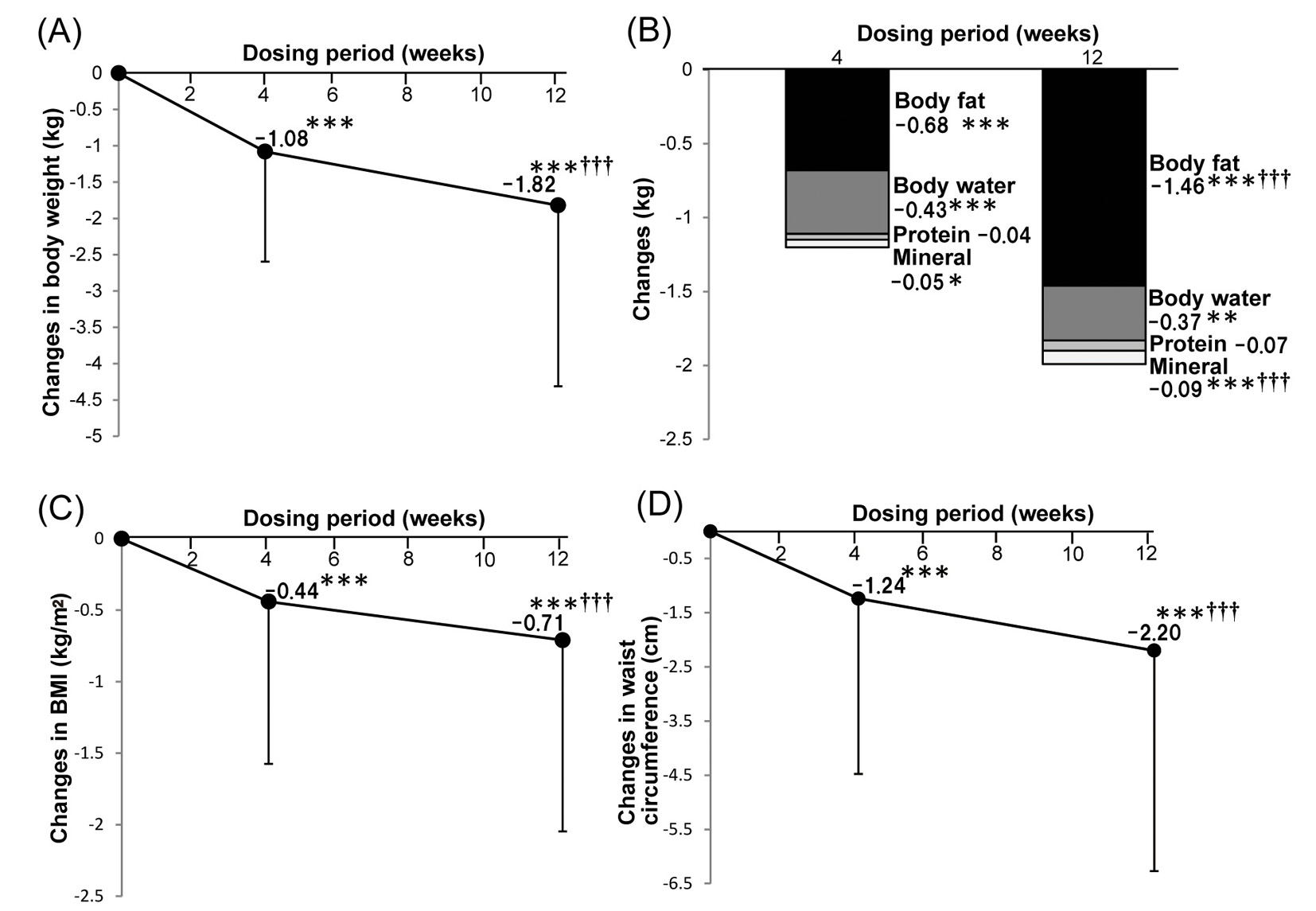
Figure 1. Effects of ipragliflozin therapy on body composition. Changes of body weight after ipragliflozin treatment (n = 240) (A). Changes of body composition parameters after ipragliflozin treatment (n = 239) (B). Changes of body mass index after ipragliflozin treatment (n = 241) (C). Changes of waist circumference after ipragliflozin treatment (n = 250) (D). Data are shown as the mean ± standard deviation. Significant differences after 4 and 12 weeks of treatment compared with baseline: ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05. Significant differences between 4 and 12 weeks of treatment: †††P < 0.001, ††P < 0.01, †P < 0.05.