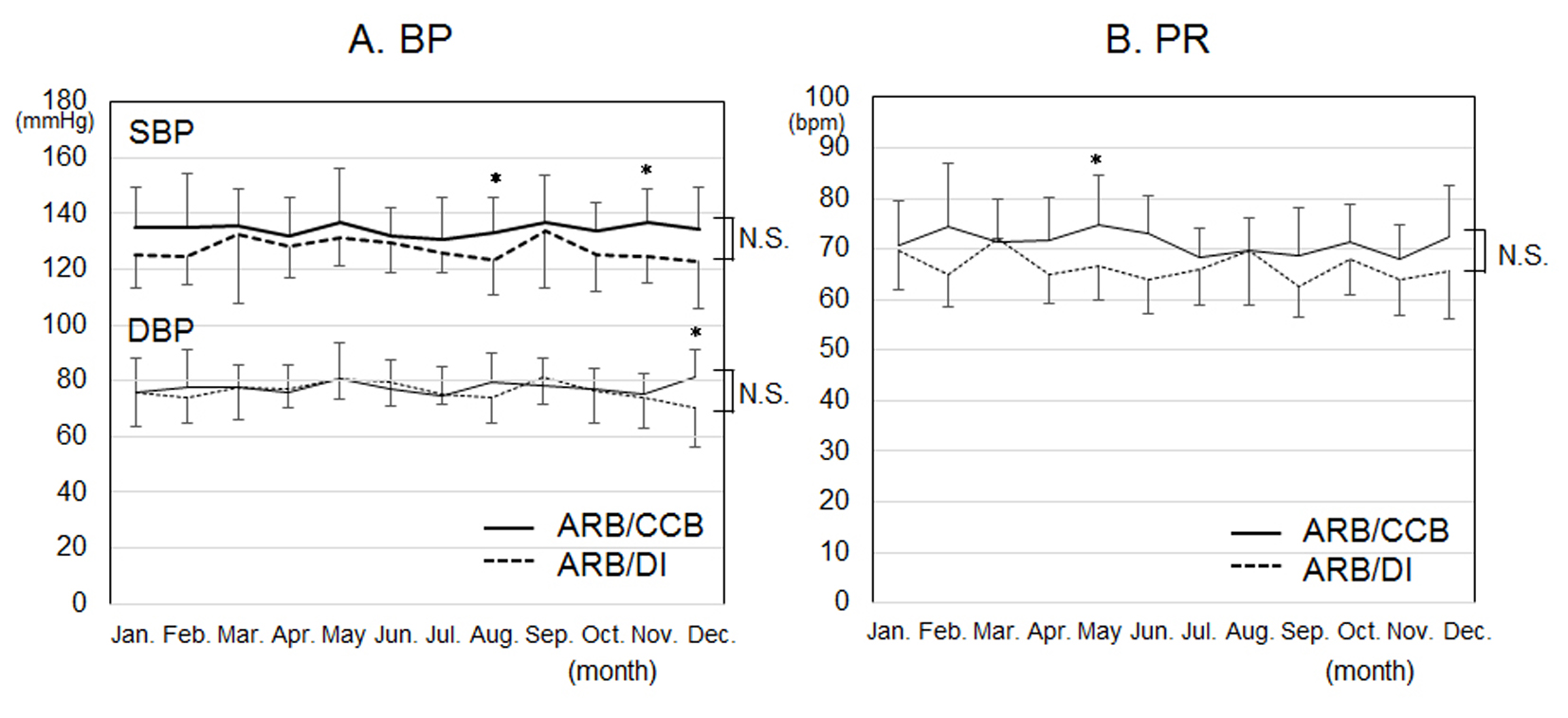
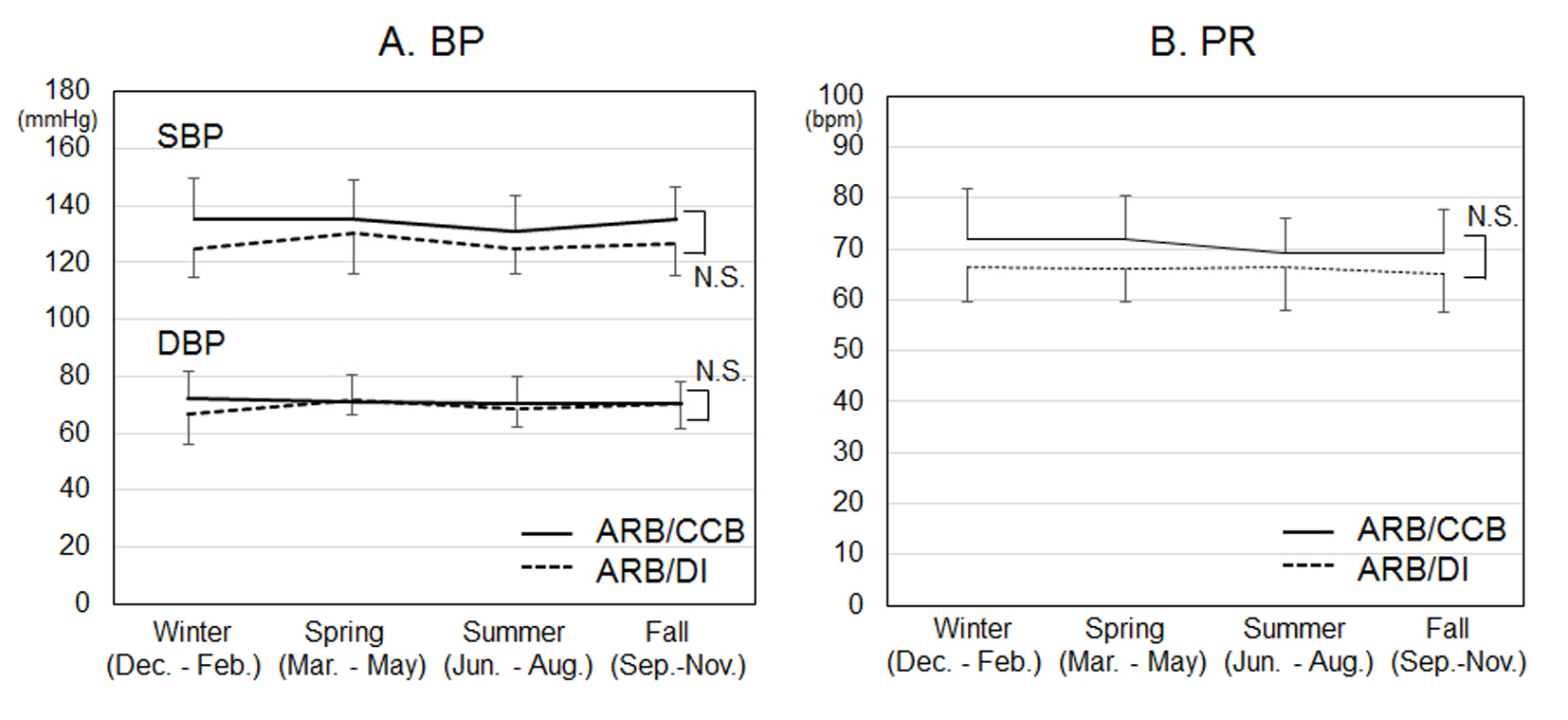
Figure 1. Time courses of blood pressure (BP) (A) and pulse rate (PR) (B) in each month for 12 months in the ARB/CCB and ARB/DI groups. *P < 0.05 vs. ARB/DI group. NS: not significant.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 7, Number 10, October 2015, pages 802-806
