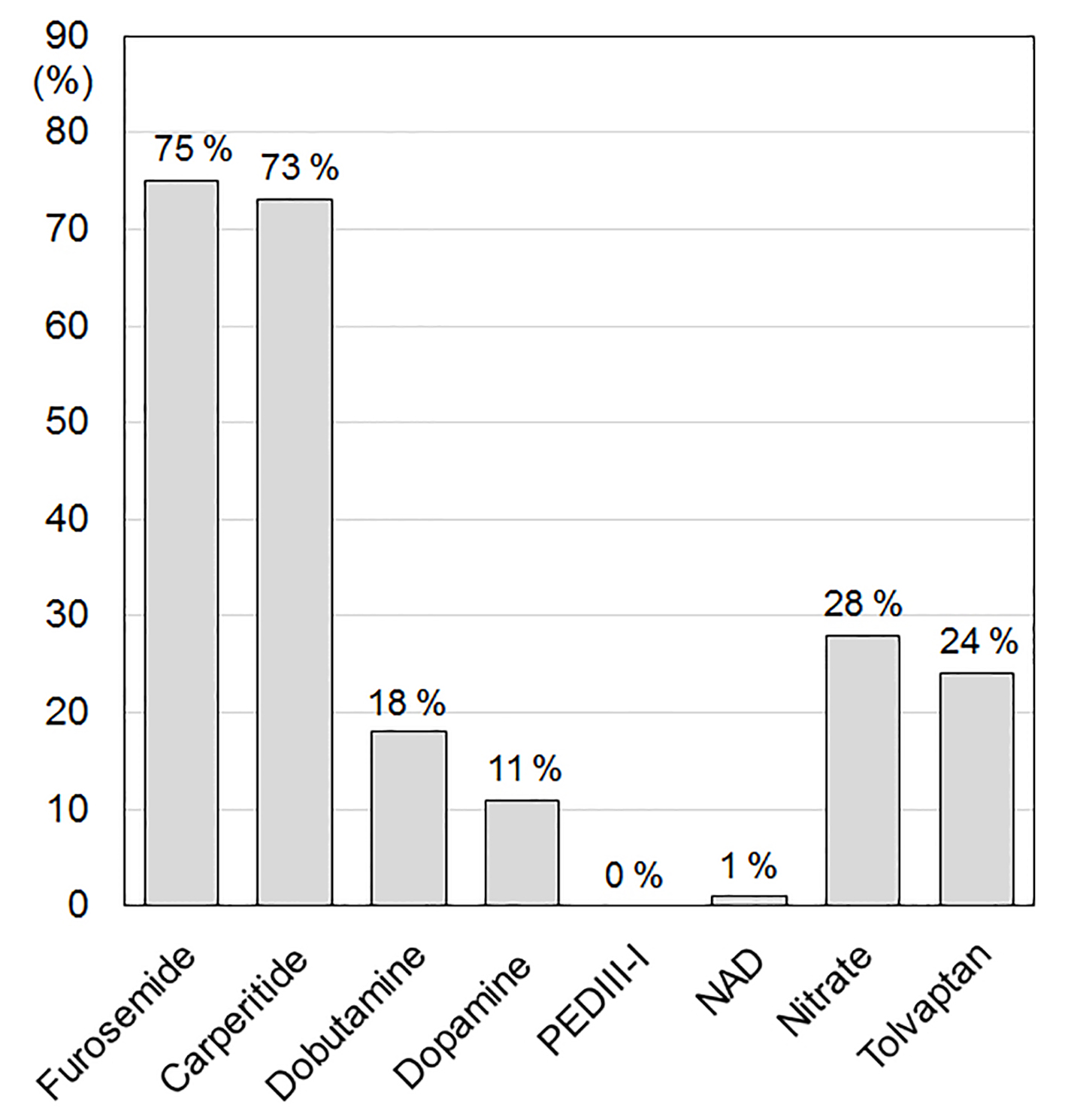
Figure 1. Medications in the acute phase of HF. PDEIII-I: phosphodiesterase inhibitor; NAD: noradrenaline.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 8, Number 2, February 2016, pages 97-104
Recent Patient Characteristics and Medications at Admission and Discharge in Hospitalized Patients With Heart Failure
Figures

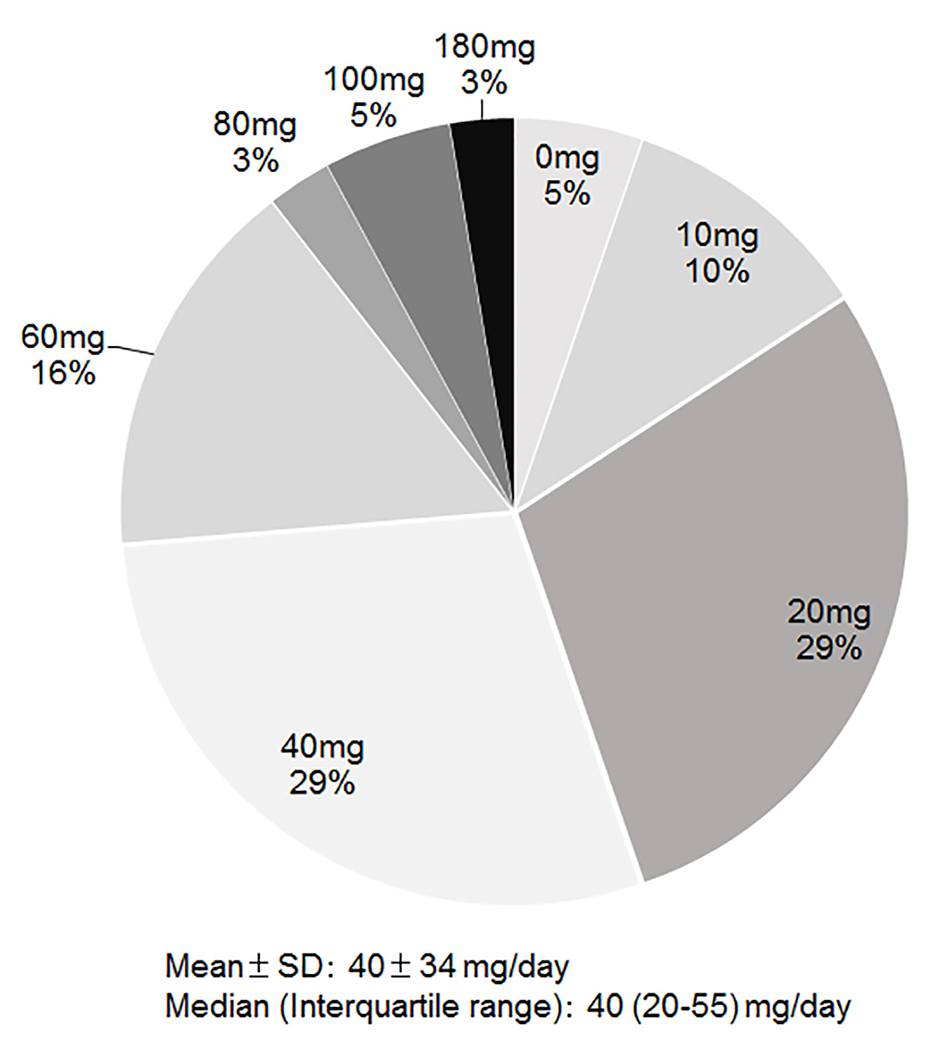
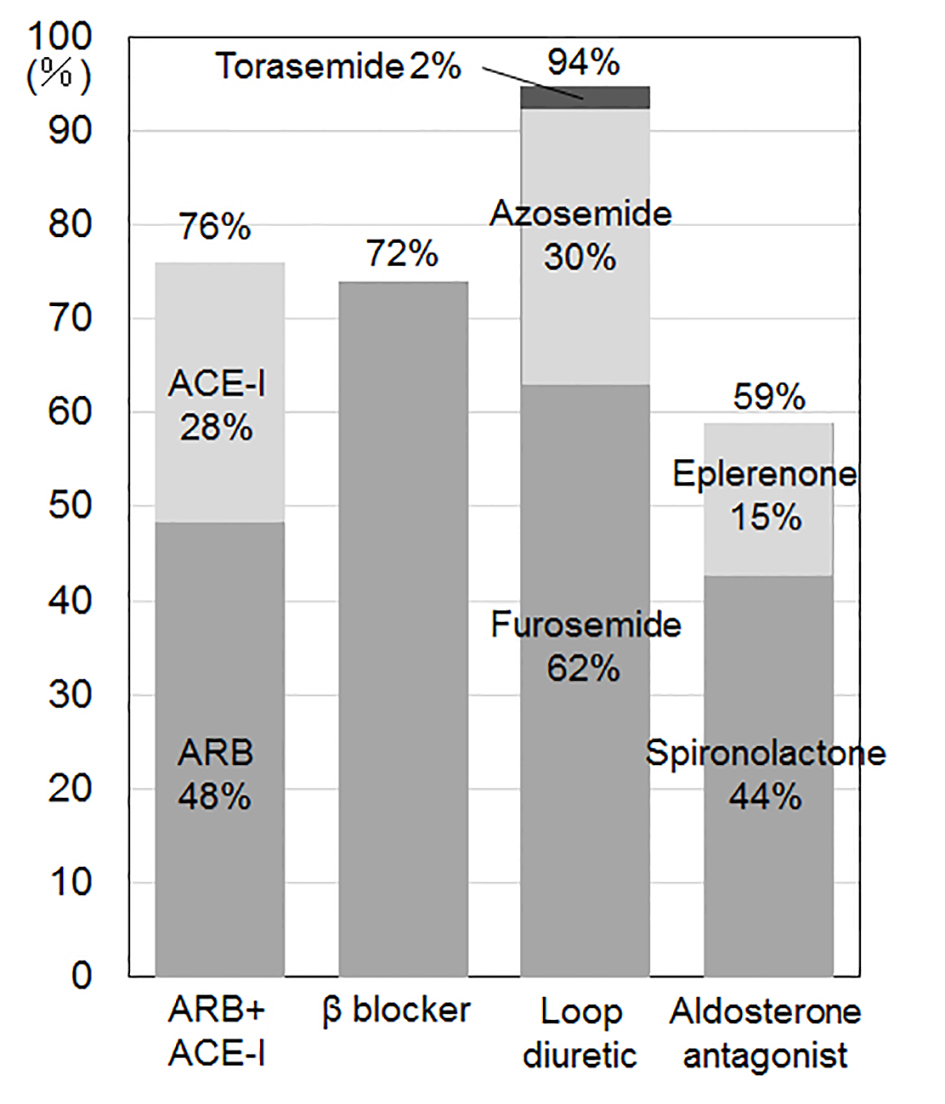
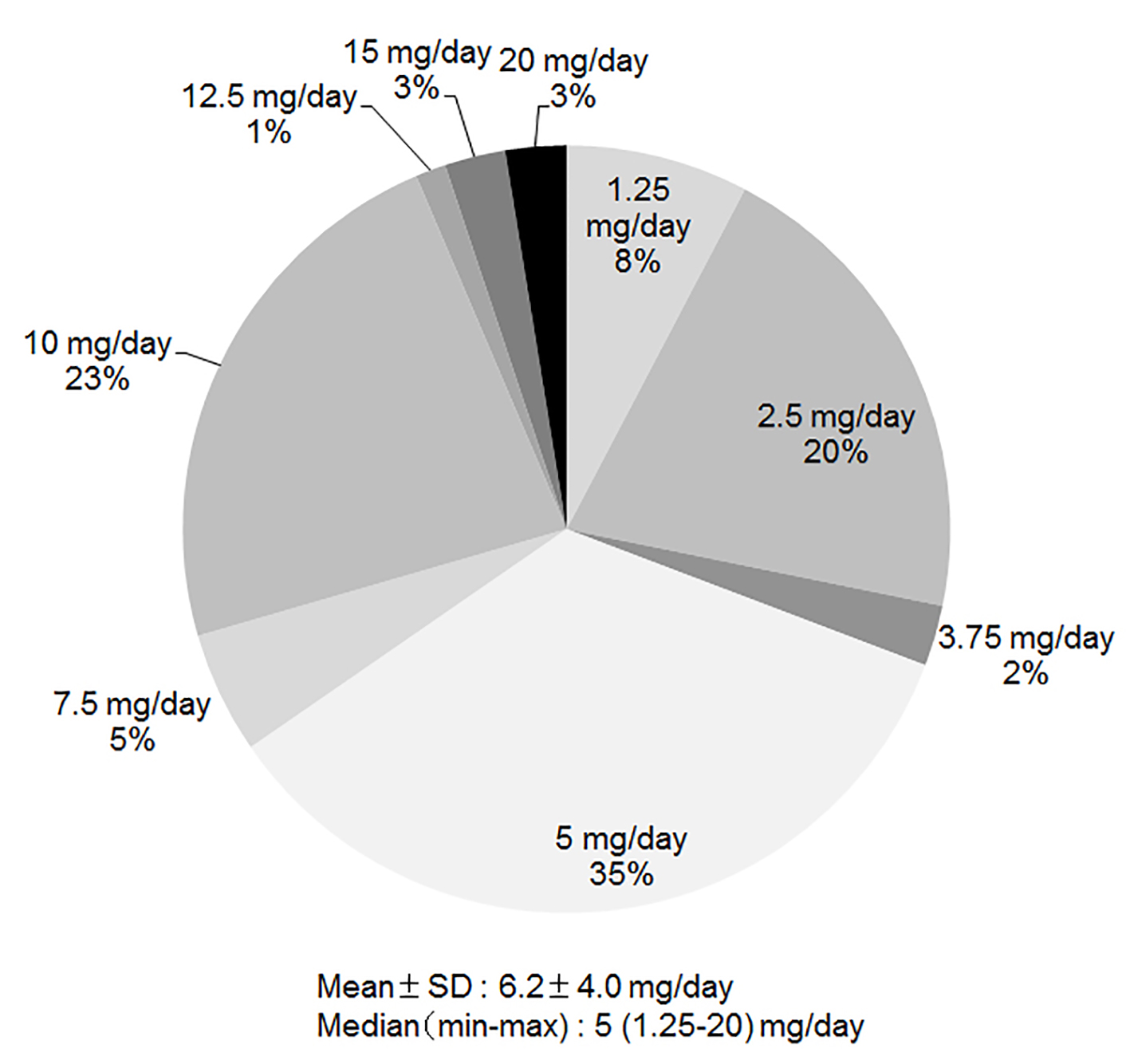
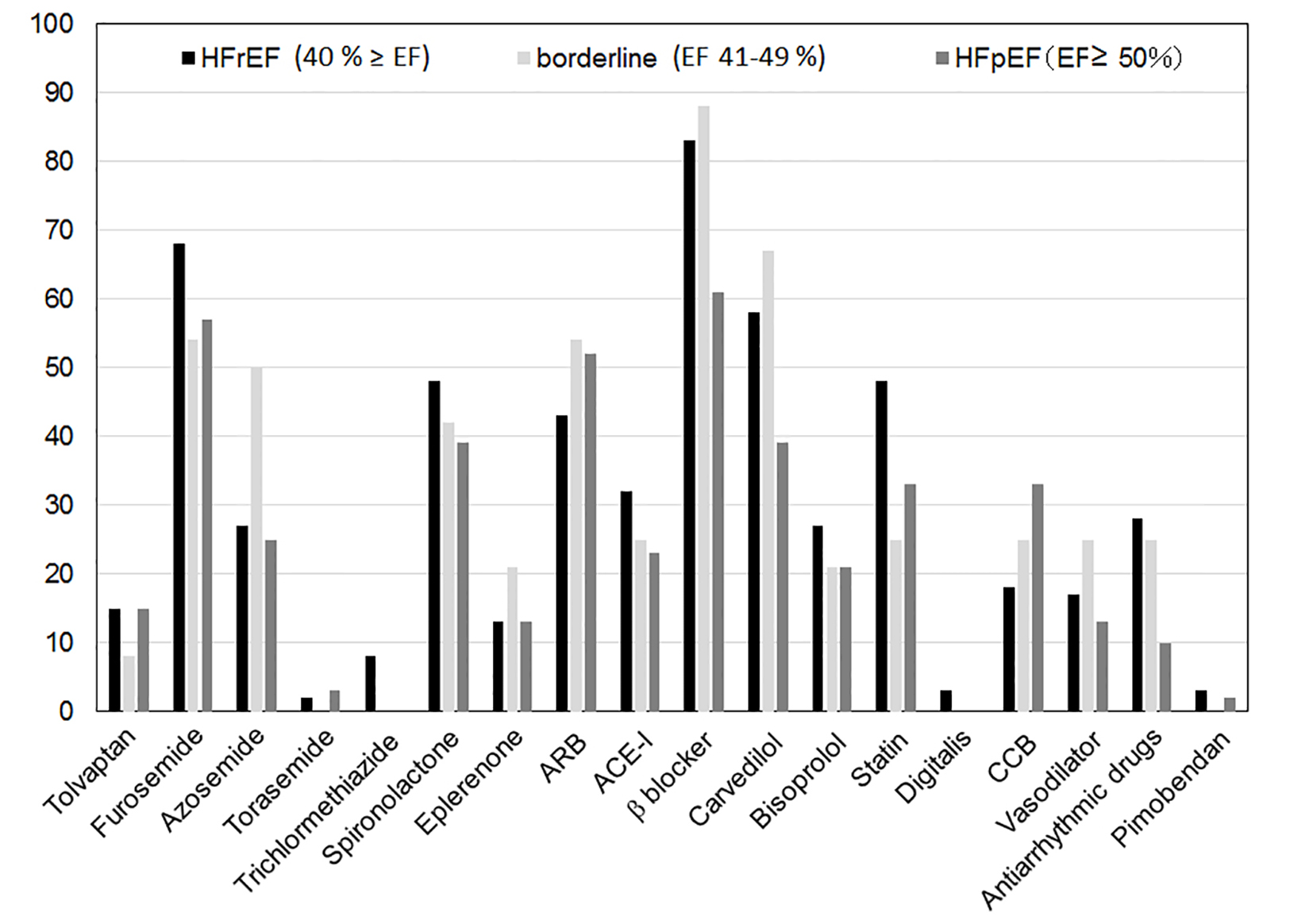
Tables
| Group 2013 (n = 158) | |
|---|---|
