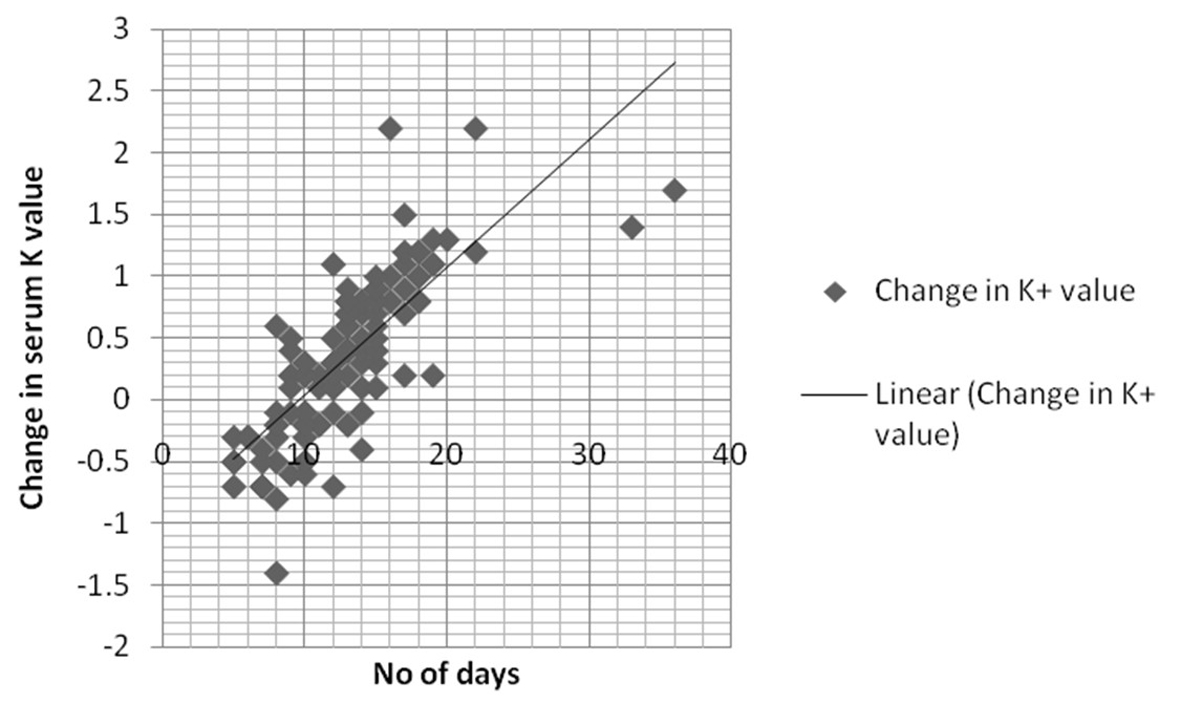
Figure 1. Linear correlation between number of days and serum potassium (K+) level.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.jocmr.org |
Original Article
Volume 7, Number 6, June 2015, pages 417-421
A Prospective Study on Red Blood Cell Transfusion Related Hyperkalemia in Critically Ill Patients
Figure

Tables
| Gender | N = 125 | % |
| Female | 71 | 56 |
| Male | 54 | 43.2 |
| Age | 63 (median) | 22 - 92 years |
| Indication for PRBC transfusion | ||
| Acute blood loss | 25 | 16.6 |
| Coronary artery disease with NSTEMI | 25 | 16.6 |
| Septic shock | 61 | 49 |
| Invasive procedure | 14 | 11.2 |
| No. of PRBC transfusions | ||
| 1 unit | 104 | 83.2 |
| 2 units | 11 | 8.8 |
| 3 units | 9 | 7.2 |
| 7 units | 1 | 0.8 |
| Intravenous access | ||
| Central line | 72 | 57.6 |
| Peripheral line | 53 | 42.4 |
| Age of blood | 15 days | 2 - 36 days |
| Medications | ||
| ACE /ARB inhibitors | 21 | 16.8 |
| Spironolactone | 8 | 6.4 |
| Insulin | 38 | 30.4 |
| Diuretics | 66 | 52.8 |
| Morbidities | ||
| Acidosis (pH < 7.3) | 63 | 50.4 |
| Acute renal failure | 75 | 60 |
| End-stage renal disease | 12 | 9.6 |
| Factors affecting K+ value | Univariate | 95% confidence interval | Multivariate | 95% confidence interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Change in K+ value pre- and post-transfusion | 0.2 | 0.58 - 1.93 | 0.3 | 0.31 - 2.88 |
| Acidosis | 0.1 | 0.22 - 1.67 | 0.2 | 0.62 - 3.02 |
| Acute renal failure | 0.64 | 0.28 - 3.33 | 0.55 | 0.47 - 2.17 |
| End-stage renal disease | 0.52 | 0.26 - 2.12 | 0.97 | 0.91 - 4.92 |
| No. of transfusions | 0.11 | 0.12 - 1.83 | 0.32 | 0.48 - 2.25 |
| Age of RBC blood | 0.02 | 0.32 - 0.91 | 0.04 | 0.14 - 0.91 |
| K+ infusion via central access vs. peripheral access | 0.43 | 0.75 - 4.17 | 0.82 | 0.76 - 3.93 |