Visit-to-Visit Variability and Seasonal Variation in Blood Pressure With Single-Pill Fixed-Dose Combinations of Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker/Calcium Channel Blocker and Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker/Diuretic in Hypertensive Patients
Figures

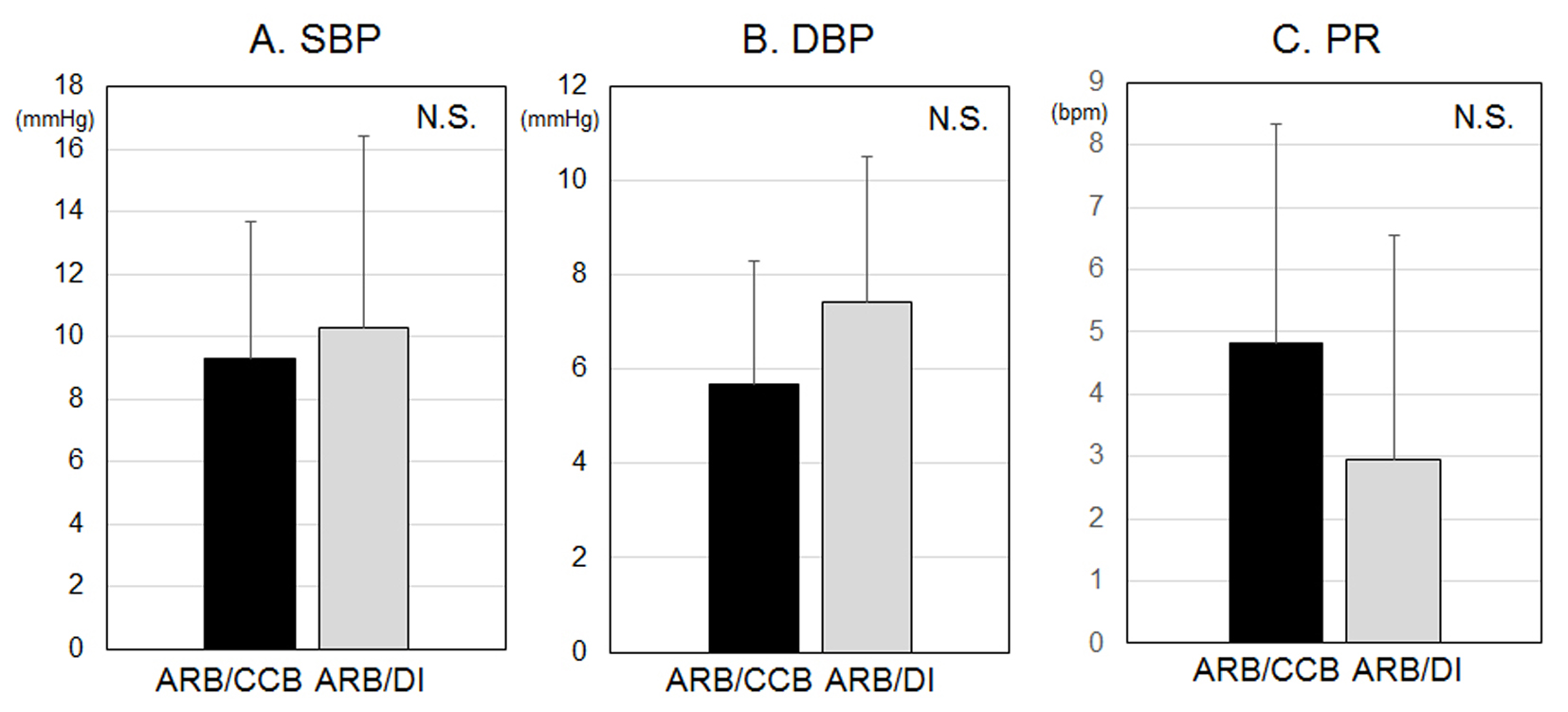
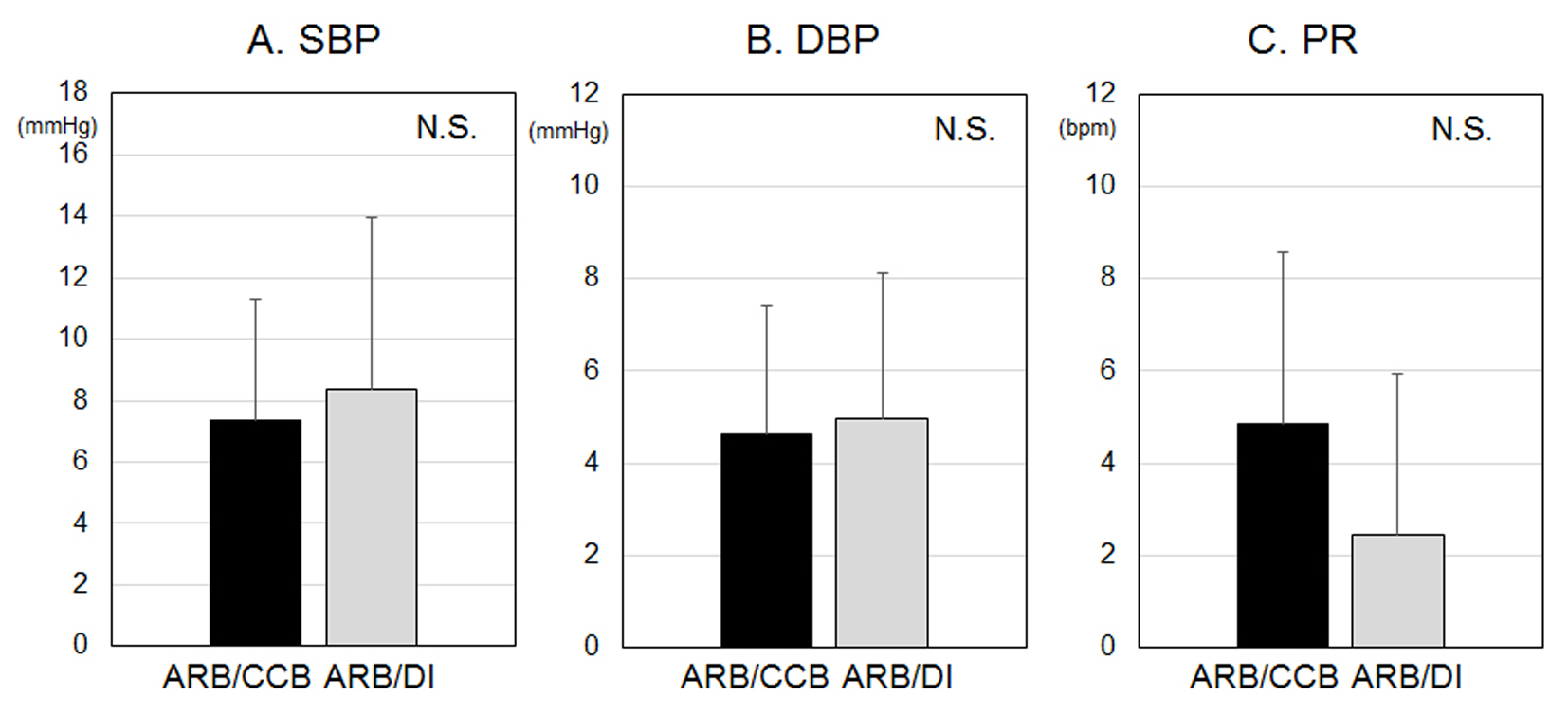
Table
| ARB/CCB (n = 30) | ARB/DI (n = 17) | |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous variables are expressed as mean ± SD. ARB: angiotensin II receptor blocker; CCB: calcium channel blocker; DI: diuretic; BMI: body mass index; DM: diabetes mellitus; DL: dyslipidemia; CAD: coronary artery disease. %CCB in the ARB/CCB group and %DI in the ARB/DI group indicate the percentages of CCB except for amlodipine and DI except for hydrochlorothiazide, respectively. *P < 0.05 vs. ARB/CCB. | ||
| Age, years | 70 ± 10 | 68 ± 10 |
| Male, % | 60 | 59 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 25 ± 3 | 24 ± 3 |
| DM, % | 13 | 6 |
| DL, % | 57 | 76 |
| CAD, % | 17 | 47* |
| Medications | ||
| CCB, % | 7 | 59* |
| DI, % | 13 | 0 |
| αβ blocker, % | 7 | 12 |
| β blocker, % | 17 | 24 |
| Aldosterone antagonist, % | 7 | 12 |