| NYHA: New York Heart Association; HTN: hypertension; DM: diabetes mellitus; DL: dyslipidemia; CKD: chronic kidney disease; PMI: pacemaker implantation; ICD: implantable cardioverter defibrillator; CRT: cardiac resynchronization therapy; SBP: systolic blood pressure; DBP: diastolic blood pressure; HR: heart rate; BNP: brain natriuretic peptide; NT-proBNP: amino-terminal pro-BNP; Cr: creatinine; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; CCr: creatinine clearance; UA: uric acid; Na: sodium; K: potassium; Hb: hemoglobin; CRP: C-reactive protein; TC: total cholesterol; TG: triglyceride; HDL-c: high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol; LDL-c: low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol; LAd: left atrial dimension; LVEDd: left ventricular end diastolic dimension; LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction. | |
| Male, n (%) | 86 (54) |
| Age | 74 ± 13 |
| Height, m | 1.58 ± 0.10 |
| Weight, kg | 59.2 ± 14.4 |
| NYHA classification | 3.5 ± 0.7 |
| Hospitalized days, days | 21 ± 13 |
| HTN, n (%) | 94 (59) |
| DM, n (%) | 53 (34) |
| DL, n (%) | 80 (51) |
| CKD, n (%) | 118 (75) |
| Anemia, n (%) | 117 (74) |
| Smoking, current, n (%) | 21 (13) |
| Smoking, former, n (%) | 36 (23) |
| PM, n (%) | 16 (10) |
| ICD, n (%) | 18 (11) |
| CRT, n (%) | 6 (4) |
| SBP, mm Hg | 137 ± 31 |
| DBP, mm Hg | 78 ± 18 |
