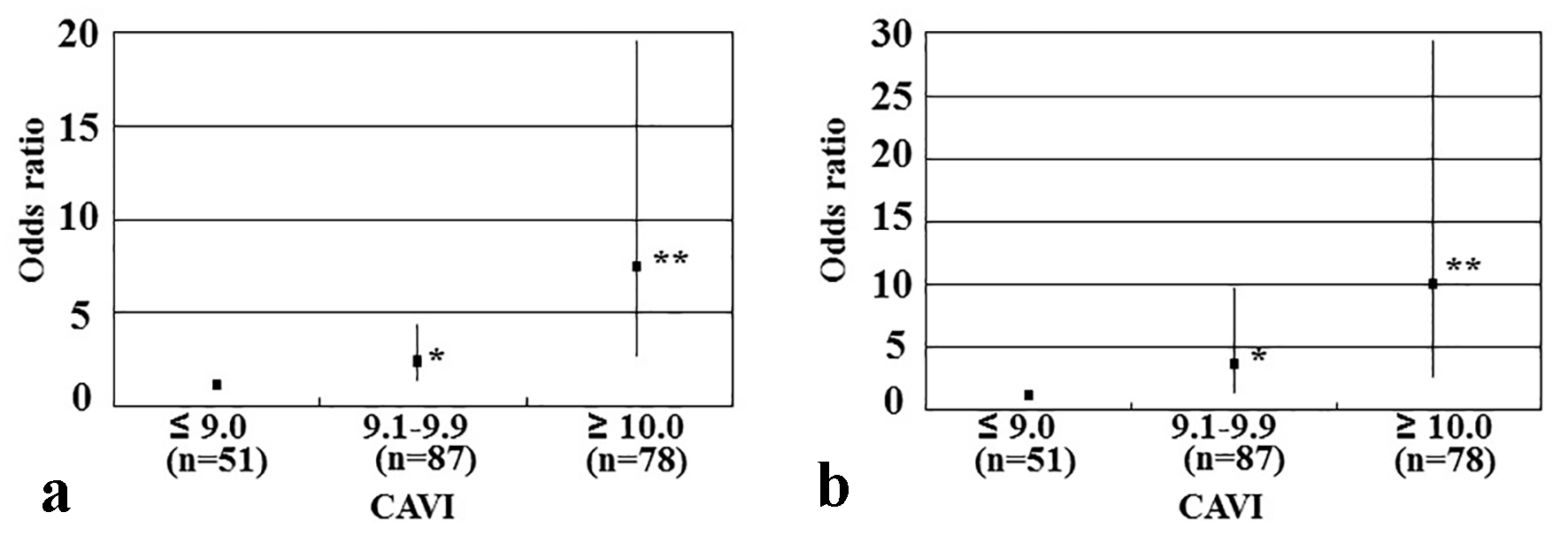
Figure 2. Results of multiple logistic regression analysis of CVD incidence or high hs-cTnT levels. (a) Subordinate factor is CVD incidence. Adjustment factors are skin autofluorescence, hs-cTnT, d-ROMs test, and age. (b) Subordinate factor is high hs-cTnT levels. High hs-cTnT was defined as hs-cTnT ≥ 0.014 ng/mL. Adjustment factors are skin autofluorescence, CVD, d-ROMs test, and age. *P < 0.05 vs. CAVI ≤ 9; **P < 0.001 vs. CAVI ≤ 9. CAVI: cardio-ankle vascular index; CVD: cardiovascular disease; hs-cTnT: high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T; d-ROMs: derivatives of reactive oxygen metabolites.