| HR, /min | 86 ± 24 |
| Biochemical parameters | |
| BNP, pg/mL | 824 ± 702 |
| NT-proBNP, pg/mL | 7,569 ± 8,993 |
| Cr, mg/dL | 1.3 ± 0.7 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 45 ± 21 |
| CCr, mL/min | 47 ± 31 |
| UA, mg/dL | 6.9 ± 2.2 |
| Na, mEq/L | 140 ± 4 |
| K, mEq/L | 4.2 ± 0.6 |
| Hb, g/dL | 11.4 ± 2.4 |
| CRP, mg/dL | 2.41 ± 4.57 |
| TC, mg/dL | 150 ± 38 |
| TG, mg/dL | 86 ± 35 |
| HDL-C, mg/dL | 39 ± 12 |
| LDL-C, mg/dL | 89 ± 30 |
| Echocardiographic parameters | |
| LAd, mm | 47.0 ± 8.9 |
| LVEDd, mm | 52.5 ± 10.5 |
| LVEF, % | 44.7 ± 17.4 |
| HF: heart failure; DCM: dilated cardiomyopathy; HCM: hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; D-HCM: dilated phase of HCM; ARVC: arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy; IHD: ischemic heart disease; HTCM: hypertensive cardiomyopathy; PH: pulmonary hypertension. | |
| DCM, n (%) | 16 (10) |
| HCM, n (%) | 4 (3) |
| D-HCM, n (%) | 1 (1) |
| ARVC, n (%) | 1 (1) |
| Congenital, n (%) | 1 (1) |
| IHD, n (%) | 47 (30) |
| HTCM, n (%) | 32 (20) |
| Valvular heart disease, n (%) | 35 (22) |
| Arrhythmia, n (%) | 5 (3) |
| PH, n (%) | 1 (1) |
| Sarcoidosis, n (%) | 1 (1) |
| Peripartum cardiomyopathy, n (%) | 1 (1) |
| Myocarditis, n (%) | 1 (1) |
| Unknown, n (%) | 12 (8) |